The patient complaints of pain at the IV site and the nurse notes that the patients peripheral IV catheter is reddened, warm, painful, and slightly edematous proximal to the insertion point of the IV catheter.

What is phlebitis
how do you confirm placement?

xray
A client is going to be transfused with a unit of packed RBCs. The nurse understands that it is necessary to remain with the client for what time period after the transfusion is started?
1. 5 minutes
2. 15 minutes
3. 30 minutes
4. 45 minutes
15 minutes!
It is super important because this is when a tranfusion reaction is most likely to occur! Also, The transfusion doe not start until the blood hits the patient(not when you hang it)!
Why is lipid emulsion given with TPN?
A lipid emulsion should usually be provided with PN to prevent depletion of essential fatty acids, lower the risk of hyperglycemia, and prevent hepatic steatosis(fatty liver).
The physician has ordered an I.V. of 500ml of 5% dextrose in lactated Ringer's solution to infuse over 5 hours. How many mL per hour does the nurse set the pump?
1.200 mL per hour
2.1000 mL per hour
3.200 mL per hour
4. 125mL per hour
4. 125 mL per hour
What is your first nursing action?

1. stop infusion
2. warm compress
3. elevate extremity
4. monitor for s/s infection
5. document
Procedure for patient with suspected air embolism during infusion/treatment?
Once suspected the procedure in process should be stopped and lines should be clamped, left side trendelenburg, admin O2, notify physician, monitor vital signs, CPR initiated if circulatory collapse
You started a transfusion of packed RBCs about 1 hour ago. Your patient has suddenly developed shaking chills, muscle stiffness, and a temperature of 101.4 Fahrenheit. He appears flushed and reports a headache and "nervousness". Your patient has most likely developed which type of transfusion reaction?
Febrile non-hemolytic.
Rationale: This is the most common type of transfusion reaction. The characteristic fever usually develops within 2 hours after the transfusion is started. Other classic symptoms include chills, headache, flushing, anxiety, and muscle pain. this type of reaction is usually a result of sensitization to the plasma, platelets, or white blood cells. although this type of reaction is not life-threatening, it can be frightening and uncomfortable for the patient.
A nurse observes the client receiving fat emulsions is having hives. A nurse reviews the client's history and note in which of the following may cause about by the complaint of the client?
A. Allergy to an egg.
B. Allergy to peanut.
C. Allergy to shellfish.
D. Allergy to corn.
A. Allergy to an egg.
Fat emulsions (lipids) contain egg yolk phospholipids and should not be given to clients with egg allergies.
Which of the following clients are most likely to develop circulatory/fluid overload? (select all that apply)
1. A premature infant
2. A 101-year-old man
3. The client on renal dialysis
4. The client with diabetes insipidus
5. A 29-year-old woman with pneumonia
6. The client with CHF
Answer: 1, 2, 3, 6
What is this adverse effect from IV therapy? 
Extravasation
Extravasation occurs when intravenous (IV) fluids or medications inadvertently leak into the surrounding tissue instead of the intended vein. This can cause significant tissue damage, especially if the substance is a vesicant, which is a drug that can cause blistering, necrosis, or other severe tissue injury.
What might happen if the tip of the catheter migrates into the atrium?
- Cause arrhythmias
A person whose blood contains a D antigen is called Rh-_______
What is Rh-positive
What trace elements are in TPN?
zinc(RNA/DNA synthesis), copper(works with iron to form RBCs), chromium(potentiates insulin reactions), manganese(antioxidant protection/carbohydrate synthesis), selenium(catalyst in important antioxidant pathway).
Where do you start an iv on an adult?
What about children?
or Neonates?
Adults: Arms and Hands
Children: Arms, Hands, Feet
Neonates: Scalp veins, umbilical cord
What is the procedure or steps the nurse should take after identifying a patient with extravasation of their IV.
-Stop infusion immediately
- Attempt to aspirate residual drug/ IV fluid prior to removal(Do NOT flush PIV)
remove iv
- Notify physician
- Use warm compress
- Elevate extremity
- Assess site regularly following infiltration
- Instruct patient to notify if symptoms worsen pharmacological antidotes if needed (phentolamine antidote for extravasation of vasopressors).
- Provide education, address symptoms and pain management.
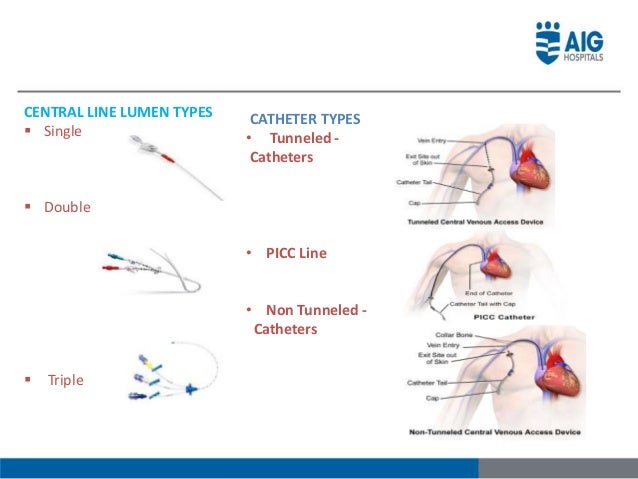
What are some examples of CVAD implant complications?
Catheter occlusion (kink/clamped, tip against wall vessel, thrombosis, precipitate buildup), Embolism (broken, dislodged clot, air entry), Infection (contamination, organism migration, immunosuppression), Pneumothorax (visceral perforation), Catheter Migration (Improper suture, Trauma, forceful flushing, spontaneous)
What is needed prior to administration of blood?
patent 20 gauge Iv or larger(18G), blood typing (y set with filter), NS IVF, Vital signs Machine, Patient consent, valid type and cross, order to administer blood or blood components.
Nurse Russell is preparing to give a total parenteral nutrition using a central line. Place the following steps for administration in the correct order?
1. Connect the tubing to the central line.
2. Regulate the electric infusion pump at the ordered rate.
3. Maintain aseptic technique when handling the injection cap.
4. Check the solution for cloudiness, particles, or a change in color.
5. Prime the IV tubing through an infusion pump.
6. Select and flush the correct tubing and filter.
A. 4, 3, 5, 6, 1, and 2.
B. 6, 4, 5, 1, 3, and 2.
C. 4, 6, 5, 3, 1, and 2.
D. 3, 4, 6, 1, 5, and 2.
C. 4, 6, 5, 3, 1, and 2.
When assessing the patient with a multi-lumen central line, the nurse notices that the cap is off one of the lines. On assessment, the patient is in respiratory distress, and the vital signs show hypotension and tachycardia. What is the nurse's priority action?
a. Administer oxygen.
b. Notify the physician.
c. Rapidly administer more IV fluid.
d. Reposition the patient to the right side.
A. Administer oxygen.
Notify physician after immediate interventions. Rapid administration of fluids would not help, the patient has an air embolism. Placing the patient on the right side would be ineffective as the patient should be placed in left side trendelenberg.
Which of the following are local complications associated with infusion therapy?
a. speed shock, septicemia, and venous spasm
b. phlebitis, infiltration, and hematoma
c. septicemia, thrombophlebitis, and hematoma
d. phlebitis, pulmonary edema, and speed shock
B. Phlebitis, infiltration, and hematoma.
How long do PICC lines stay in?
PICC line: Long term up to 6 months- 1 year and sometimes 18 months
Blood type AB can receive blood from what other types?
AB can receive blood from: AB, A, B, O

What is Parenteral Nutrition (PN/TPN)
What would present a limitation or prohibit a patient from receiving a CVAD?
Conditions such as coagulopathy, venous stenosis, acute thrombosis and local skin infection at or around insertion sites are factors that may affect the decision making process.
Also:
Previous surgical interventions: lymph node dissection, presence of vena cava filter, myocutaneous flap reconstruction, skin grafts, previous vein harvesting, presence of AV grafts/dialysis fistulas, presence of intravascular stents.
Cutaneous lesions in proximity to VAD exit or puncture site: herpes zoster and skin tears, malignant cutaneous lesions, bacteria/fungal lesions and non intact skin, burns, extensive scarring or keloids.