Identify two abnormalities. 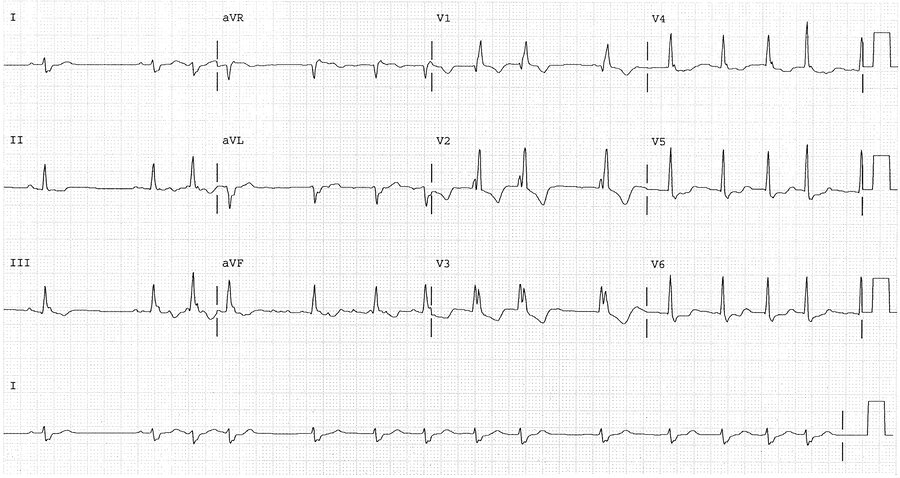
A-fib and RBB
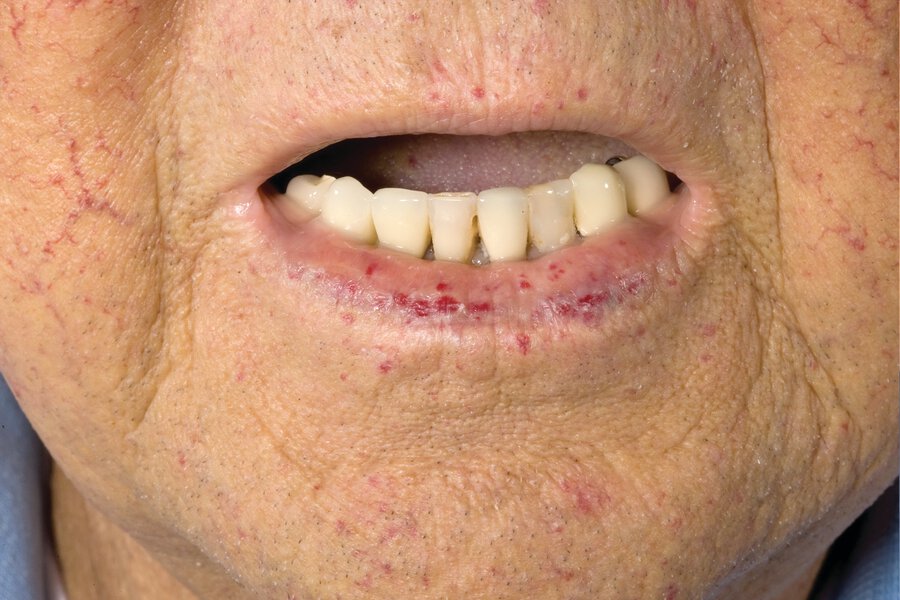
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome) is a disorder of development of the vasculature characterized by telangiectases and arteriovenous malformations in specific locations. The most common features of the disorder—nosebleeds and telangiectases on the lips, hands, and oral mucosa—are often subtle.
Identify peripheral smear finding. 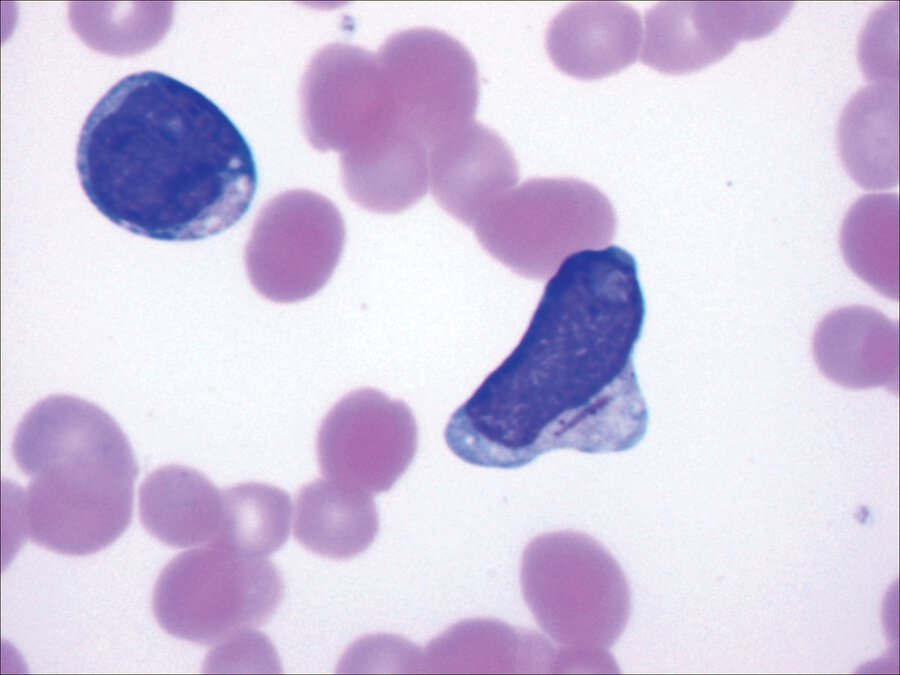
This peripheral blood smear shows an immature granulocyte with a rod-shaped inclusion body (Auer rod) characteristic of acute myeloid leukemia.
Name the medication that Increases smoking cessation rates about 2 times more than control. Avoid with seizure disorder and eating disorder. May be associated with suicidal ideation. Safety in pregnancy is unclear.
Bupropion
Define Type I and Type II errors.
A type I error is incorrectly concluding that a statistically significant difference exists between the experimental and control groups. If the study's P value is <0.05, then a <5% chance exists that a type I error has occurred. A type II error is incorrectly concluding no difference exists between the experimental and control groups. Studies with small numbers of subjects may not have the statistical “power” to detect true differences between groups and may be subject to type II errors.
Medication to Initiate or substitute for an ACE inhibitor or ARB in HFrEF (NYHA class II-IV and EF <40%).
Valsartan-sacubitril/Entresto.
Non tender, multiple lesions. 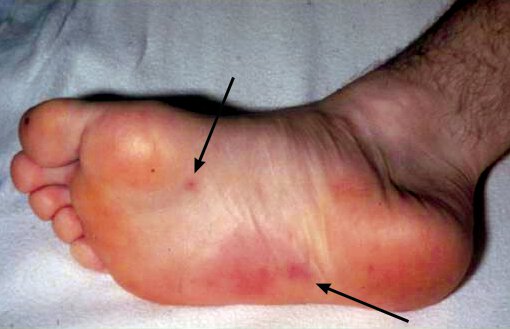
Janeway lesions are macular, erythematous, nontender microabscesses in the dermis of the palms and soles caused by septic emboli that are considered pathognomonic for IE.
Diagnose the condition. What is the criteria to diagnose? 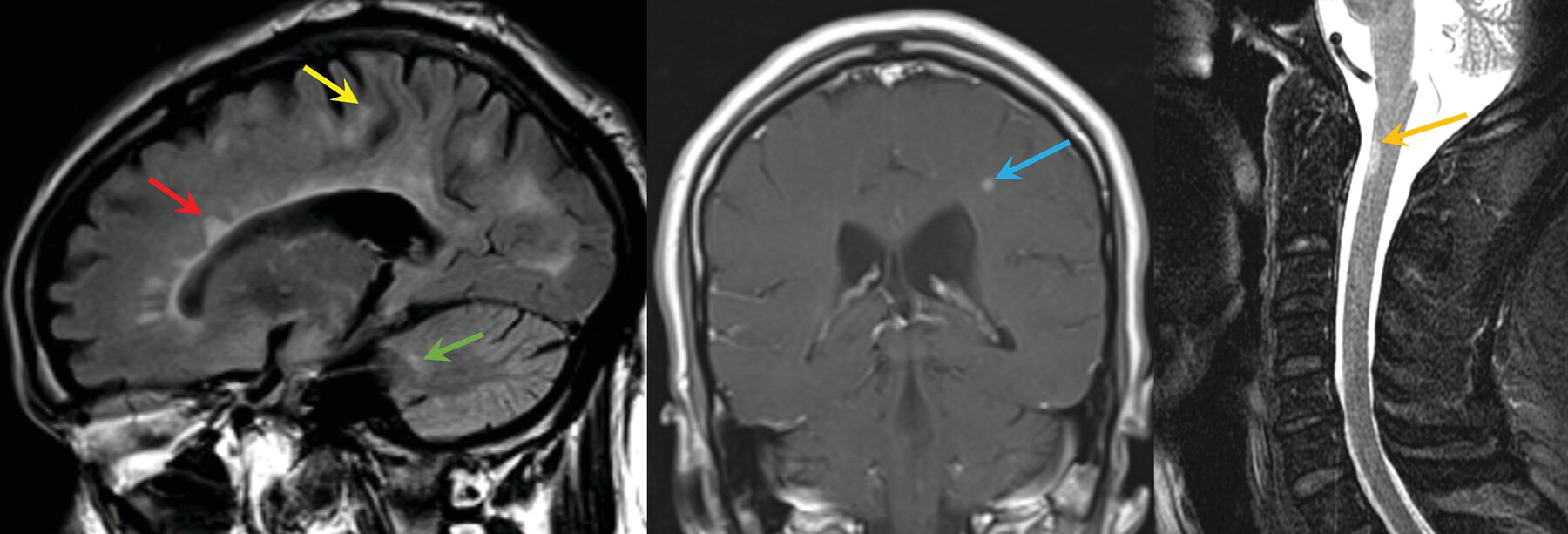
- The McDonald criteria for diagnosing multiple sclerosis require symptoms of central nervous system demyelination separated in space and time from a series of clinical relapses or progression, signs on physical examination, distribution of lesions on MRI, and (if necessary) the presence of CSF-unique oligoclonal bands.
- Proper application of diagnostic criteria can prevent unnecessary neurologic testing, referrals, and misdiagnoses in patients suspected of having multiple sclerosis.
All-cause mortality benefit of smoking cessation? Percentage
Smoking cessation reduces all-cause mortality by up to 50%.
Define PPV and NPV of a test.
The positive predictive value is the probability that a positive test is a true positive result, and the negative predictive value is the probability that a negative test is a true negative result.
Name the medication that is recommended if EF ≤35% who are in sinus rhythm with a heart rate ≥70/min despite maximal β-blocker therapy.
Ivabradine
Diagnose the lesion. It is painful. 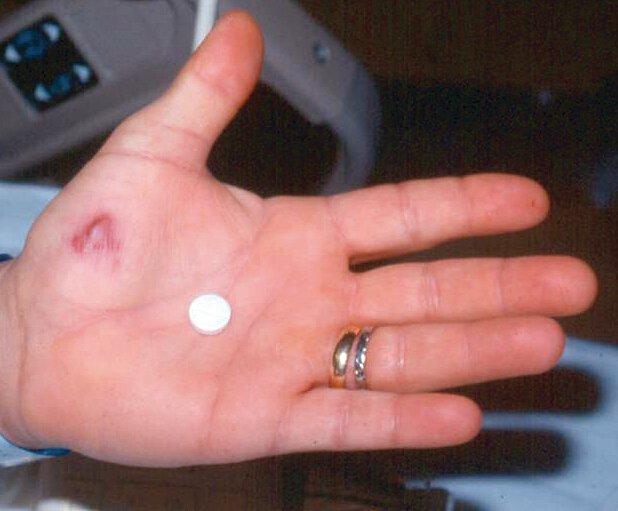
Osler nodes are red to purple painful papules, papulopustules, or nodules found in the pulp of fingers or occasionally on hands and feet.
Identify the findings in a HIV patient. 
Kaposi sarcoma, presenting as firm purple nodules on the face and purple palatal nodules, is seen in a patient with AIDS.
What is BMI cutoff for bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery should be reserved for patients with a BMI of 40 or greater or for those with a BMI of 35 or greater who have obesity-associated comorbid conditions.
What are the recommendations for obesity screening for adults?
- Multiple organizations, including the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and The Obesity Society, recommend annual screening of adults with BMI and waist circumference measurements.
Guidelines for ICD in HFrEF.
For ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy in patients with an EF ≤35% and NYHA functional class II-III or with an EF ≤30% and NYHA functional class I to improve survival.
Diagnose the skin condition. 
BCC: Pearly nodule with arborizing telangiectasias (bottom left of nodule) and ulceration characteristic of nodular basal cell carcinoma.
Most common type of skin cancer. Metastasis rarely occurs; however, without treatment, it can cause significant local tissue destruction. The most common causative factor is UV light exposure.
Prevention with sun protection, including routine use of sunscreen with sun protection factor greater than 35, protective clothing (wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves), and avoidance of midday sun (10:00 AM to 2:00 PM), is highly recommended.
Tx: Surgery, MOHS, electrodessication and curettage; cryosurgery; topical chemotherapy; radiation therapy; and, for metastatic or inoperable lesions, oral hedgehog pathway inhibitors (vismodegib, sonidegib).
Identify EGD finding pointed by the arrow. 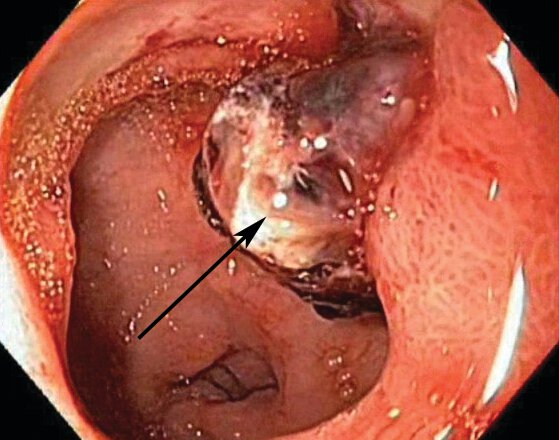
Duodenal ulcer with adherent clot (arrow) that is at risk for rebleeding. This can be treated medically or by clot removal and endoscopic therapy in addition to standard medical therapy.
Name 3 lifestyle modifications for treatment of obesity.
- Lifestyle modifications that are effective for the treatment of obesity include a calorie deficit of at least 500 kcal/d, at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week, and the use of trained interventionists (nutritionists, behavioral therapists, or exercise therapists).
What are BMI cutoffs for Pharmacologic therapy for obesity?
Pharmacologic therapy may be used as an adjunct to lifestyle modifications in patients with a BMI of 30 or greater or in patients with a BMI of 27 or greater who have overweight- or obesity-associated comorbid conditions.
Diagnose the condition. 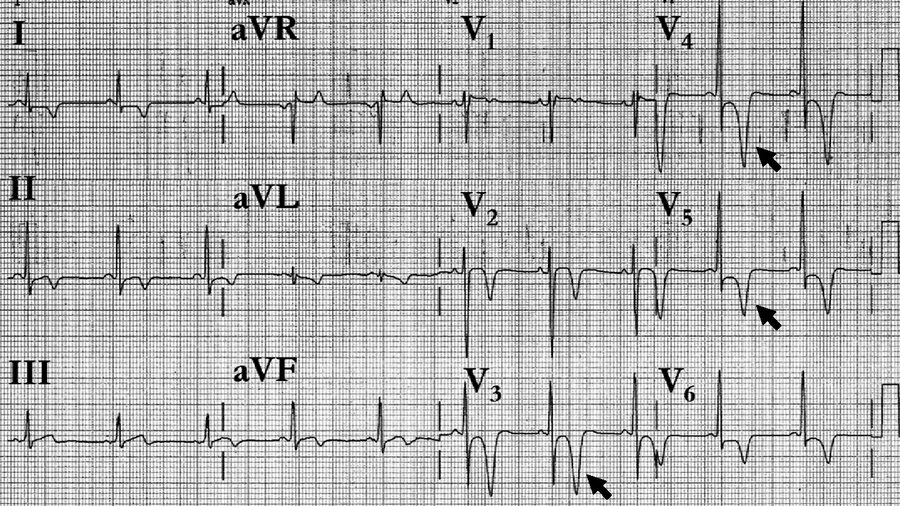
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
The ECG shows ST-segment depression and deeply inverted T waves (arrows) in the precordial leads, consistent with marked apical hypertrophy.
Diagnose the nail condition.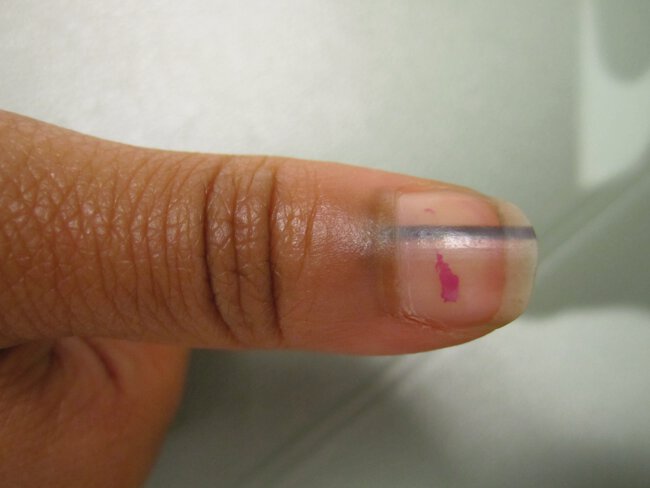
Melanonychia is a brown-banded pigmentation of the nail plate that can be caused by increased melanin production in the nail matrix, benign hyperplasia, and melanoma. Longitudinal melanonychia is benign and is most commonly found on dark-skinned patients on multiple nails. Longitudinal, irregular melanonychia on a single nail can be a sign of melanoma.
identify and what is the timeline for treatment? 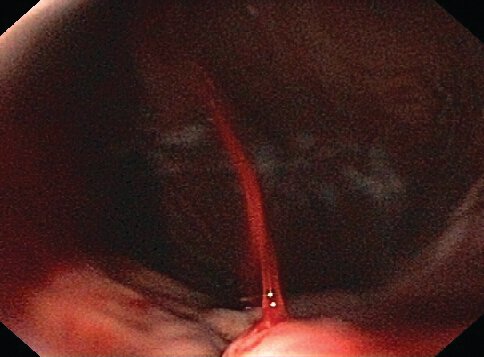
Acute esophageal variceal hemorrhage. A varix in the distal esophagus is seen spurting bright red blood.
- Endoscopic variceal ligation within 12 hours of presentation is the endoscopic treatment of choice for hemostasis of active variceal hemorrhage.
Name the medication that Increases smoking cessation rates about 3.5 times more than control and almost 2 times more than bupropion; more effective than nicotine replacement monotherapy.
Varenicline
Define sensitivity and specificity of a test.
Sensitivity is the ability of a test to detect a disease when it is truly present. Specificity is the ability of a test to exclude disease when it is truly absent.