3. Complete the following analogy:
Carbon: element
NaCl: __________
Compound
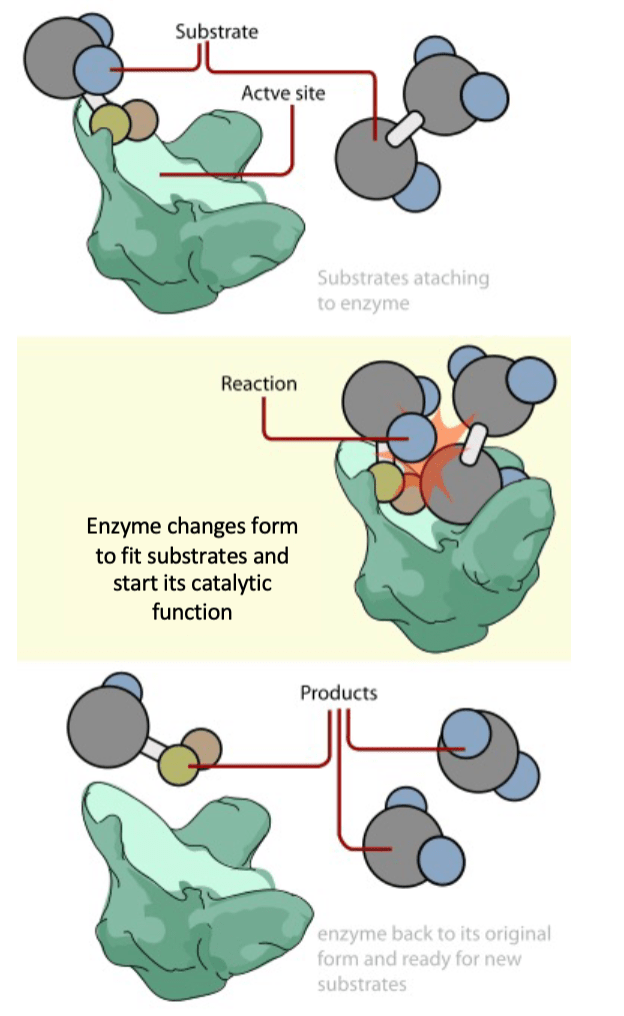
20. Write a sentence that explains these parts of a chemical reaction: Substrate, product, active site.
Answers will vary.
When the substrate attaches to the enzyme’s active site, bonds are formed or broken to create a different
molecule, or product.
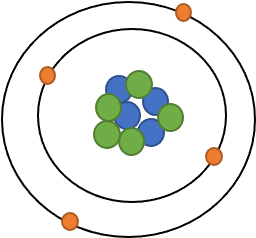
6. Draw an atom of Beryllium.

4 protons, 5 neutrons, 4 electrons
16. Which macromolecule is...
a. Responsible for storing genetic information?
b. Used to form bones & muscles?
c. Important for support & quick energy?
d. Used as a chemical messenger?
a. nucleic acids
b. proteins
c. carbohydrates
d. lipids
4. Name & describe the 3 types of bonds discussed in class. Are they strong or weak?
Ionic- electrons are transferred, strong
Covalent- electrons are shared, strong
Hydrogen- attraction between polar molecules, weak
11. What is the difference between adhesion and cohesion? Use an example to support your answer
- Adhesion-same molecule to a different molecule(water to side of glass for example)
- Cohesion-same molecule to same molecule(water to water in dew drops, etc)
10. Name 2 properties of acids and 2 properties of bases.
Acids- pH below 7, sour, corrode metal, high concentration of H+ ions,
Bases- pH above 7, slippery, high concentration of OH- ions,
EXTRA: The tightness on the top layer of water due to cohesion is _______ ________.
surface tension
14. Name the 4 types of macromolecules and the monomer for each.
Carbohydrates- monosaccharides, simple sugars (ex: glucose)
proteins- amino acids
lipids- fatty acids & glycerol . . . don't have a monomer so structure is ok
nucleic acids- nucleotides
19. Name and describe the 2 types of chemical reactions that are caused by enzymes.
Decomposition- breaking down of a molecule
Synthesis- joining together of two molecules
8. Name the 5 unique properties of water.
Water creeps up thin tubes
has high surface tension
high heat of vaporization
resists temperature change
and expands when frozen.
23. What is the difference between atomic number and atomic mass?
Atomic number is protons
Atomic mass is protons plus neutrons
1. List the 3 subatomic particles, their charges, and where they are found in an atom.
Proton- positive, in nucleus; neutron- no charge, in nucleus, electron- negative, outside nucleus
17. This is an example of what reaction? Is it exothermic or endothermic and why?
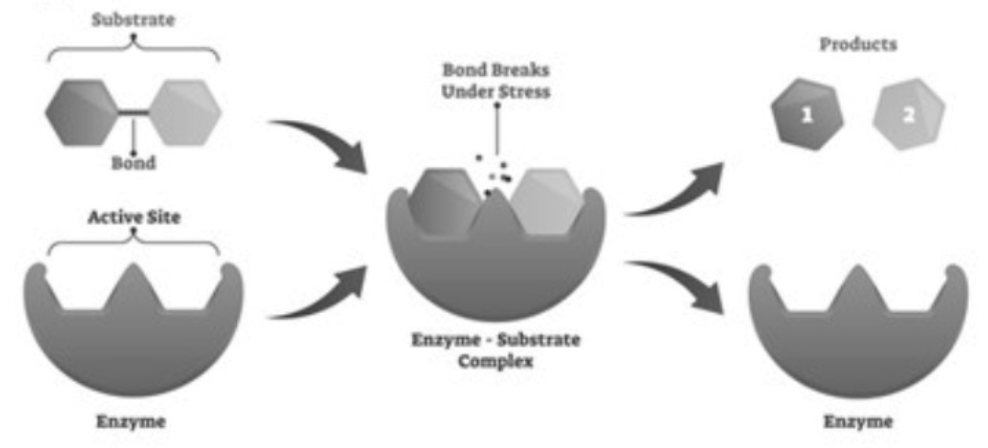
Decomposition-The molecule is breaking apart into smaller products.
It is Exothermic (energy releasing) due to the bond breaking.
9. Describe how one of the unique properties of water contributes to an organism’s survival.
Answers will vary:
Capillary action so plants can draw water up from their roots
Evaporates to maintain inner temperature of living things.
High specific heat enables water temp to be more stable for aquatic creatures to survive ambient temp changes.
18. If a chemical reaction can occur naturally, why is an enzyme still needed?
Enzymes reduce the activation energy required to get the reaction started, making it occur more frequently and easily.
13. Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic _______ but different atomic _______.
number, mass
22. Name 2 ways an enzyme can be denatured.
High temperatures, extreme pH
12. Fill in acids & bases in the correct blank.
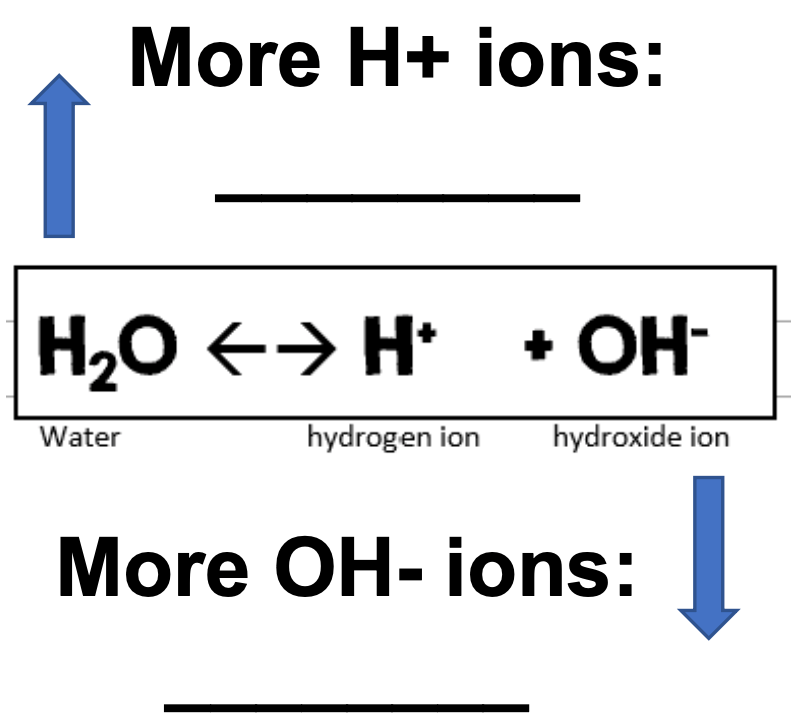
blank 1- acids; blank 2- bases
Who is the amazing singer-songwriter-producer and all around wonderful person who Mrs. Vosseller is a HUGE fan of?
Stevie Wonder 😊⭐️🎹🎶💕
5. What is the chemical formula for a molecule with 1 Carbon atom and 4 Hydrogen atoms?
CH4
15. What 3 elements are found in all 4 macromolecules? What other elements can be found in them?
Carbon, Hydrogen, & Oxygen;
Nitrogen & Phosphorous
7. Why is water a “polar” molecule & what bonds are created from this polarity?
The electrons don’t spend the same amount of time around the Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms, making the O side more negative and the H side more positive. Hydrogen bonds are created by this polarity.
21. Explain what happens when an enzyme is denatured.
The enzyme loses its shape and does not work anymore.
2. What is matter?
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.