1) Is this cell eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Explain why you chose this answer.
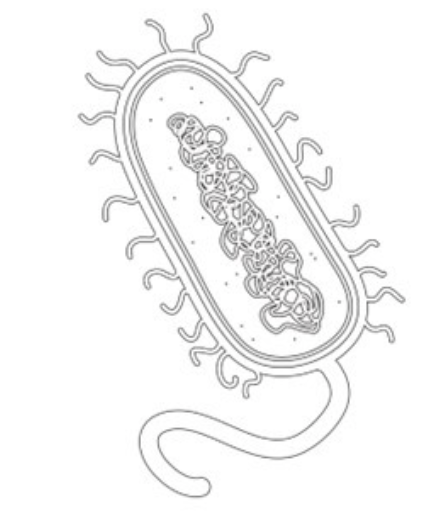
Prokaryotic- It does not have cellular organelles (just DNA, ribosomes, & a cell membrane)
17) What scientists contributed to the cell theory?
Schleiden: All plants are made of cells
Schwann: All animals are made of cells
Virchow & Remak: all cells come from division of other cells
9) Explain the difference in function between vacuoles and vesicles.
Vacuoles store food and water
Vesicles transport
18) Describe the process of protein synthesis (making a protein) in a cell and the organelles involved.

3) Name 2 structures that are common to both prokaryotes & eukaryotes.
Cell membranes & DNA
4) For the given structures, list their name and function.
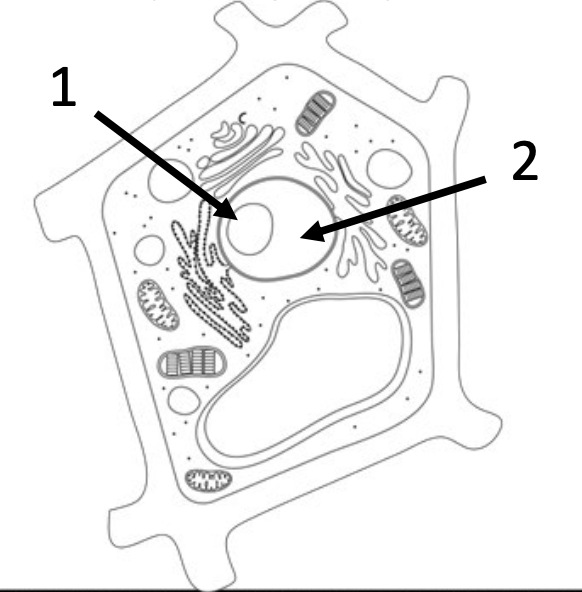
1- nucleolus: makes ribosomes
2- nucleus: stores genetic information
6) For the given structures, list their name and function.
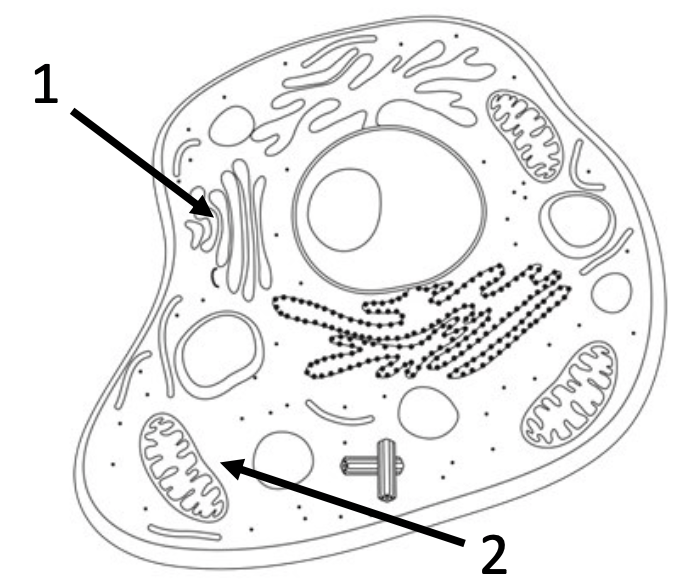
1- Golgi apparatus: modifies and packages proteins for their final destination
2- mitochondria: breaks down nutrients into usable energy
8) Name 3 organelles that are involved in the building and transporting of proteins.
Ribosomes, rough ER, Golgi apparatus
13) Write a sentence to explain why phospholipids align like this:(use the words heads, tails, hydrophobic & hydrophilic)
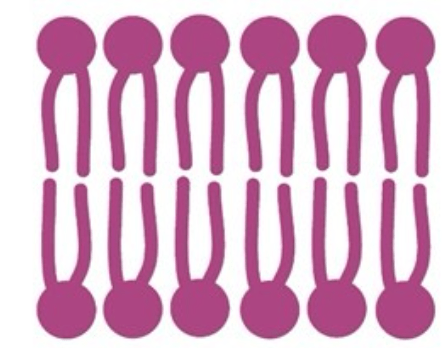
The heads of the phospholipids are hydrophilic so they face towards the watery interior and exterior of the cell, but the tails are hydrophobic so they face inwards away from the watery environments.
16) What is homeostasis and how does the cell membrane help maintain it?
Homeostasis is the constant internal environment of the cell and it is maintained by the cell membrane moving materials into the cell and out of the cell in order to maintain the concentrations necessary for survival.
10) Name 3 parts and their functions of the cytoskeleton.
Microfilaments- Maintain the shape of the cell
Microtubules- Form cilia and flagella
Intermediate Filaments- Move and/or anchors organelles within the cytoplasm
14) Put the following terms in order from smallest to largest: system, cell, organism, organ, tissue
Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Why don't we have school on Tuesday, November 11th?
It's Veteran's Day
19) What is an example of a eukaryotic organism?
Example of a prokaryotic organism?
eukaryotic: animals/plants
prokaryotic: bacteria
11) Why is the cell membrane said to be selectively permeable?
The cell membrane is selectively permeable because it only allows certain materials to pass through it.
15) Give two ways cells can cooperate.
plant cells have openings in their cell walls that allow water and solutes to flow between cells
and
animal cells can be held together with junctions or use receptors to communicate with each other.
12) What are the 4 major molecules that make up the cell membrane?
Proteins
Phospholipids
Carbohydrates
Cholesterol
5) For the given structures, list their name and function.
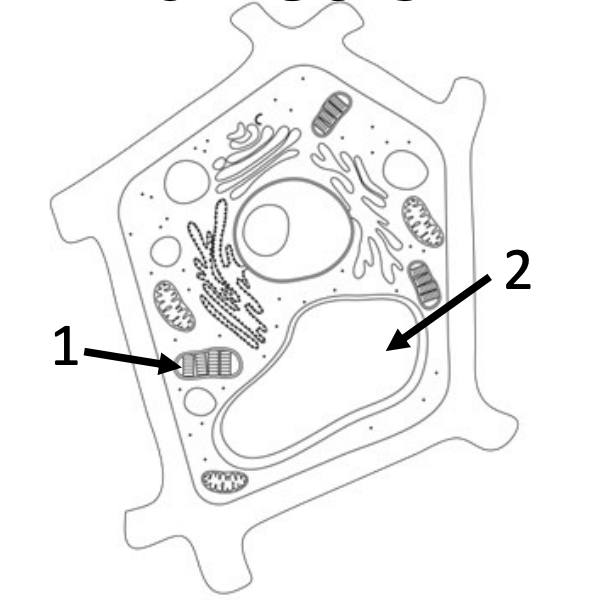
1- chloroplast: makes food from sunlight
2- vacuole: stores food, water, and waste
7) List 3 differences between plant cells and animal cells.
Plant cells have one large central vacuole, while animal cells have several smaller vacuoles.
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts while animal cells do not.
Plant cells prefer a hypotonic solution while animal cells prefer an isotonic solution.
2) What are the 3 principles of the cell theory?
Cells are the basic unit of living things.
Cells perform all the functions of living things.
Cells come from preexisting cells.