A 67-year-old man is evaluated for multiple scaly spots on the forehead, cheeks, ears, and hands. The lesions are thin and have a rough, sandpaper-like quality when palpated. What is the most appropriate treatment?

Topical fluorouracil cream
topical chemotherapy creams, such as fluorouracil, imiquimod, or ingenol mebutate; however, a randomized clinical trial demonstrated that fluorouracil is the most effective treatment.
A 55-year-old woman is evaluated for worsening muscle weakness. She has end-stage kidney disease.
Serum potassium level is 8.0 mEq/L (8.0 mmol/L) and blood glucose is 114 mg/dL (6.3 mmol/L).
What is the first finding you will see on an EKG?
tall, peaked T waves.
This test is the most specific antibody for rheumatoid arthritis.
anti-CCP
Elderly patient with isolated thrombocytopenia, no splenomegaly, normal smear except large platelets
immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)
This murmur becomes louder with Valsalva and standing, and softer with squatting.
hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
This skin cancer has the highest metastatic potential.
melanoma
This electrolyte abnormality is the most common cause of refractory hypokalemia.
Hypomagnesemia
This disease presents with proximal muscle weakness, high CK, and a rash on the knuckles.
dermatomyositis
Patient on heparin develops platelets <50% baseline and new thrombosis. Best test?
PF4 ELISA followed by serotonin-release assay
Cardiac stress testing is contraindicated in patients with this ECG finding
left bundle branch block (requires vasodilator nuclear test instead)
This life-threatening dermatologic emergency presents with mucosal involvement and >30% BSA detachment
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
This diagnostic ratio differentiates prerenal azotemia from intrinsic AKI.
BUN:Cr ratio (>20:1
What is the treatment used as a steroid-sparing agent in Giant cell arteritis?
Tocilizumab
Painless lymphadenopathy, “waxing and waning,” and t(14;18).
follicular lymphoma
A patient with tearing chest pain, acute diastolic murmur, and widened mediastinum most likely has this condition.
acute aortic regurgitation from aortic dissection
This neutrophilic dermatosis is associated with IBD, hematologic malignancy, and painful ulcerations with violaceous borders.
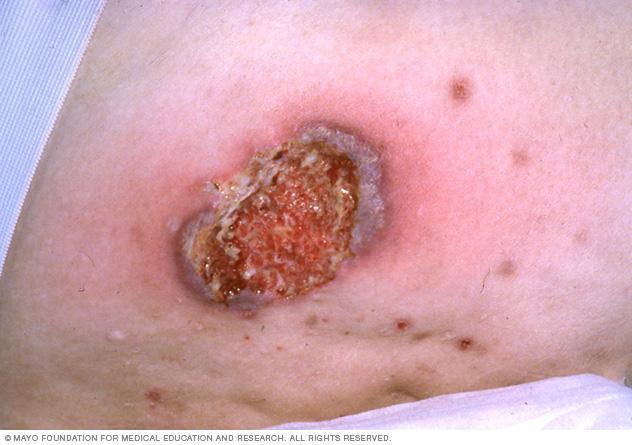
pyoderma gangrenosum
This type of renal tubular acidosis is associated with kidney stones and inability to acidify urine (pH >5.5).
Type 1 (distal) RTA
This condition presents with purpura, arthralgias, low complement, and Hepatitis C. What is the most common type of that disease?
Mixed type II most common cryoglobulinemia
Young patient with mediastinal mass, ↑β-hCG, ↑AFP
non-seminomatous germ cell tumor
Post-MI complication within 2–7 days presents with acute pulmonary edema and a new holosystolic murmur.
papillary muscle rupture causing acute MR
This dermatologic condition presents with target lesions and is commonly caused by HSV.
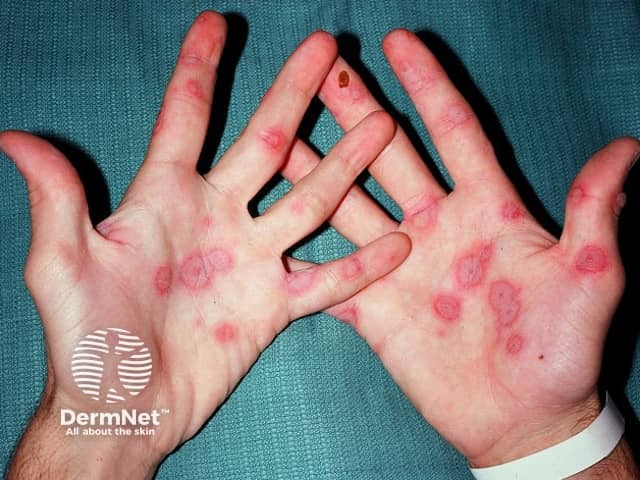
erythema multiforme
This electrolyte abnormality presents with QT prolongation and perioral numbness and is treated with IV calcium gluconate.
hypocalcemia
This serologic marker is highly specific for limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis and predicts pulmonary arterial hypertension.
anti-centromere antibody
Microcytic anemia, normal ferritin, normal iron studies, high RBC count.
thalassemia trait
This arrhythmia must never be treated with AV nodal blockers if WPW is present.
AF with WPW