First line pharmacotherapy for Stable Angina?
3 medications
B-blockers, Aspirin, and Statin therapy.
How do we Treat COPD Exacerbation? (at least 3 of 4 treatments)
Supp O2, Oral Steroids, SABAs +/- anticholinergics, antibiotics*
1. 125 Solumedrol IV then 40mg q8h (followed by taper) MKSAP
2. DuoNebs q4hr sched & q4h prn (Ipratropium bromide & albuterol sulfate - SAMA & SABA).
3. If suspect tracheobronchitis (change in sputum color or volume) add Azithromycin 500 mg po qd x3d (or Doxycycline 100mg BID or Augmentin 875/125 bid)
4. Supp. O2 to maintain SpO2 88 to 92%. No NRB masks!
How would you, an actual doctor, diagnose CKD?
Abnormal Kidney structure or function present for > 3 months.
A patient can have CKD and a normal GFR. An old person can have a low GFR (60 – 90) but not have CKD.
What is the treatment of SBP in patients with Cirrhosis? (2 things)
IV Albumin and 3rd Gen Cephalosporin
What is the most common cause of Liver Disease in the world?
A.MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver disease).

True or False: Primary goal of revascularization for patients with Stable Ischemic Heart Disease without high-risk features is to improve overall mortality.
The primary goals of revascularization in stable syndromes are to lessen angina and improve quality of life.
Which type of pleural effusions should get Pleural drainage?
A.Complicated Parapneumonic effusions (including empyema's) and Recurrent pleural effusions (e.g. malignant, hepatic hydrothorax), especially where the lung doesn’t completely re-expand.
Indicated for pts with evidence of incomplete lung expansion on post-thoracentesis CXR. They will need indwelling pleural catheter.
What is the target Hgb in CKD patients and which labs should be measured prior to ESA administration?
Hgb ~ 10. ESA for Hgb <10.
Iron studies (Ferritin, TSAT) must be checked.
KDIGO suggests maintaining transferrin saturation levels >30% and serum ferritin levels >500 ng/mL using either oral or intravenous iron supplementation.

What treatments do we provide for cirrhotic patients presenting with UGIB? (2 treatments, not including pRBC or PPI)
A.IV Ceftriaxone and Somatostatin. IV PPI until peptic ulcer disease ruled out.
T or F: All patients with a single unprovoked seizure should be started on AED?
False. We can start Anti-Epileptic therapy for Unprovoked Seizure with EEG or MRI abnormalities OR 2 Unprovoked seizures
Elements of GDMT for Ischemic Heart Disease (name at least 3 of them)?
Thrombotic Risk, Lipids (LDLc), BP, Glycemic control, Obesity, Sleep apnea.
Which patients warrant a pleurodesis? (give me 2 of 4)
A.Pneumothoraxes and Pleural effusions
Recurrent malignant pleural effusions in patients with expandable lung.
1. First episode of Secondary Spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP)
2. Second episode of Primary Spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) on ipsilateral side
3. First episode of PSP in patient with high risk profession (Pilot, Scuba diver)
Not indicated for pts with evidence of incomplete lung expansion on post-thoracentesis CXR. They will need indwelling pleural catheter.
What is the indication for Sodium Bicarb tabs in CKD? What is the therapeutic target?
A.CKD resulting in HAGMA and HCO3 < 18.
Target is HCO3 between 18 and 28 (ULN)
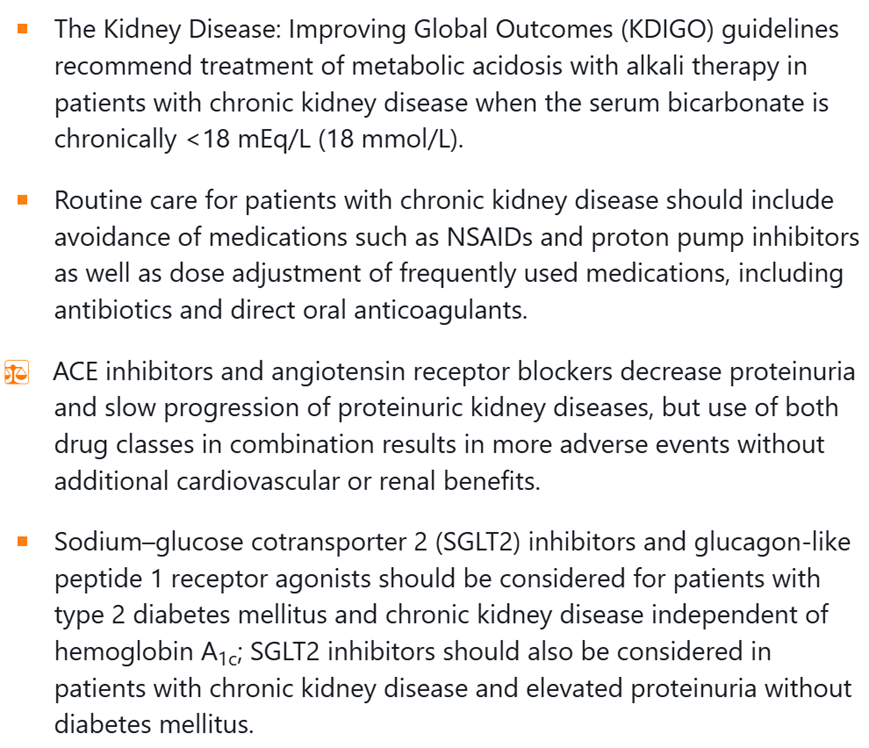
When do we give IV Albumin for patients with non-infected ascites?
+300 bonus pts if you know how much Albumin we give.
A.If more than 5 L of ascitic fluid is removed at one time, supplemental 25% albumin at a dose of 6 to 8 g/L of ascitic fluid removed should be administered to prevent circulatory dysfunction after paracentesis.
* Hepatorenal syndrome in the setting of ascites is also an acceptable answer.
Pt with CKD Stage 4 is found to have hs-cTnT 45 and 42. No chest pain, epigastric pain, nausea, or palpitations. How do we classify his Troponin elevation?
Non-cardiac Troponin elevation OR Chronic Myocardial injury.
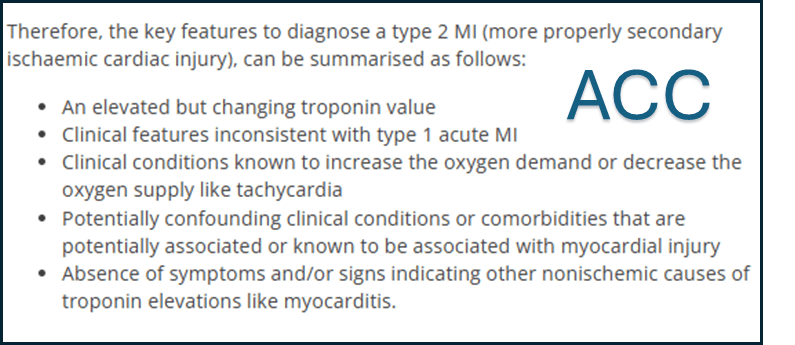
When is CABG indicated in treatment of ischemic heart disease?
A.(1) Left Main (2) Three-vessel CAD, and (3) Multi-vessel CAD w/ Diabetes Mellitus
Also: For STEMI: CABG is necessary if there is Extensive area of infarction not amenable to PCI, Failed PCI attempts, extensive CAD with multi-vessel involvement, Cardiogenic shock, or Mechanical complication.
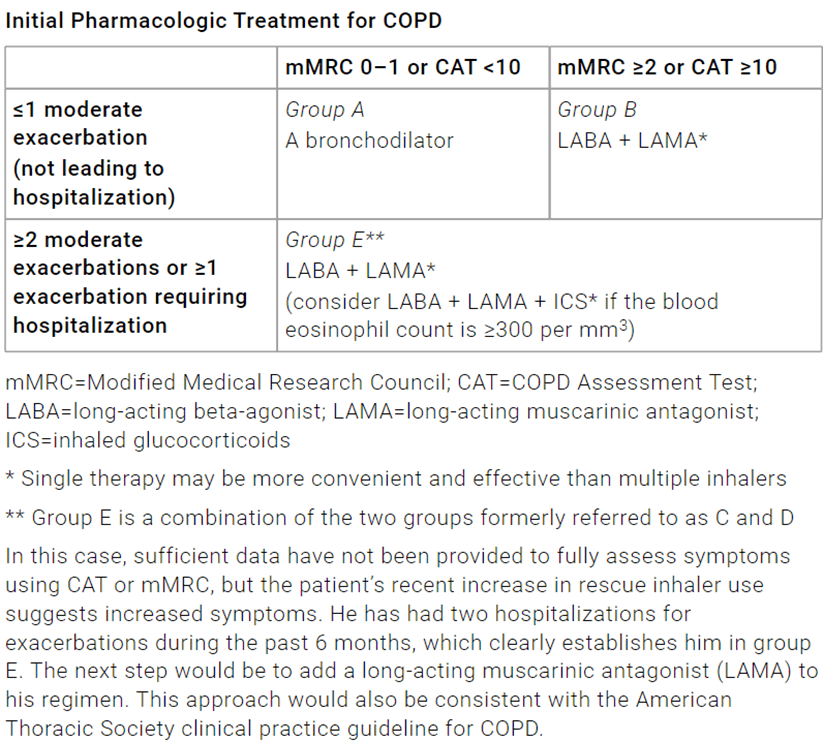
What are the 3 treatment groups for which COPD is categorized?
A.Diagnose based on clinical presentation and Spirometry showing FEV1/FVC < 0.7.
Classify into groups A, B, and E based on symptom and hx of exacerbations.
Name 3 indications for Kidney biopsy.
Indications for kidney biopsy include: glomerular hematuria, severely increased albuminuria, kidney disease of unclear cause, and kidney transplant dysfunction or monitoring.

Name a cause of Ascites where SAAG ~ 1.5 and Ascitic protein 3g/dL
A.SAAG > 1.1 indicates portal hypertension. Ascitic fluid total protein > 2.5g/dL post-hepatic process à CHF, Early Budd-chiari

How long should patients with a High risk Peptic ulcer be on twice daily PPI after intervention with endoscopy?
A.Start BID IV PPI on presentation. Continue for at least 72 hours post endoscopy. Twice daily PPI for 2 weeks.
Which NSTE-ACS patients get a heart cath? How do we choose? Name at least clinical indicator and 1 risk scoring system.
*Bonus 100 pts if you know others*
A.Risk stratification based on Clinical presentation (HD instability, refractory chest pain, Heart failure, ventricular arrhythmia) or scoring system (GRACE & TIMI)
Treatment regimen for newly diagnosed Ventilator Associated PNA in a patient on their 10th day of hospitalization?
A.MRSA Coverage + 2 Anti-Pseudomonal Agents from different antibiotic classes (eg β-lactam and a fluoroquinolone)
e.g. Ceftazidime, Ciprofloxacin and Vanco
OR Cefepime, Levofloxacin, Vancomycin
For ESKD patients who elect to discontinue dialysis, death usually occurs at what time point?
2 weeks
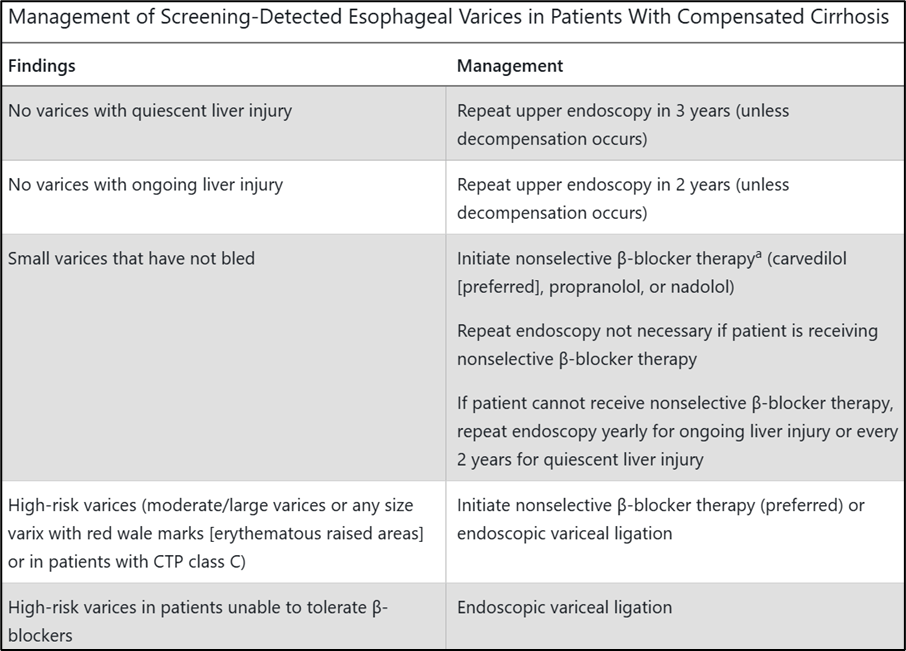
What are the options for Primary Variceal prophylaxis in patients with Compensated Cirrhosis?
A.Non-Selective Beta blocker therapy OR Endoscopic variceal ligation.
Secondary variceal PPX (varicies that have bled) includes Non-selective Beta blockers and Follow up endoscopy for band ligation.
What treatment can we give for acute dystonic reaction in a Schizophrenic patient on antipsychotics?
Diphenhydramine or Benztropine
•Dystonia is an involuntary contraction of major muscle groups that is highly disturbing to the patient. Some types of dystonia, for example laryngospasm, may be life threatening.
For treatment of acute dystonia secondary to antipsychotic, use authors recommend treatment with diphenhydramine or benztropine.
Diphenhydramine –50 mg IV or IM acutely followed by 50 mg orally q6h. Milder cases may be treated with 50 mg PO 2 to 3 times daily.
Βеոztrоpinе – dose of 1 to 2 mg IM or IV acutely followed by 1 to 2 mg orally daily. Milder cases may be treated with oral benztropine 1 to 2 mg once or twice daily.