Who proposed the theory of evolution by Natural Selection?
Charles Darwin
Who discovered the double helix structure of DNA through X ray crystallography?
Rosalind Franklin
Which nitrogenous base is found in RNA but not in DNA?
Uracil (U) which replaces thymine (T)
What is the main function of DNA in the cell?
To store genetic information
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA → RNA → Protein
Refers to the flow of genetic information within the cell
Explain the difference between “adaptation” and “mutation.”
A mutation is a random change in DNA; an adaptation is a beneficial trait that increases survival, often caused by a mutation.
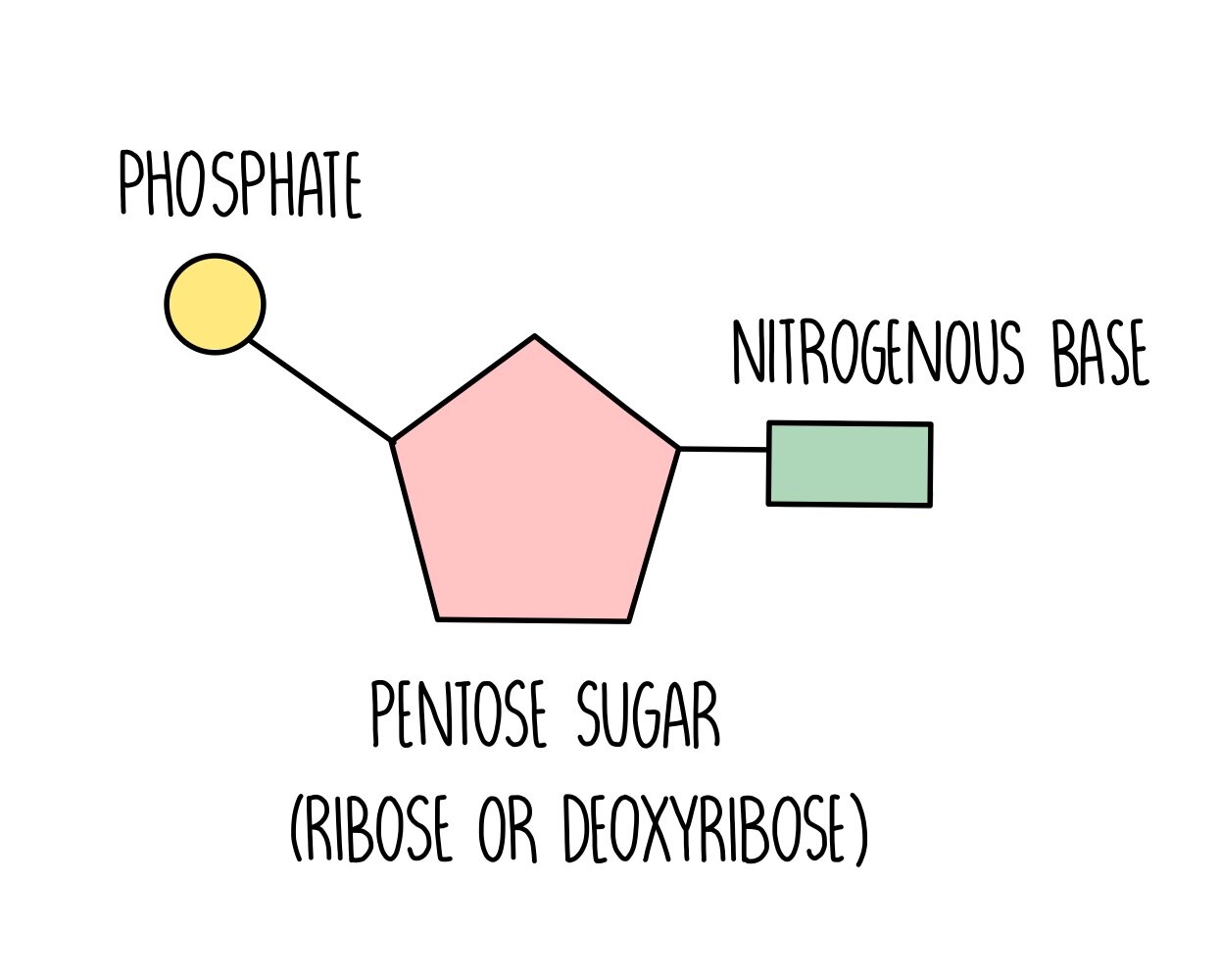
Draw and label all parts of a nucleotide (include the specific type of sugar that makes up DNA)
What are the three main types of RNA and their functions?
mRNA: messenger, carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome
tRNA: transfer, brings the corresponding amino acid to the mRNA chain during translation
rRNA: ribosomal, the component of the ribosome
During which stage of interphase does the cell make a copy of its DNA? Does this happen before or after mitosis?
S phase of interphase.
This happens before mitosis in order to make sure that the new cells have an identical copy of the genetic information
Translate the following DNA code into mRNA
ATG-AAC-TAT-CGC-ATA
Resulting mRNA strand:
UAC-UUG-AUA-GCG-UAU
What is evolution?
In order for your answer to be valid in needs to have 4 key words
Random change in the genetic pool of a population through time
What type of chemical bond holds the nitrogenous bases together in the DNA double helix?
Hydrogen bonds
What are the two main structural differences between DNA and RNA?
RNA is commonly single-stranded and has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose.
What is a gene?
Gene: the smallest unit of inheritance, or a section of DNA that contains a code for a specific trait
What would happen if a mutation occurs in the mRNA sequence?
It could change the amino acid sequence, resulting in a mutation and possibly altering or damaging the protein’s function.
Explain divergent evolution and homologous structures making an example
Divergent evolution: Two similar species with a recent common ancestor develop different traits are they are exposed to different selective pressures
Homologous structures: structures that are evidence of common ancestry and they are similar in their form (limbs in humans and whales for example)
TACATTTACCGCTA
Base strand: TAC-ATT-TAC-CGC-TAC
Complementary strand: ATG-TAA-ATG-GCG-ATG
What is the difference between chromatin and a chromosome?
Chromatin: loose DNA
Chromosome: tightly packaged/condensed DNA
What is an allele? Define it and make an example
allele: a version of a gene.
Example: allele for eye color can be brown, green or blue
Why is genetic diversity essential for life?
Genetic diversity is essential for life because it provides species with the ability to adapt to environmental changes, resist diseases, and maintain population resilience. This variation in genes allows for a wider range of traits within a population and increases probabilities of survival.
How can genetic variation in a population lead to speciation over time?
Accumulated genetic differences can lead to reproductive isolation(inability of breeding) and eventually create new species.
What does it mean when we say that DNA is antiparallel and complementary? Explain the meaning of both terms WITH examples
Antiparallel: Runs in opposite directions, one strand runs from 5' to 3' and the other runs from 3' to 5'
Complementary: N-bases pair up in a specific way in order to maintain the accuracy of the code. A-T and C-G always
Which is more unstable DNA or RNA? Why? Explain listing at least two reasons.
RNA is more unstable since it contains U (uracil), it is single stranded and it contains ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose
If mRNA did not exist and the cell tried to translate directly from DNA, what structural or functional problems might arise?
Problem of using DNA directly (either response is accepted!)
DNA is located in the nucleus (in eukaryotes), so it cannot reach ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
DNA is double-stranded and stable; exposing or unwinding segments constantly for translation might damage it.
Direct translation would expose the DNA to cellular machinery and increase chances of mutations or digestion by enzymes.
Some viruses use RNA as their genome instead of DNA. Given what you know, how might the absence of a DNA stage change how their life cycle or mutation rate behaves?
RNA viruses and their implications (any answer is correct!)
RNA tends to have higher mutation rates (less proofreading) → faster evolution/adaptation.
Without DNA, there is no stable “archive” genome; viruses must replicate quickly and risk more errors.
The life cycle may be more streamlined but more prone to errors and variation, which may help in evading host defenses.