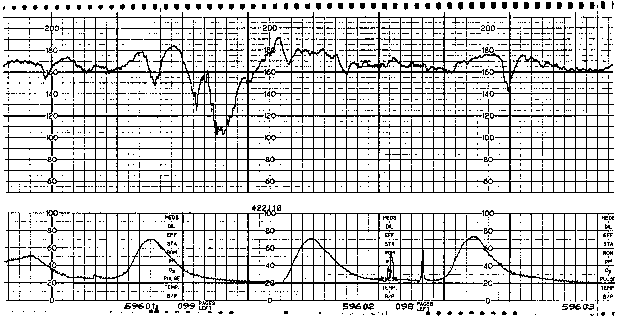
What is a variable deceleration? Abrupt decrease 15 beats below baseline (or more) x 15 seconds or more
that involves cord compression
A nurse is caring for Wilma who is pregnant and undergoing a non-stress test. Wilma asks the nurse why she is using an acoustic vibration device. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
A. "It is used to stimulate uterine contractions."
B. "It will decrease the incidence of uterine contractions"
C. "It lulls the fetus to sleep."
D. "It awakens a sleeping fetus."
What is ........It awakens a sleeping fetus. The acoustic vibration device is activated for 3 secs on the maternal abdomen over the fetal head.
Changes from baseline patterns in FHR that occur with uterine contractions.
What are periodic changes
Explain a Non-Stress Test
To determine fetal well being
Normal baseline, moderate variability, and 2 accelerations within a 20 min period (no decelerations)
normal acid base balance
neurologically intact
This is the normal baseline range, in beats per minute, for a fetal heart rate
What is 110 to 160 beats per minute?
HR increase 15 beats above baseline for atleast 15 seconds (> 32 weeks gestation).
10 x 10 < 32 weeks gestation
What are accelerations? Everything is okay
Nurse Jonna is caring for a client who is in preterm labor and is scheduled to undergo an amniocentesis. Nurse Jonna should evaluate which of the following tests to assess fetal lung maturity?
A. Alpha-fetoprotien (AFP)
B. Lecithin/Sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio
C. Kleihauer-Betke test
D. Indirect Coombs' test
What is ....... B. L/S ratio is done as a part of an amniocentesis to determine lung maturity.
Expected irregular fluctuations in the baseline fetal heart rate (FHR), known as variability, are classified into these four categories based on amplitude.
What is: Absent = amplitude undetectable
• Minimal = amplitude 0 to 5 bpm
• Moderate = amplitude 6 to 25 bpm
• Marked = amplitude over 25 bpm
What is a CST and explain the difference between a POSITIVE contraction stress test and a NEGATIVE contraction stress test.
2 methods: Nipple stimulated contraction stress test and Oxytocin stimulated contraction stress test
Interpretation
Positive--persistent late decelerations--associated with poor fetal outcomes.
Negative--no late decelerations with the contractions and are associated with good fetal outcomes.
This term describes the presence of more than 5 uterine contractions in a 10-minute period, averaged over 30 minutes, and may compromise fetal oxygenation.
What is uterine tachysystole?
This type of deceleration begins after the peak of a contraction and indicates uteroplacental insufficiency.
What is a late deceleration?
Nurse Avril is reviewing findings of a client's biophysicial profile (BPP). Nurse Avril should expect which of the following variables to be included in this test? Select all that apply
A. Fetal Weight
B. Fetal Breathing Movement
C. Fetal tone
D. Fetal Position
E. Amniotic fluid volume
What is ....B, C, E
Fetal breathing movement, fetal tone, and amniotic fluid volume
This part of the external fetal monitor is placed on the mother’s abdomen and uses ultrasound to detect the fetal heart rate.
What is the ultrasound transducer?
This fine spiral wire attaches directly to the fetal presenting part and captures R-wave signals from the fetal ECG for precise heart-rate tracing.
What is a fetal scalp (spiral) electrode?
These maternal factors are potential etiologies contributing to fetal heart rate tachycardia.
What is: Fever,
• Infection
• Dehydration
• Hyperthyroidism
• Endogenous adrenaline/anxiety
• Medication of drug response
• Anemia
 379 × 314
379 × 314
What is an early deceleration? Head compression.
decelerations mirror contractions
Nurse Samantha is caring for Katrina who is pregnant and is to undergo a contraction stress test. Which one of the following findings are indications for this procedure? Select all that apply
A. Decreased fetal movement
B. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
C. Postmaturity
D. Placenta previa
E. Amniotic fluid emboli
What is A, B, C,
Decreased fetal movement
IUGR, and postmaturity
An abrupt decrease anytime during a contraction in response to umbilical cord compression.
What is a variable deceleration?
The decrease is ≥15 bpm, lasting ≥15 secs and <2 minutes from onset to return to baseline.
Maternal and Fetal indications for more frequent NST/EFM (external fetal monitoring)
What are Maternal DM, chronic HTN, GHTN, IUGR, post maturity, hx stillbirth, other chronic medical conditions.
This mnemonic helps you remember the types of fetal heart rate decelerations and their causes.
What is VEAL CHOP?
Variable = Cord compression, Early = Head compression, Accelerations = Okay, Late = Placental insufficiency.
What are the interventions to decelerations?
Position change, IVF bolus, Oxytocin off, notify provider, Oxygen (as needed)
A nurse is caring for a client at 34 weeks of gestation who is undergoing a non-stress test (NST). The nurse observes two accelerations of the fetal heart rate (FHR), each lasting 15 seconds and peaking at least 15 beats per minute above the baseline, within a 20-minute period. How should the nurse interpret these findings?
A. Nonreactive result indicating the need for further testing
B. Reactive result indicating normal fetal well-being
C. Inconclusive result due to fetal sleep cycle
D. Abnormal result requiring immediate delivery
What is....... B. Reactive result indicating normal fetal well-being
Changes in the FHR from baseline that are not associated with uterine contractions
What are episodic changes
These are the four main characteristics of uterine contractions assessed during labor.
Frequency – How often contractions occur, measured from the start of one contraction to the start of the next.
Duration – How long each contraction lasts, measured from the beginning to the end of a single contraction.
Intensity – The strength of the contraction, often described as mild, moderate, or strong. Assessed by palpation externally or measured accurately with an intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC).
Resting Tone – The level of uterine tone (firmness) between contractions. It indicates how well the uterus relaxes and is assessed via palpation or IUPC.
This is the leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide.
What is a PPH
SVD EBL > 500ml
C/S EBL >1000ml