Q: Repetitive, stereotyped, suppressible movements
A: Tics
Q: Measure of the fidelity of a study's results compared to what is correct or true
A: Validity
Q: Term for a paradoxical rise in jugular venous pressure on inspiration
A: Kussmaul sign
Q: Noninfectious morphological form of Giardia that adhere to the mucosa of the small bowel
A: Trophozoites
Q: Term for marked hypertension with acute kidney injury, hematuria, and proteinuria
A: Malignant nephrosclerosis (accept acute hypertensive nephrosclerosis)
Q: Syndrome of hyperthermia and hyperreflexia and clonus
A: Serotonin syndrome
Q: Method for randomized controlled trials that analyzes all participants on the basis of their original randomized intervention
A: Intention to treat
Q: Formula for calculating mean arterial pressure
A: ([Diastolic BP x 2] + Systolic BP) / 3
Q: Most common viral cause of recurrent benign lymphocytic meningitis
A: Herpes simplex virus, type 2 (accept HSV-2; do not accept HSV alone)
Q: Pathophysiologic mechanism of systemic hypotension in a mechanically-ventilated COPD patient with incomplete exhalation
A: Auto–positive end-expiratory pressure (accept auto-PEEP; dynamic hyperinflation)
Q: Preferred initial drug therapy for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
A: Acetazolamide (accept carbonic anhydrase inhibitor)
Q: A negative likelihood ratio of 0.1 decreases the probability of disease by approximately this amount
45%
Q: Three potential major mechanical cardiac complications associated with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
A: Left ventricular free wall rupture, rupture of the intraventricular septum, mitral papillary muscle dysfunction (accept acute mitral regurgitation or flail valve)
Q: Primary syphilis in HIV-infected individuals is more likely to have this distinguishing clinical feature
A: Multiple chancres
Q: Pulmonary complication associated with rapid removal of a large volume of pleural fluid
A: Reexpansion pulmonary edema (accept pulmonary edema)
Q: Diagnosis associated with anti–N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibodies
A: Autoimmune encephalitis (accept limbic encephalitis)
Q: Type of bias that overestimates survival due to earlier detection by screening than clinical presentation of disease
A: Lead time bias (do not accept length time bias)
Q: Term for the direct hemodynamic influence of the left and right ventricles on each other
A: Interdependence (accept ventricular interdependence)
Q: Bacterial genus associated with cellulitis in patients treated with leeches
A: Aeromonas
Q: Treatment of patients with smoke inhalation that do not require intubation
A: 100% inspired oxygen
Q: Recurrent throbbing headache typically occurring after the age of 50 that awakens the patient from sleep
A: Hypnic headache
Q: Eponym for index used to predict one-year mortality initially based on 22 comorbid conditions
A: Charlson Index (accept Charlson Comorbidity Index; Charlson/Deyo, Charlson/Romano, Charlson/Manitoba, and Charlson/D'Hoores indices - must include Charlson)
Q: Name for condition with low transvalvular pressures in patients with severe aortic stenosis but preserved left ventricular function
A: Paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient aortic stenosis
Q: Likely diagnosis for patient with relative bradycardia, pulse-temperature dissociation, abdominal pain, and this skin rash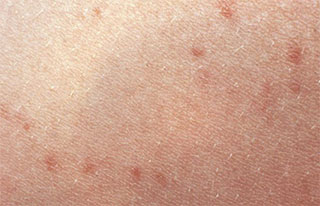
A: Enteric fever (accept typhoid fever; typhoid and paratyphoid infection)
Q: Mode of ventilation with long duration of high airway pressure followed by short duration of lower pressure
A: Airway pressure release ventilation