This instrument is used to separate and analyze compounds that can be vaporized without being decomposed. We have one in the instruments room.
What is a gas chromatograph?
This Nobel prize-winning German chemist developed a design for the symbolic "projection" of asymmetric carbon atoms, which bears his name
Who is (Emil) Fischer?
This branch of chemistry helps us catch the bad guys. It is also the reason we have cocaine in the prep room fridge.
What is forensic chemistry?
When performing a dilution, one may use this equation, which relates initial and final concentrations and volumes
What is M1V1 = M2V2
The element with atomic number 99 was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952. It is named in honor of everyone's favorite physicist, pictured here:
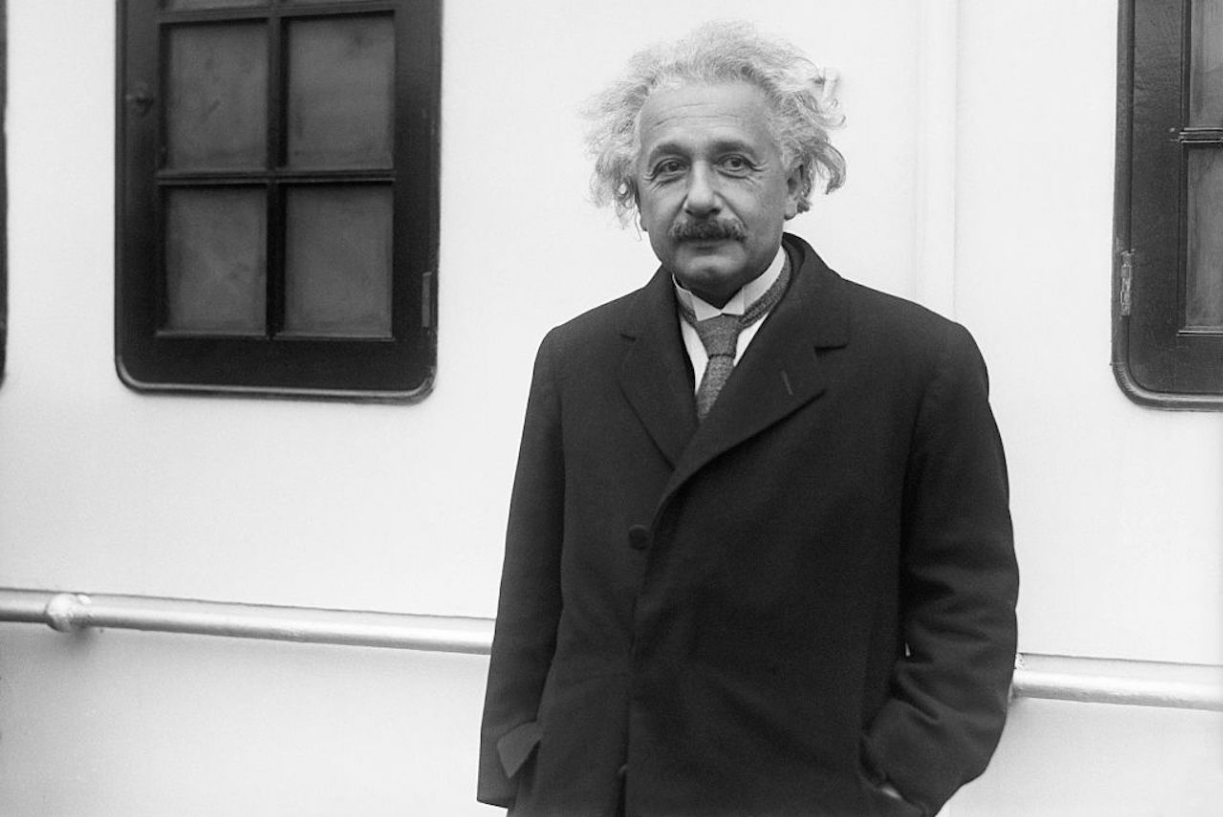
What is Einsteinium
The concentration of a solution can be determined through this technique, involving the addition of a stock solution until some end point is reached
What is a titration?
This UC Berkeley biochemist pioneered the PCR technique of DNA amplification. He once remarked that his use of LSD had helped him in his research.

Who is Kary Mullis?
This is the most important branch of chemistry. Jk lol. It is where biology and chemistry intersect and the major of the person reading this question.
What is biochemistry?
If diluting by a large factor, one may require the use of these pictured below, to transfer very small amounts of solution
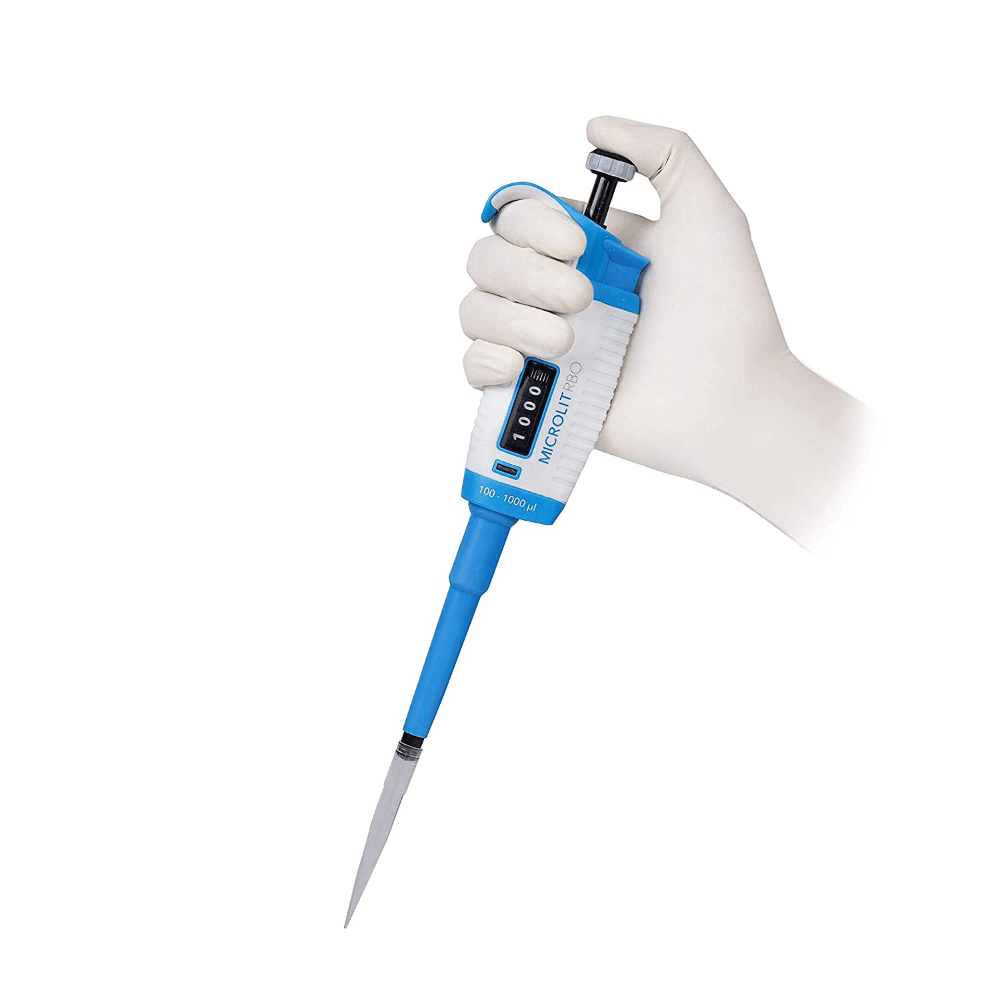
What is a micropipette
This number 88 element was first isolated by Marie Sklowdoska Curie in Paris, for which she won the noble prize a year later. Not to be confused with the element named after her.
What is radium?
This technique involves measuring the absorbance or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength, often in order to determine the concentration of an analyte via the Lambert-Beer law
What is spectrophotometry?
This German chemist was a pioneer in spectroscopy and discovered the elements caesium and rubidium. There is also a very hot laboratory device named after him.
Who is (Robert) Bunsen?
This branch of chemistry deals with the study of hydrocarbons
What is organic chemistry?
Referred to as a dilution this, it is a genetic element that lightens the coat color of certain species such as mice
What is a dilution gene or dilution allele?
Marvel fans will find it easy to identify this element named after a hammer-wielding Norse god
What is thorium?
This type of microscope utilizes electrons as a source of illumination. The physics department has one in Adams Business Park
This German chemist won the Nobel prize in 1907 for his work on fermentation. A ceramic laboratory funnel bears his name
Who is (Eduard) Buchner?
This branch of chemistry focuses on studying metals and minerals
What is inorganic chemistry?
An important technique for achieving large dilution factors, this technique involves successive additions of a number of solutions, multiplying the dilution factor with each transfer
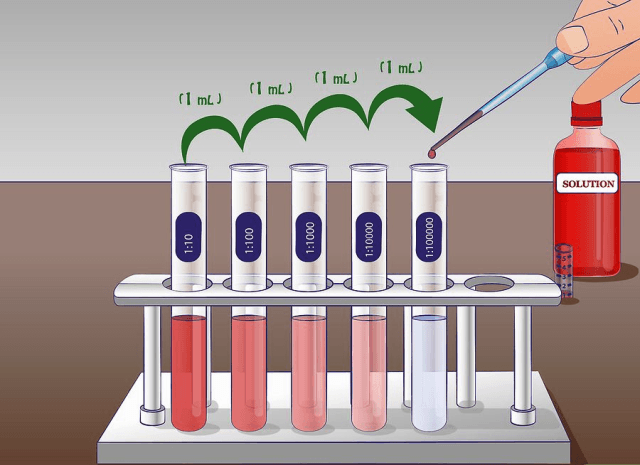
What is a serial dilution?
This number 94 element is named after a planet... or is it a moon
What is plutonium?
This instrument measures the mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio of molecules using electric and magnetic fields. It is often used for isotope dating and protein characterization
What is a mass spectrometer?
The first modern chemist who made his name in the 17th century is known for a law that relates volume to pressure, P1V1=P2V2
Who is (Robert) Boyle?
A subset of physical chemistry, this branch of chemistry focuses on subatomic mechanics of molecules and electron contribution. The chancellor of Germany, Angela Merkel, was awarded a Ph.D. in this field.
What is quantum chemistry?
This term means "the widening of the luminal diameter of the blood vessels"
What is vasodilation?
This element is named after a Renaissance astronomer who caused a lot of 14th-century controversy with his book On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres
What is Copernicium?