A type of cell with an organized nucleus.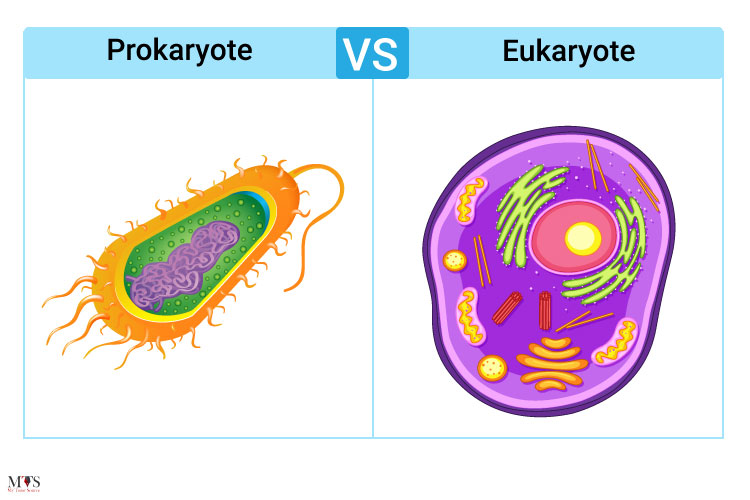
Eukaryote
The name of a monomer that joins together to make polysaccharides like sucrose.
Monosaccharide (or glucose).
Process in which light is used to combine CO2 and H2O to make glucose.
Photosynthesis.
Process in which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Passive transport.
The smelliest cell that we studied through the microscope.
Onion cell
The layer that surrounds a cell and creates a boundary.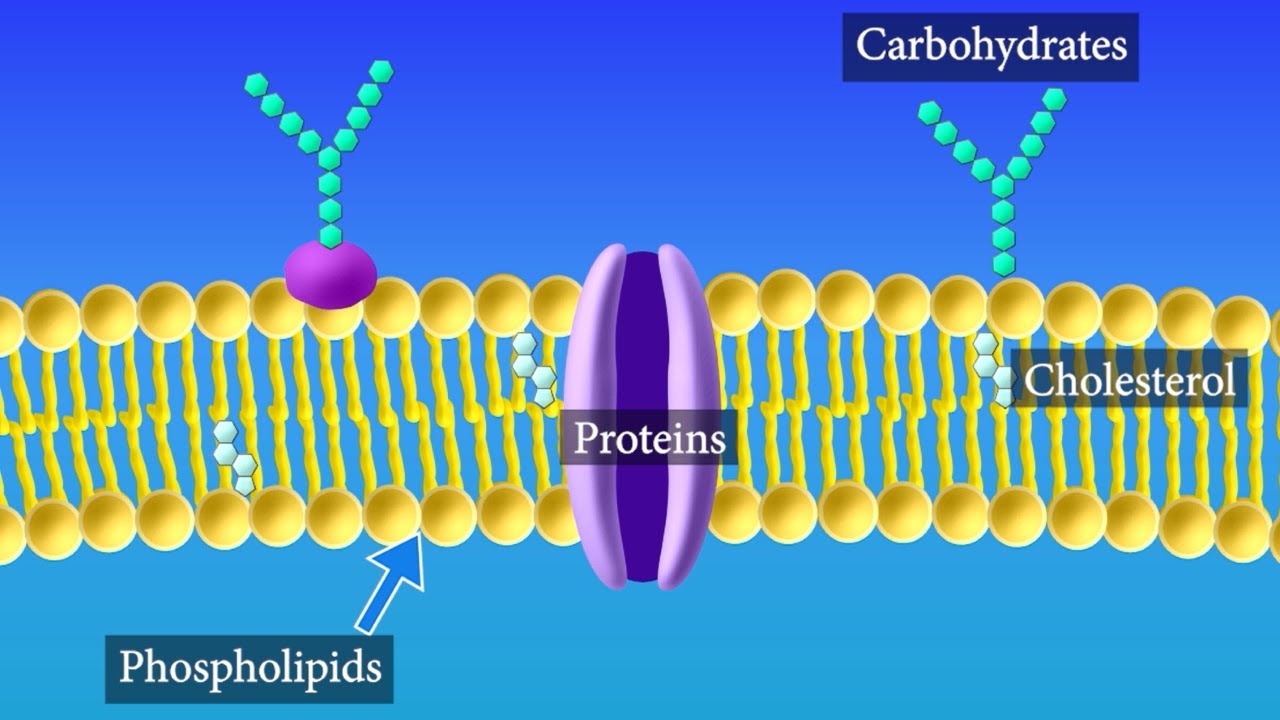
Plasma (cell) membrane
Biological protein catalysts that speed up reactions are called:

Enzymes
Process in which cells break down glucose to create lots of ATP while releasing CO2 and H2O.
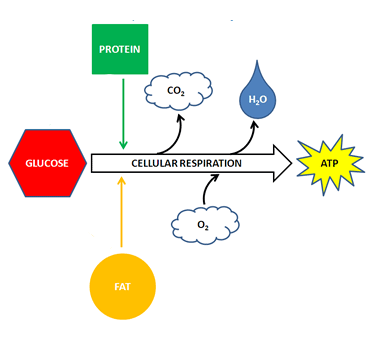
Respiration
The cell barrier that includes the "fluid mosaic model" and is highly selective about what passes through:
Plasma (cell) membrane.
A form of passive transport that is assisted by proteins in the plasma membrane.
Facilitated diffusion
The plant organelle that conducts photosynthesis.
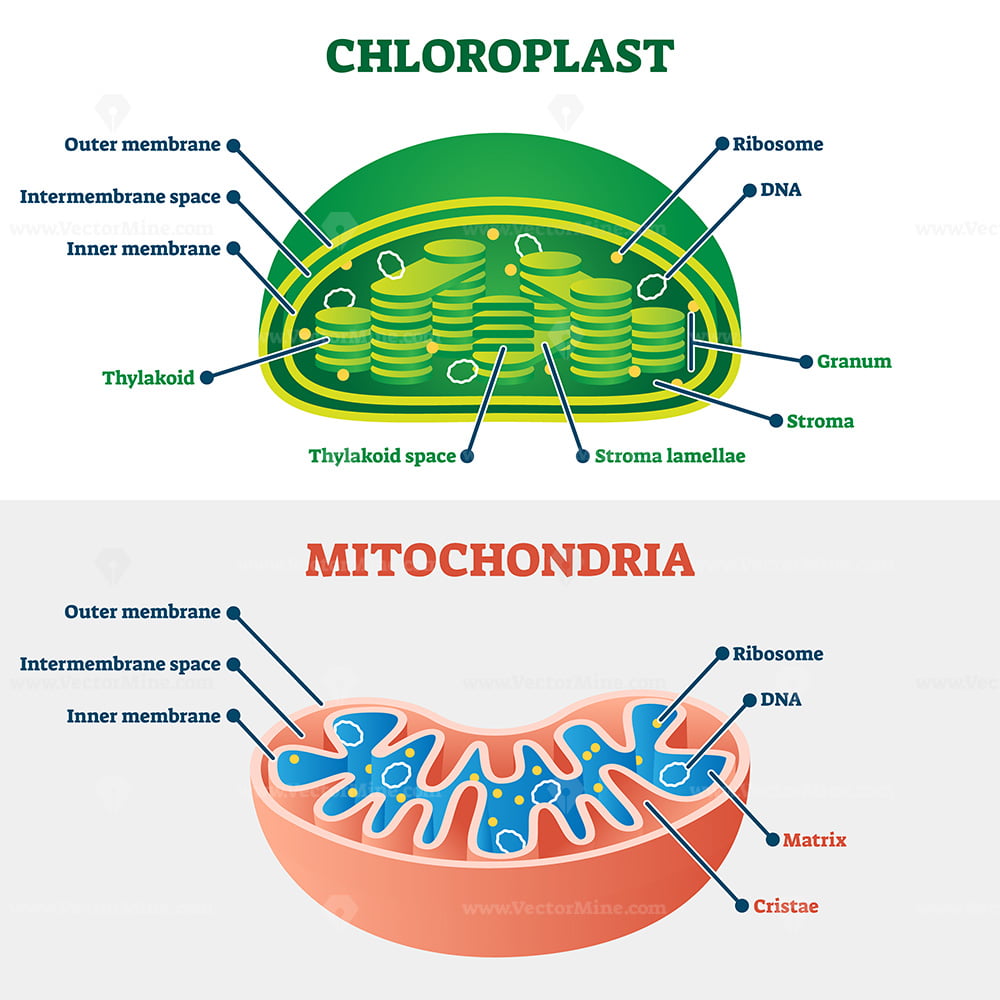
Chloroplasts
A bio-chemical that has the formula CnH2nOn and is made in photosynthesis.
Glucose. C6H12O6
Process in which glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to create CO2, H2O, and 36 ATP.
Respiration
A form of cellular transport that moves AGAINST the concentration gradient and requires ATP.
Active transport.
Daily Double:
The 4 types of organic macromolecules are called
proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids
Organelle in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes that is the site of protein synthesis.
Ribosome
Biomolecule made of long chain of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.
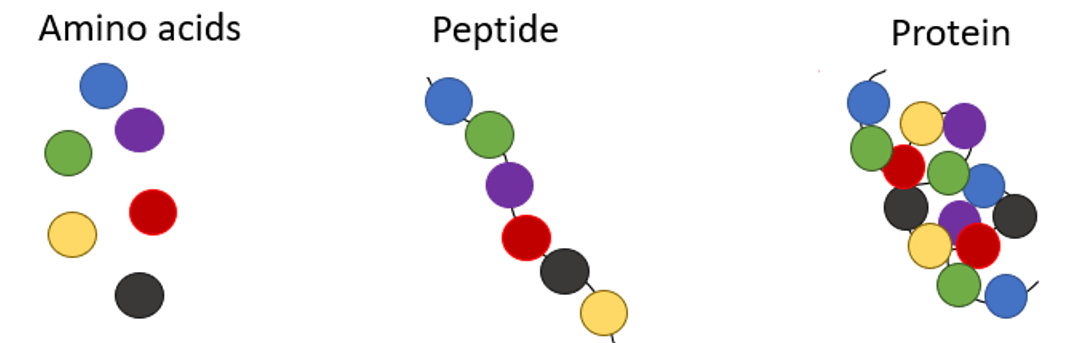
Protein.
For eukaryotes, photosynthesis take place in which organelle.
Chloroplast.
A type of biomolecule found on the plasma membrane that helps move items across a membrane in facilitated diffusion: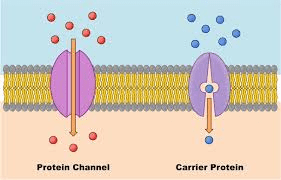
Protein.
The of RNA found in the cytoplasm of the cell that helps with protein synthesis by transporting amino acids to the ribosome.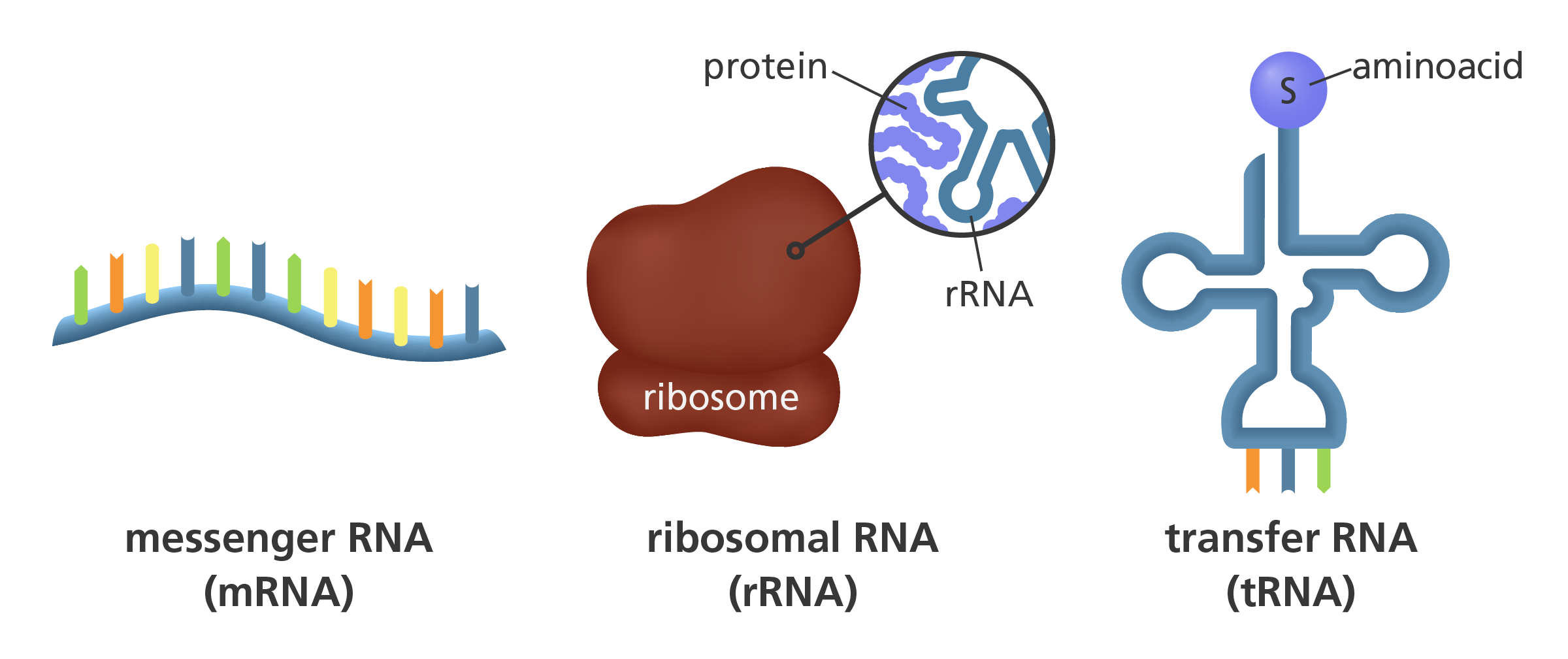
tRNA or transfer RNA
Nucelic acid found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
DNA.
Any biochemical made up of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, and hormones.
Lipids
During respiration, the most ATP is generated during which "system?"
Electron transport system.
The diffusion of water across a membrane is known as:
Osmosis.
A type of active transport that involves the creation of vesicles that export materials out of the cell.
Exocytosis
