The basic unit of structure and function in living things
What is a cell?
"Mini organs" inside cells-perform unique functions
What is an organelle?
Particles moving from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
What is cell specialization?
Molecule that can release and store energy by breaking and reforming the bonds between its phosphate groups
What is ATP?
All cells have DNA and a ___________
What is a cell membrane?
"Power plants" of the cell because they transfer chemical energy from food to compounds the cells can use
Process in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels
What is facilitated diffusion?
A group of similar cells that perform a particular function
What is a tissue?
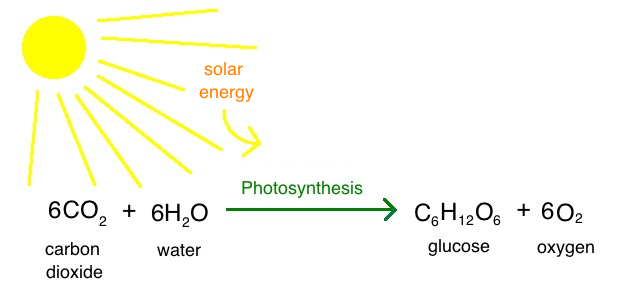
What is photosynthesis?
Idea that new cells can only be produced by the division of existing cells
What is cell theory?
Proteins are assembled on these organelles
What are ribosomes?
The state of relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions
What is homeostasis?
A group of tissues working together
What is an organ?
Light-absorbing compounds; the principal one in plants is chlorophyll
What are pigments?
Image from a microscope
What is a micrograph?
The portion of the cell outside the nucleus
What is the cytoplasm?
Water channel proteins
What are aquaporins?
Accepts and responds to molecular signals
What are receptors?
A stack of thylakoids
What is grana/granum?
Allows scientists to study cells and cellular components that are too small to see with your eye alone
What are microscopes?
Two organelles that are responsible for movement of a cell in its environment
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
What is osmosis?
Nervous system is an example of a ____
What is an organ system?
Electron carrier that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them to another molecule that helps in photosynthesis
What is NADP+