This antiarrhythmic medication slows AV conduction and may inhibit reentry pathways. It is given rapidly at a dose of 6 mg followed by 20 cc flush and may be repeated at 12 mg.
What is Adenosine
The nurse is caring for a client who has just had implantation of an automatic internal cardioverter-defibrillator. Which assessment is the nursing priority?
1. Anxiety level of client and family
2. Activation status and settings of the device
3. Presence of Medic Alert card for client to carry
4. Knowledge of restrictions on post discharge physical activity
What is assess device settings as the priority, similar to the permanent pacemaker
* Is device activated
* What is the heart rate cutoff above which it will fire
* Number of shocks it is programmed to deliver
Name this rhythm
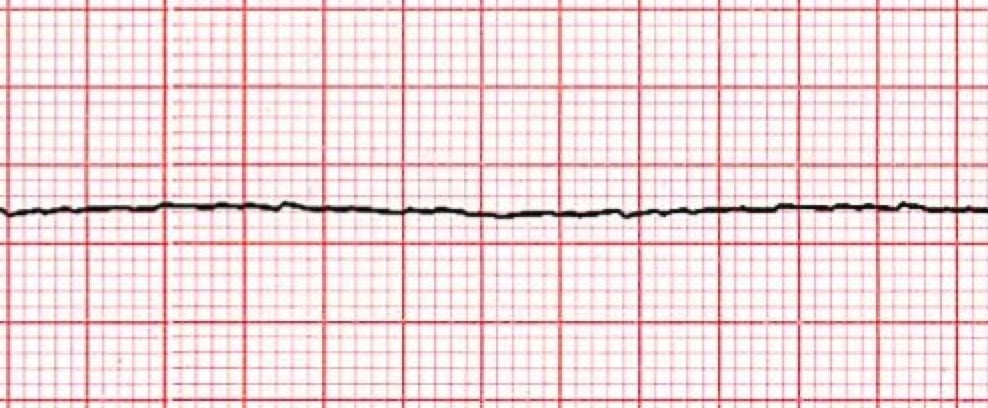
What is asystole?
A client's electrocardiogram strip shows atrial and ventricular rates of 110 beats per minute. The PR interval is 0.14 sec, the QRS complex measures 0.08, and the RR intervals are regular. How would the nurse interpret this rhythm?
Sinus tachycardia
May cause failure to thrive, fatigue during feeding or activity, irregular heart rate and murmur in infants
An antiarrhythmic medication used to control of ventricular rate in A-fib and A-flutter. Second line after adenosine for narrow complex SVT. It inhibits calcium transport into the cell, decrease SA and AV node conduction, prolongs AV node refractory period. Cardiac contractility and PVR is decreased.
What is Cardizem
The nurse is assisting to defibrillate a client in ventricular fibrillation. Which intervention is a priority after placing pads on the client.
1. Ensure the client has been intubated
2. Set the defibrillator to "synchronize" mode
3. Administer an amiodarone bolus
4. Confirm the cardiac rhythm
What is confirm the cardiac rhythm
Name this rhythm.
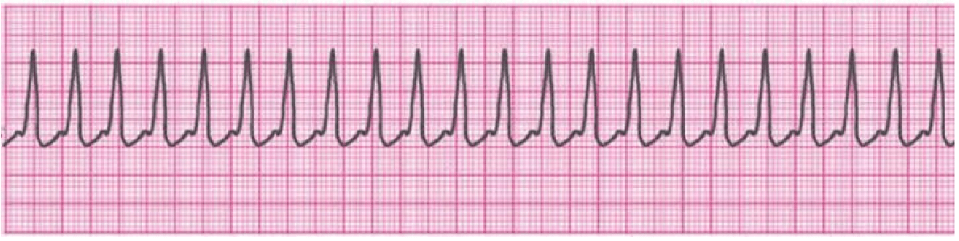
What is SVT?
The nurse is reviewing an electrocardiogram strip. The P waves and QRS complexes are regular. The PR interval is 0.16 sec. and QRS complexes measure 0.06 sec. The overall heart rate is 64 bpm. What is the priority action of the nurse?
1. Check vital signs
2. Check lab test results
3. Monitor for any rhythm change
4. Notify the hospitalist
What is monitor for any rhythm change?
Rhythm: NSR
Atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect often cause blood to return to the right ventricles and recirculate resulting in?
What is increased pulmonary blood flow?
A class III antiarrhythmic medication that prolongs action potential and refractory period; slows sinus rate, increasing PR interval and QT interval, decreases peripheral vascular resistant. Indicated for VF and VT.
What is Amiodarone
A client in sinus bradycardia, with a heart rate of 45 bpm and blood pressure of 82/60 reports dizziness. Which intervention would the nurse anticipate will be prescribed?
1. Administer digoxin
2. Defibrillate the client
3. Continue to monitor the client
4. Prepare for transcutaneous pacing
What is prepare for transcutaneous pacing
n irregularly irregular narrow complex rhythm that has an erratic wavy baseline and loss of atrial kick.
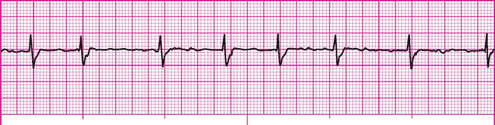
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
A client's cardiac rhythm suddenly changes on the monitor. There are no P waves; instead, there are fibrillatory waves before each QRS complex. How would the nurse interpret the rhythm?
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
What non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug inhibits prostaglandin E synthesis promoting patent ductus arteriosus closure
What is Indomethacin?
This medication is a parasympatholytic use as first line treatment for unstable bradycardia at a dose of 1 mg IVP.
What is Atropine
A client is wearing a continuous cardiac monitor, which begins to alarm. The nurse sees no electrocardiographic complexes on the screen. What is the priority nursing action?
1. Call a code
2. Check the client's status
3. Call the hospitalist
4. Document the lack of complexes
What is check the client's status immediately
A wide (and bizarre) complex, regular rhythm at a rate of 101-250 bpm. The P waves are usually absent or, with retrograde conduction to the atria, may appear after the QRS. T wave is frequently in the opposite direction of the QRS complex.
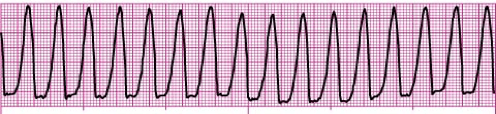
What is Ventricular Tachycardia
The nurse is monitoring the cardiac monitor and notices that a client's rhythm suddenly changes. There are no P waves, the QRS complexes are wide, and the ventricular rate is regular but more than 150 bpm. The nurse determines that the client is experiencing which dysrhythmia?
An abrupt increase in systemic vascular resistance and pulmonary blood flow causing a sudden decrease in cardiac output and venous return is called _________.
"tet" spell or "hypercyanotic episode"
Catecholamine, adrenergic agent, vasopressor, bronchodilator. Mechanism of action: Beta 1 & 2 agonist, Alpha 1 agonist. Used for cardiac arrest or symptomatic bradycardia.
What is epinephrine
This supraventricular arrhythmia that is characterized by a "saw toothed" appearance
What is Atrial Flutter
Rapid and chaotic with no pattern or regularity
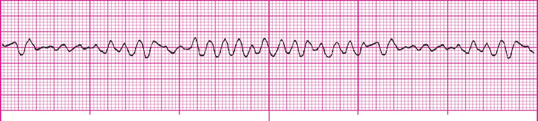
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
A client has frequent bursts of ventricular tachycardia on the cardiac monitor. Which factor is the highest priority with regards to this dysrhythmia?
1. It can develop into v.fib at any time
2. it is almost impossible to convert to a normal rhythm
3. it is uncomfortable for the client, giving a sense of impending doom
4. It produces a high cardiac output with cerebral and myocardial ischemia
What is it can develop into v.fib/cardiac arrest at any time
Prevalent symptoms include: Feeding problems, failure to thrive, frequent respiratory infections, severe dyspnea on exertion, polycythemia to compensate for lack of oxygen
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?