Its the hormones that are talking:)
Could be lupus, right?
Bug Spray
Don't be nervous:)
Trust your GUT feeling!
100
Name the most common type of thyroid cancer.
Papillary Thyroid Cancer.


100
 What is the diagnosis?
What is the diagnosis?It is Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis.
A noninflammatory condition defined by the presence of flowing osteophytes involving the anterolateral aspect of the thoracic spine at four or more contiguous vertebrae with preservation of the intervertebral disk space and the absence of apophyseal joint or sacroiliac inflammatory changes such as erosions.
100
Who should be screened for HIV (USPSTF)
Adolescents and adults, age 15-65 years old.
100
The intervention for patients with Dementia, that is associated with increased physical conditioning and delay in cognitive decline.
Exercise Training.
100
Sigmoidoscopic finding associate with anthraquinone laxative abuse
What is Melanosis Coli?



200
Give the 3 biochemical tests used to diagnose Cushing's syndrome. How many from them need to be positive before the diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome can be made.
1. Overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
2. 24-hour urine free cortisol (UFC)
3. Late-night (LN) salivary cortisol.
Atleast 2/3 must be positive for diagnosis of CS.
The 24-hour UFC and LN salivary cortisol tests should be performed at least twice to ensure reproducibility of results.


200
1.  2.
2.  What are these findings in a 55 year old male? Give 2 additional clinical signs/symptoms he may present with.
What are these findings in a 55 year old male? Give 2 additional clinical signs/symptoms he may present with.
 2.
2.  What are these findings in a 55 year old male? Give 2 additional clinical signs/symptoms he may present with.
What are these findings in a 55 year old male? Give 2 additional clinical signs/symptoms he may present with. These are 1. Dactylitis (“sausage digit”) and 2. Pencil-in-cup deformity in psoriatic arthritis.
Other features present in patient with Psoriatic arthritis include: arthritis, onycolysis, nail pitting, rash with scales.
Severity of skin disease neither predicts nor correlates with severity of arthritis. Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of mortality.


200
Bloody diarrhea caused by which organism can mimic appendicitis. Give one complication and the antibiotic of choice.
By Yersenia Enterocolita.
Complication: Reactive Arthritis.
Antibiotic of choice: Fluoroquinolones and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
Infection usually occurs through ingestion of contaminated food products, especially undercooked pork. When mesenteric lymph nodes become infected, abdominal pain may localize to the right lower quadrant; this may mimic the presentation of appendicitis, so the diagnosis is often made at surgery.
200
Name a condition that presents with psychiatric symptoms, seizures, choreoathetoid movements and autonomic instability in association with a malignancy. Which malignancy is it associated with?
Condition__Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (anti-NMDAR) antibody encephalitis (Autoimmune Encephalitis).
Association__ Ovarian teratomas in greater than 50% of patients with the disease because of production of an antibody to a tumor protein that cross-reacts with neuronal tissue.
Treatment__ includes removal of the teratoma to eradicate the immune stimulus and immunosuppression with glucocorticoids or intravenous immune globulin.
200
Constipation diagnosis associated with failure to relax the puborectalis and external anal sphincter muscles
What is Dyssynergic constipation (or pelvic floor dysfunction or pelvic floor dyssynergia)


300
Give two overall and two CT scan findings of Adrenal Cell Carcinoma.
1. Overall findings: >4 cm, irregular margins, calcifications, necrosis.
2. CT scan findings:Density >10 HU, Contrast washout <50% (10 min)
Additional information.
3. MRI signal intensity: Hyperintense on T2-weighted images.
300
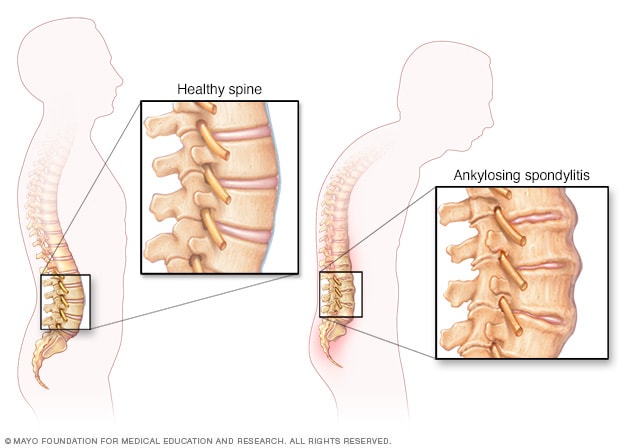
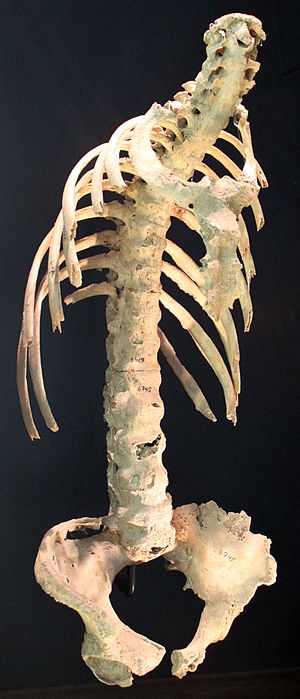
 What is the diagnosis? What would be the expected bone density- higher or lower compared to the matched control group?
What is the diagnosis? What would be the expected bone density- higher or lower compared to the matched control group?It is Ankylosing spondylitis. It can also present with enthesitis, uveitis, urethritis, aortic valve disease, restrictive lung disease, falsely elevated bone mineral density with increased risk of spine fractures. It is associated with HLA B27. C/F: Inflammatory low back pain, 20s-30s, M:F 3:1, syndesmophwytes develop and cause ankylosis leading to kyphosis and rigidity. Mortality increased due to CVD, Cancer and infection.
 ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 
300
In the summer of 1969, Jane Doe presented to her PCP in New York with the following rash for 3 days. She went to the Central Park 4 days ago. Labs: Elevated AST levels. Give the diagnosis and treatment.


Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF). Infections predominate in warmer months when ticks are active. Thrombocytopenia and elevated aminotransferase levels are common. Doxycycline is effective against all spotted fever group rickettsioses.
300
What treatment is as effective as plasma exchange for Guillain-Barre syndrome?
IVIG.
Management options for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) include supportive management, plasmapheresis or intravenous immune globulin (IVIG). Both therapies are equally effective and shorten the time to recovery by as much as 50%. Compared with IVIG, plasmapheresis has a faster mode of action but is less convenient and potentially requires longer hospitalization.
300
59 year old female with history of severe daily migraines and HTN presents with fecal incontinence and watery diarrhea for last 2 months. Her medications include HCTZ and daily ibuprofen.
Colonoscopy finding: What is the most likely diagnosis? How can we confirm it? and give 2 management options.
What is the most likely diagnosis? How can we confirm it? and give 2 management options.
 What is the most likely diagnosis? How can we confirm it? and give 2 management options.
What is the most likely diagnosis? How can we confirm it? and give 2 management options. Microscopic colitis secondary to long term NSAID exposure.
On biopsy: Collagenous or lymphocytic variants.
Management: Discontinue the use of NSAIDS and budesonide. Anti-diarrheals like bismuth can help with symptoms.
The diagnosis of MC is made by histologic evaluation of colonic biopsies; the classic finding is intraepithelial lymphocytosis (>20 intraepithelial lymphocytes per 100 epithelial cells). In collagenous colitis, the main histologic feature is thickening of the subepithelial collagen band (usually >10 µm).
A diagnosis of microscopic colitis should prompt a careful review of prescription and over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs, aspirin, proton pump inhibitors, and others. Celiac disease should also be considered, as it can be associated with microscopic colitis.
For patients who do not respond to or do not tolerate budesonide, treatment with a bile salt binder such as cholestyramine may be effective. In severe cases, treatment with an anti-TNF agent may be needed.
400
Give three indications for parathyroidectomy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism.
1. In asymptomatic patient, increase in serum calcium level ≥1 mg/dL (0.25 mmol/L) above upper limit of normal.
2. Creatinine clearance must be <60 mL/min (0.06 L/min)
3. Age 50 years or younger.
4. Surgery also indicated in patients in whom medical surveillance is neither desired nor possible, including those with significant bone, kidney, gastrointestinal, or neuromuscular symptoms typical of primary hyperparathyroidism.
When one or more of these criteria are met, surgery is recommended.
400
 What is the diagnosis? Give two drugs of choice for the management of coexisting hypertension in this patient.
What is the diagnosis? Give two drugs of choice for the management of coexisting hypertension in this patient. It is Gout. DOC: Losartan and Calcium channel blockers.
Imaging shows punched-out bone lesions and erosions with overhanging edges associated with severe or long-standing gout. Both losartan and calcium channel blockers lower serum urate.
400
Identify all 4 imaging findings.


(A)“Box-car”–shaped, gram-positive Bacillus anthracis bacilli in the cerebrospinal fluid of the index case of inhalational anthrax resulting from bioterrorism in the United States. (B) Terminal and subterminal spores of B. anthracis. (C) Black eschar lesion of cutaneous anthrax. (D) Chest radiograph of a patient with anthrax showing a widened mediastinum due to hemorrhagic lymphadenopathy.
400
This drug is a recently approved treatment for primary progressive (and secondary progressive) MS; it is the first disease-modifying therapy approved to treat primary progressive MS.
What is Ocrelizumab?
In a phase III clinical trial involving patients with primary progressive MS, this drug was associated with lower rates of clinical and MRI disease progression than placebo. The long-term risks of serious adverse effects of ocrelizumab are still being assessed.
400
What is Milan Criteria? Give the management strategy for patients with ESLD who meets the Milan Criteria.
Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma can be made in a patient with cirrhosis in the presence of lesions larger than 1 cm that enhance in the arterial phase and have washout of contrast in the venous phase. Patients who meet the Milan criteria (up to three hepatocellular carcinoma tumors ≤3 cm or one tumor ≤5 cm) have excellent 5-year survival rates after LIVER TRANSPLANTATION. HCC can be diagnosed for lesions>1 cm only, smaller lesions need surveillance.
500
Give the diagnostic criteria for PCOS and four different medications for management of PCOS.
Polycystic ovary syndrome can be diagnosed if two of the following three findings are present:
(1) oligo-ovulation or anovulation, (2) clinical or biochemical evidence of hyperandrogenism (such as hirsutism or acne), or (3) ultrasound findings of polycystic ovarian morphology in at least one ovary.
For management of PCOS:
1. OCP: For irregular menses
2. Clomiphene or Letrozole: For anovulation
3. Spironolactone: For hyperandrogenism s/s like hirsutism and acne
4. Metformin: for insulin resistance.
500
 What is this test? When can you say that it is positive?
In a 44 year old female, this test is positive. She also reports painful tender skin nodules and multiple canker sores. What is the diagnosis?
What is this test? When can you say that it is positive?
In a 44 year old female, this test is positive. She also reports painful tender skin nodules and multiple canker sores. What is the diagnosis?It is Pathergy test. It is positive when a pustule-like lesion or papule appears 48 hours after a sterile skin prick by a 20- to 21-gauge needle.
She has Behçet syndrome.
Diagnostic Criteria for Behçet Syndrome:
Recurrent painful oral ulceration (≥3 times in a 12-month period) is a mandatory feature for diagnosis.
additionally, we need any two from the following four criteria.
1. Recurrent painful genital ulceration- which may lead to scarring.
2. Eye involvement: Panuveitis, isolated anterior uveitis or posterior uveitis, or retinal vasculitis. Hypopyon is a distinctive feature of the anterior uveitis of Behçet, in which a fluid collection of leukocytes is visible in the anterior chamber.
3. Skin involvement: Erythema nodosum, pseudofolliculitis, or acneiform lesions. 2/2 Vasculitis.
4. Pathergy test positivity.
500
Three prescription Neuraminidase inhibitors recommended by CDC for use during the 2017-2018 Influenza season their route of administration and the most common side effect for all three medications.
1. Oseltamivir - PO- nausea/vomiting.
2. Zanamivir - Inhalational- bronchospasm
3. Peramivir - IV: diarrhea.
500
Name 3 characteristics and 3 treatment strategies of Tourette syndrome.
Tourette syndrome is characterized by 1. childhood onset, 2. persistence of multiple complex motor tics for at least 1 year, and 3. presence of vocal tics.
Treatment of Tourette syndrome includes reassurance (often appropriate in mild disease), cognitive behavioral therapy, and treatment of psychiatric comorbidities.
Anti-tic medications like pimozide and haloperidol are indicated when tics cause educational, occupational, or social dysfunction.
500
State all the diagnostic criteria to diagnose primary biliary cirrhosis/cholangitis (PBC)
1. No extrahepatic biliary obstruction
2. No other comorbidity affecting the liver
3. PLUS two of the following: ALK P > 1.5X ULN, anti-mitochondrial Ab's 1:40 or higher, histologic evidence of PBC