Problems
The diagnosis that is most compatible with the physical examination finding shown here.
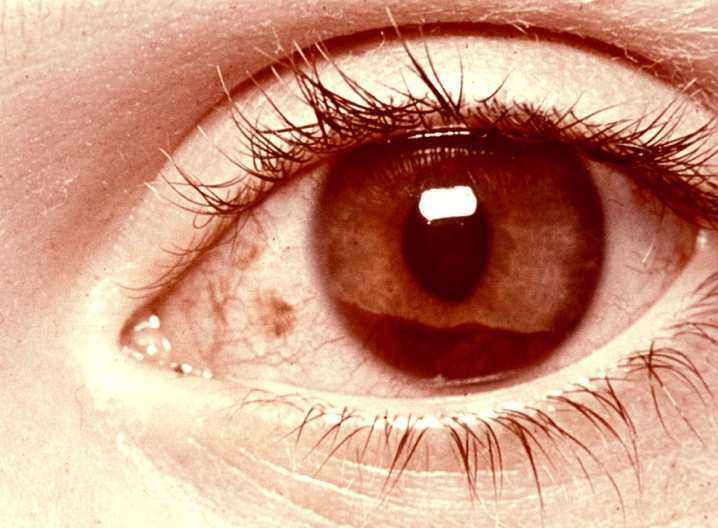
Hyphema
The likely diagnosis for a patient with this urine sediment analysis. Her urine pH was 12.
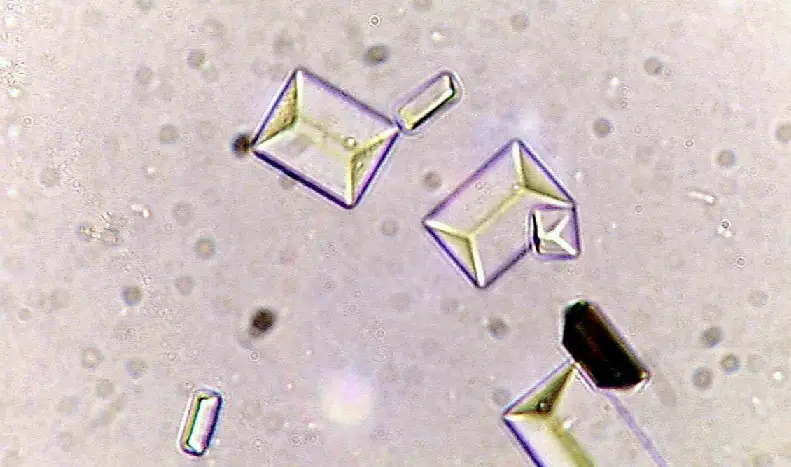
Triple phosphate crystals ("coffin lids")
Typically with alkaline urine and associated with proteus infection (urea splitting bacteria)
Patients can have "staghorn calculi" on imaging
The 2 findings on this cardiogram can be seen in patients with HFrEF

•S3 gallop and Mitral Regurgitation
Loop diuretics act on this receptor in the loop of Henle
•Na/K/2Cl co-transporter
These are 4 causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis

The likely diagnosis for patient with this rash
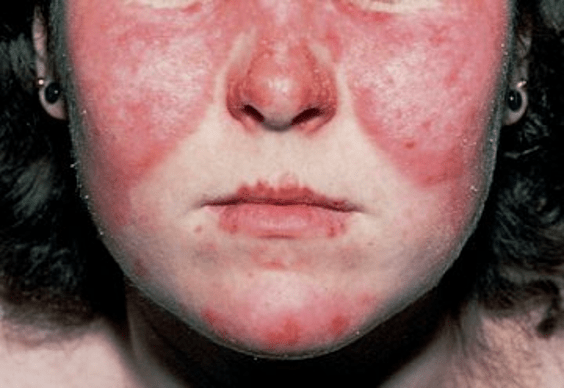
•Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) is characterized by erythema/edema over the cheeks and bridge of the nose, sparing the nasolabial folds.
•Occurs in 50% of patients with SLE
The most likely diagnosis for this painless eye finding that appeared spontaneously overnight
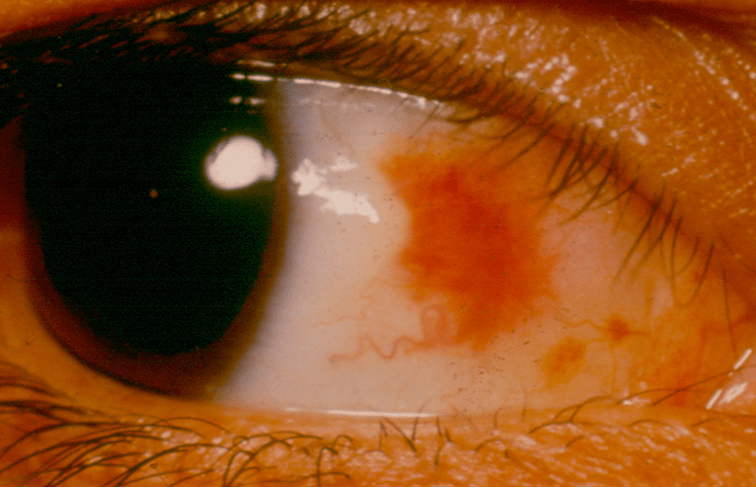
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
The most likely diagnosis in a patient with this urine sediment analysis
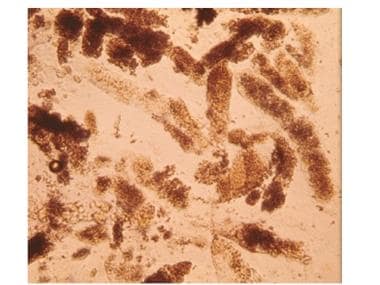
Acute Tubular Necrosis
In a patient with difficult to assess JVP, these are two techniques that could be used to help estimate the R atrial pressure
•Change position, HJR, bedside US
•Beside US (evaluate the IVC)
–IVC diameter (>2.5cm indicates high RA pressure)
–“sniff test” tests for collapsibility of the IVC (If <50% collapse on sniff = high RA pressure)
The ECG finding shown here can be seen in patients taking this drug for heart failure
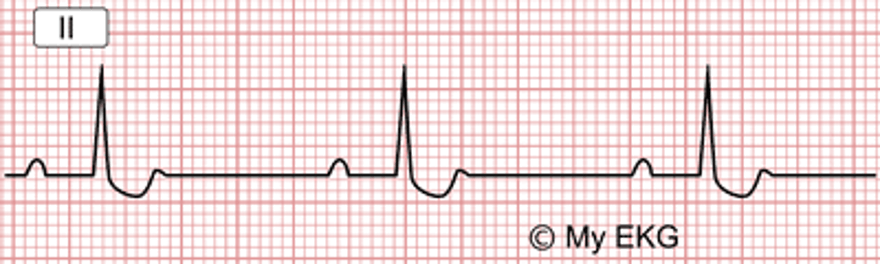
Digoxin
•ST depression in a concave shape, known as a "reverse tick sign" or as "Salvador Dali sagging sign".
•Flat, negative or biphasic T waves.
•Short QT interval.
•Prolonged PR interval (secondary to increased vagal tone).
•Prominent U waves.
The anion gap calculated from these labs:
Na 143
K 3.8
Cl 102
HCO3 16
Albumin 4.0
BUN/Cr 18/1.2
30
Anion gap: Na – (HCO3 + Cl)
Anion gap = 143– (102+16) = 25
Remember to correct for albumin!
Every drop of albumin by 1.0, AG increased by 2.5
AG = Agobs – 2.5(4-albumin)
The most likely diagnosis for a woman with bilateral hand pain as well as elbow and knees worse in the morning on-going for 2 months.
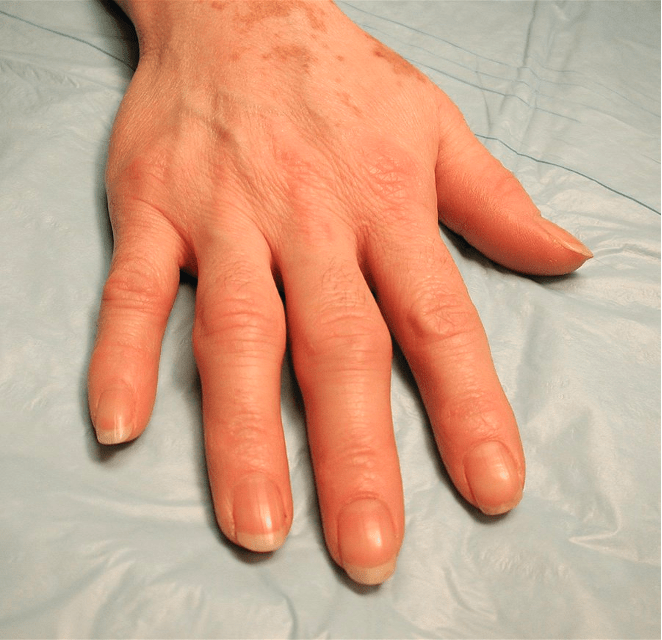
•Rheumatoid arthritis
•Symmetric involvement
•RA often spares the DIP joints
•Check anti-CCP Ab
A patient with ankylosing spondylitis developed this painful red eye condition. What is the most likely diagnosis
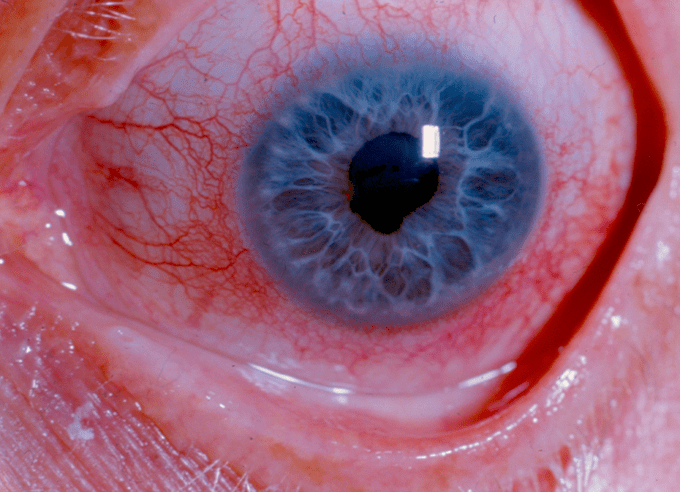
Iritis
The finding shown in this phase-contrast urine microscopic image for a young man presenting with hematuria, proteinuria, and acute kidney injury . Which of the following diagnoses is most compatible with the urinalysis finding shown on this phase-contrast microscopic image
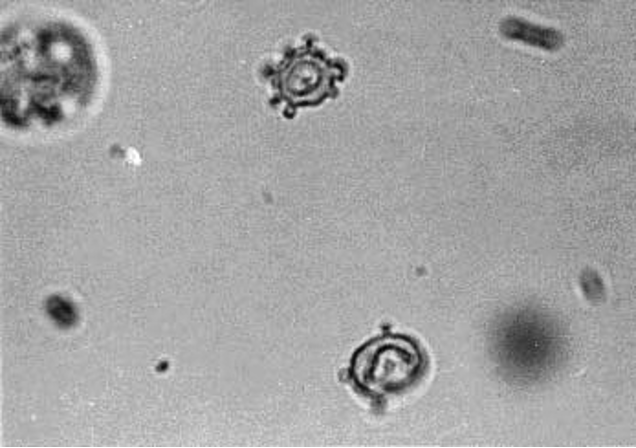
Findings show dysmorphic red blood cells ("micky mouse" RBC with out-pouching of the membrane) often seen in glomerulonephritis
This maneuver can be used to assess for inflammation of the sacro-iliac (SI) joint.
FABER test
Drugs like alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha) inhibit this molecule and can improve cardiovascular mortality
PCSK9
Usually adjunct with statins
In patients with hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis (non-anion-gap), the urine anion gap, which is an indirect measurement of this molecule, can be used to differential GI versus renal causes.
•NH4+ (ammonium)
•Urine anion gap = (UNa + UK) – UCl
•Indirect marker of acid excretion (cannot measure NH4+ but binds to Cl- for exrection)
•NeGUTive anion gap – consider GI causes
•Positive anion gap – consider renal causes
This is the likely diagnosis the following patient presentation:
A 75 y/o woman with 2 weeks of increasing pain in both shoulders and hips that radiates down to both arms to the elbows and down both hamstrings to the knees. The pain and stiffness is worse in the morning She reports no headache, jaw claudication, or vision changes. ESR level is 115 mm/hr
•Polymyalgia Rheumatica
•Consider Gian Cell Arteritis (similar spectrum of disease process)
•Key - responds dramatically to low dose steroids (10-20mg/day)
What is the diagnosis for this chronic, painless finding in a patient with slowly progressive, painless visual loss?
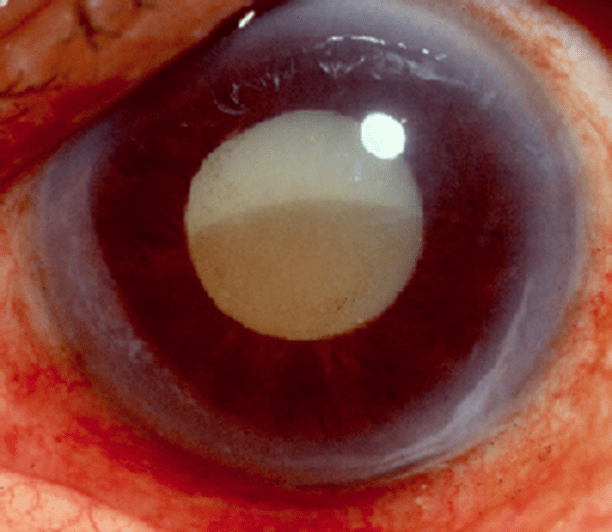
Cataract
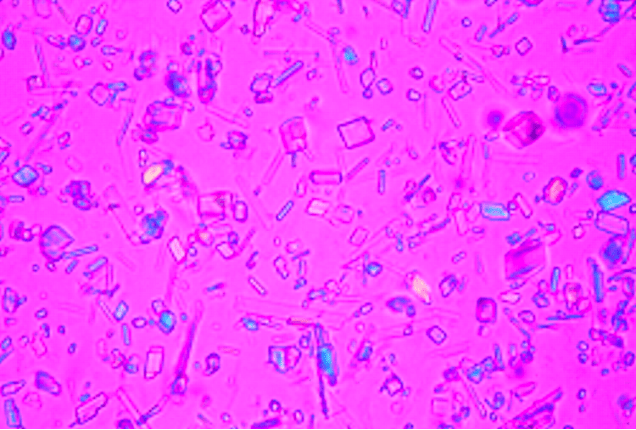
The composition of these crystals on urine sediment that can be seen in acidic urine
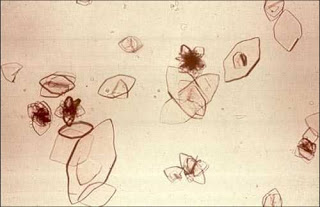
Uric acid crystals - pleomorphic often described as rhomboid or parallelograms or rosettes
This finding can be seen in patients with right heart failure or restrictive cardiomyopathy
•Kussmaul sign
Paradoxical increase in JVP on inspiration
A side-effect of this drug shown below
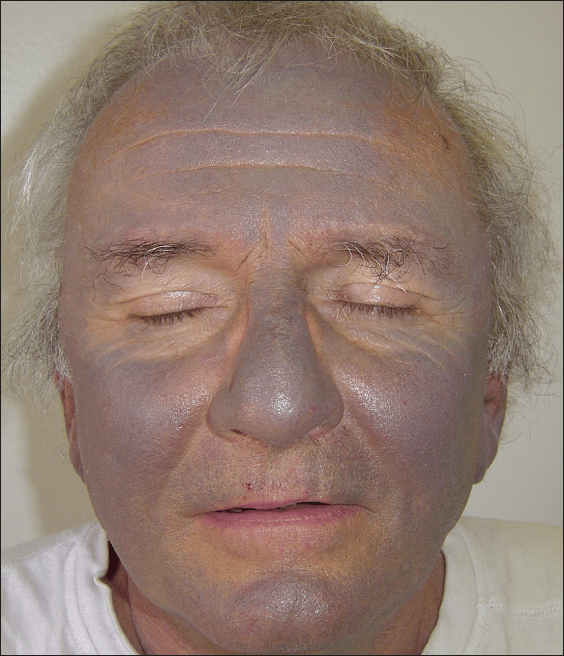
•Amiodarone
•Blue-Gray skin syndrome
This is the expected pCO2 by Winter’s formula for these labs:
pH 7.24
pCO2 23
pO2 80
Na 130, K 3.2, Cl 100, HCO3 10
Glc 72, BUN/Cr 30/1.7
Primary anion gap metabolic acidosis with appropriate compensation with non-gap metabolic acidosis
pH<7.4, acidemia
HCO3 10, pCO2 23, primary metabolic;
AG = 20, anion gap
Winter’s equation: pCO2=1.5*HCO3 + 8
Expected pCO2= 23 (appropriate)
D HCO3 = 14 and D AG = 8
HCO3 = Observed HCO3 + DAG which is low so additional metabolic acidosis
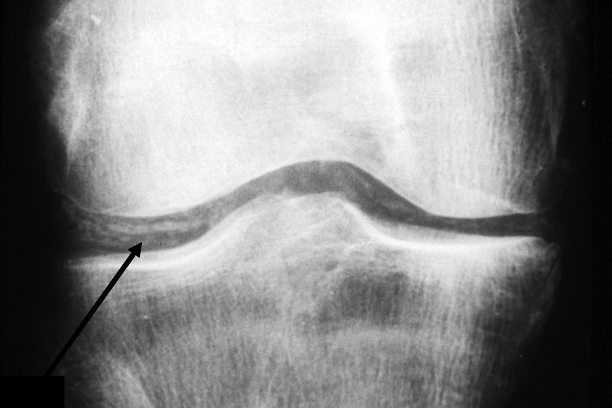
This is the diagnosis for a 43-year-old woman with 3-day history of left knee pain and swelling with large effusion over the Left knee with XR showing a thin white line at the chondral surfaces of both knees and at the pubic symphysis and joint aspiration showing a leukocyte count of 35,000/µL (35 × 109/L), with 90% neutrophils and polarizing microscopy shows numerous positively birefringent rhomboid crystals within neutrophils.
•Acute CCP (Pseudogout)
The likely diagnosis for these fundoscopic findings
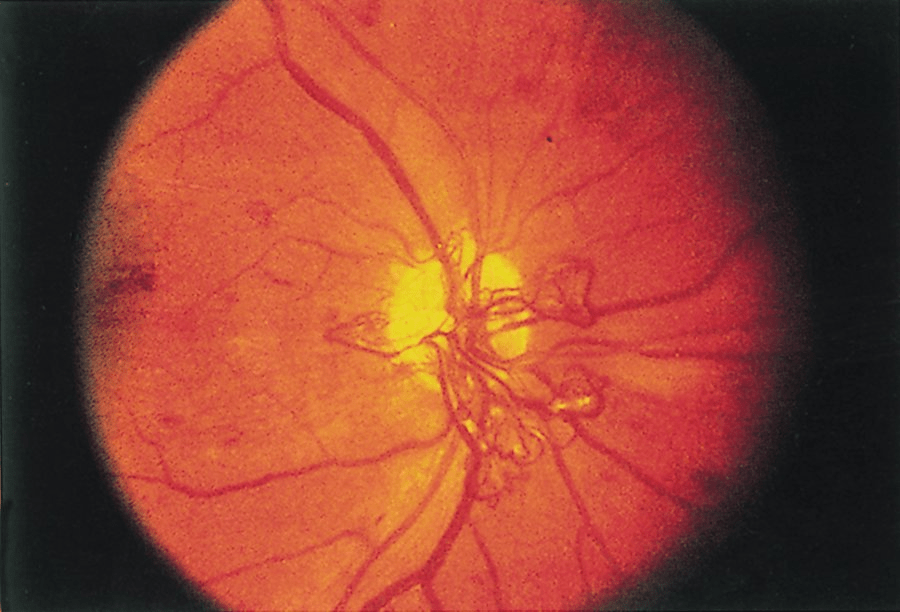
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
-Exudates, hemorrhage, neovascularization
The composition of these crystals seen on urine sediment suggest an inherited disorder involving amino acid reabsorption at the proximal tubule.
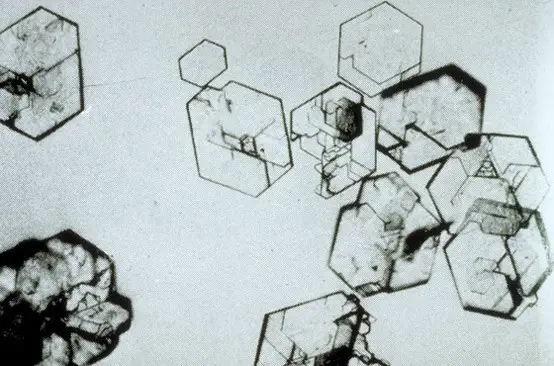
Cystine crystals - hexagonal shaped crystals
This murmur
Aortic regurgitation is a high-pitched diastolic murmur heard best along the mid-left upper sternal border.
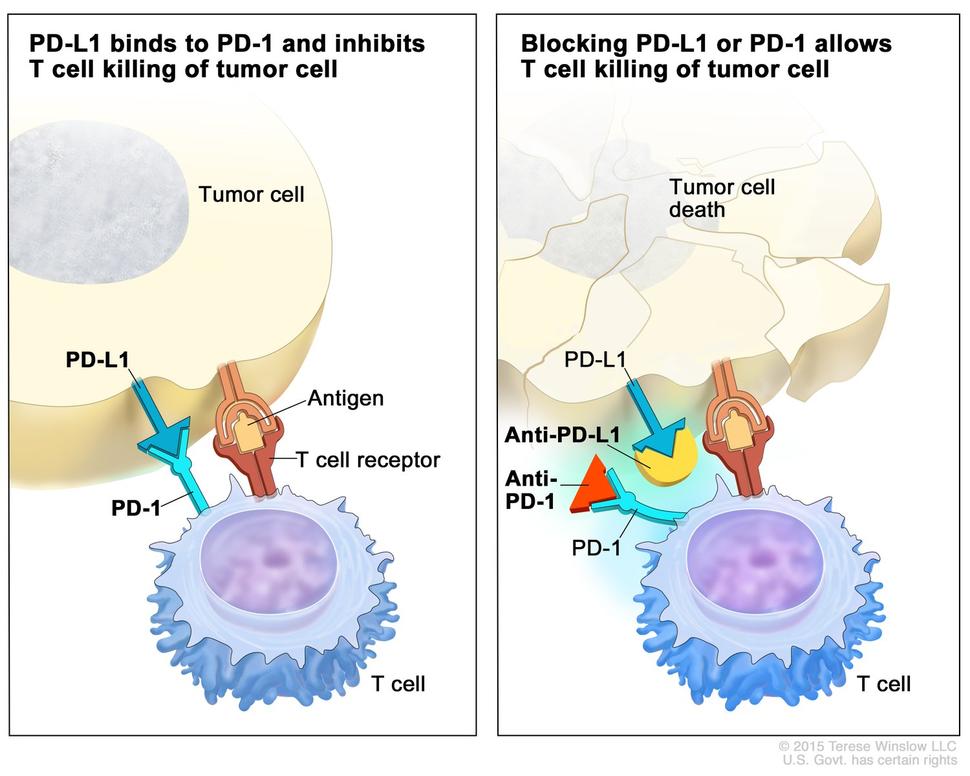
Drugs such as Pembrolizumab and Nivolumab target this protein and can be used to treat cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer
PD-1 and PD-L1
PD-1 is a checkpoint protein on immune cells called T cells. It normally acts as a type of “off switch” that helps keep the T cells from attacking other cells in the body. It does this when it attaches to PD-L1, a protein on some normal (and cancer) cells.
When PD-1 binds to PD-L1, it basically tells the T cell to leave the other cell alone. Some cancer cells have large amounts of PD-L1, which helps them hide from an immune attack.
Monoclonal antibodies that target either PD-1 or PD-L1 can block this binding and boost the immune response against cancer cells.
This is the likely diagnosis for patient with prior history of bulimia with orthostasis with these labs:
pH 7.50
pCO2 45
pO2 92
Na 141, K 3.1, Cl 98, HCO3 34
Urine Cl 84
Surreptitious diuretic use
Appropriately compensated metabolic alkalosis that is saline resistant
pH 7.50 – alkalemia
HCO3 >24 and pCO2 > 40, primary metabolic alkalosis
Expected pCO2:
DpCO2 = 0.6*DHCO3
pCO2 = 0.6*(34-24)+40 = 46
Urine Cl>20, “saline resistant”
These are three diagnostic findings for Behçet disease
•Associated with HLA-B51
