This is the most common posterior mediastinal neurogenic tumor
What is schwannoma?
This degenerative mitral valve disease is characterized by thinning of leaflet tissue from insufficient collagen, elastin and proteoglycan
What is fibroelastic deficiency?
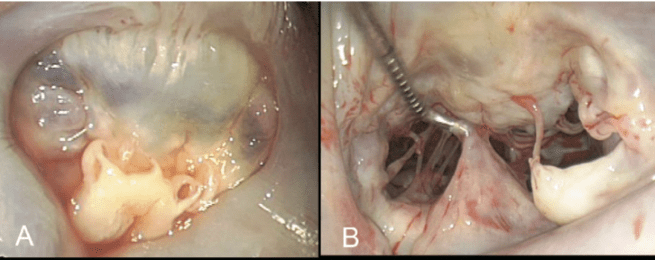
This malignant tumor originating from cartilaginous tissue at the costochondral joint is often resistant to chemotherapy
What is chondrosarcoma?
Papillary muscle most prone to rupture from inferior myocardial infarction
What is the posteromedial papillary muscle?
This coronary artery must be significantly diseased for minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass to be considered as a standalone operation
What is the left anterior descending (LAD) artery?
The posterior insertion of the first rib is between these 2 nerve roots
What are C8 and T1?
Dynamic condition shown at the blue arrow
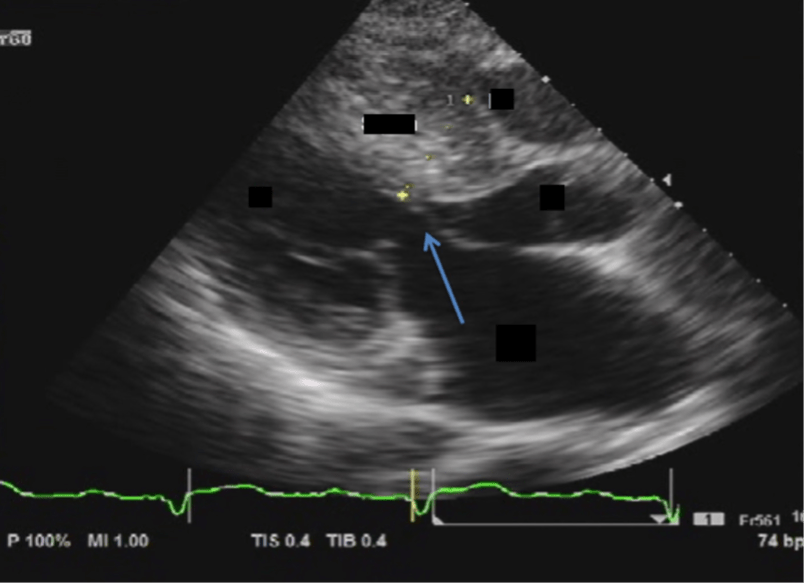
What is systolic anterior motion (SAM)?
This coronary angiogram view from a left heart catheterization clearly shows the entire circumflex artery and OM branches
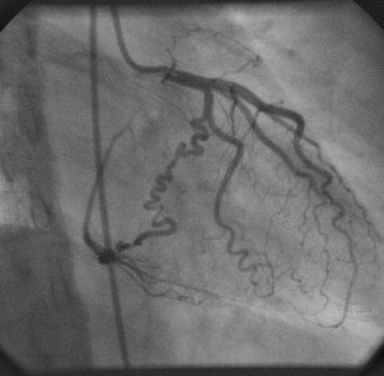
What is RAO caudal?
The vascular structure most at risk of injury during posterior fissure dissection in a right upper lobectomy
What is the posterior ascending artery?
CABG is recommended to improve survival in ischemic cardiomyopathy when LVEF is at or below this percentage
What is ≤35%?
In neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome, conduction velocity > 60 m/s in this nerve predicts good response to conservative management
What is the ulnar nerve?
An LV end-systolic diameter above this measurement is a Class I indication for surgery in asymptomatic severe primary MR
What is LVESD ≥40 mm?
In a 5-chamber view of the heart, this is the structure marked “A”
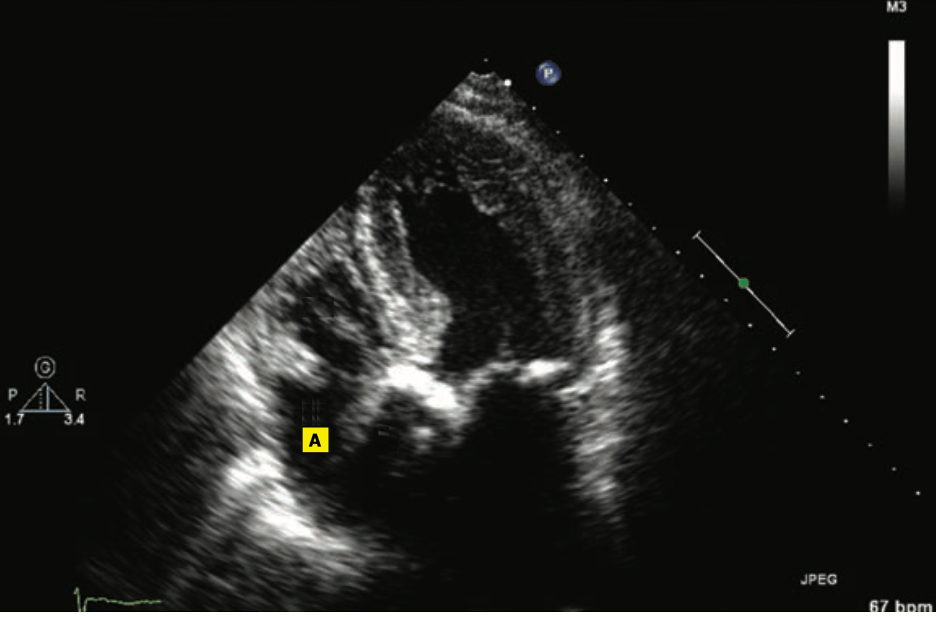
What is the right atrium?
This structure stretches from the Eustachian ridge to the central fibrous body and forms a boundary of the triangle of Koch
What is the tendon of Todaro?
According to the SYNTAX trial, patients with scores above this threshold have greater survival benefit from CABG than from PCI
What is > 22?
Interruption of this sympathetic chain level is most associated with severe compensatory hyperhidrosis
What is T2?
In asymptomatic severe MR with preserved LV function, a resting pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) above this value is a Class IIa indication for surgery
What is >50 mmHg?
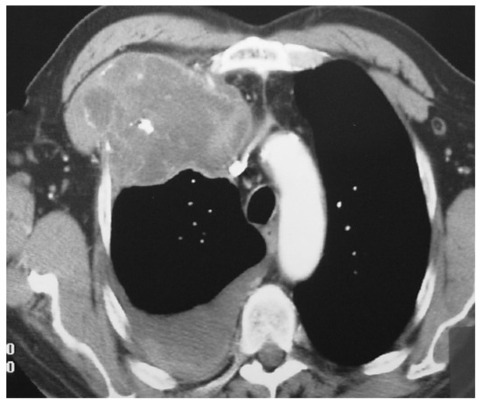
A radiographic sign of a mobile intracavitary fungus ball surrounded by air, classically seen in aspergillosis
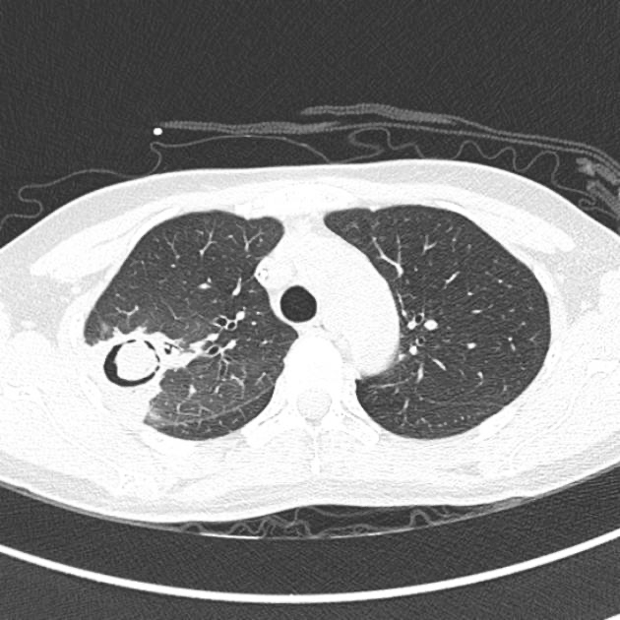
What is Monod sign?
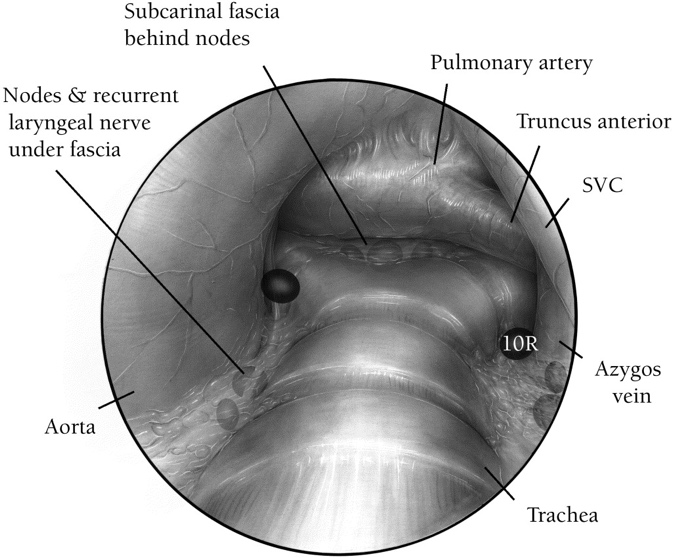
During cervical mediastinoscopy, this structure is at risk of injury when dissecting too anteriorly over the right main bronchus
What is the truncus arteriosus? (will also accept right PA)
The coronary bypass conduit whose patency is most affected by competitive native coronary flow
What is the radial artery?
When performing sympathectomy, these are the two target levels most likely to effectively treat palmar hyperhidrosis
What is T3-T4?
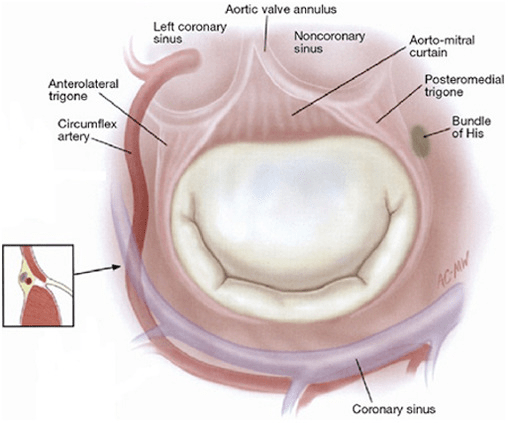
The structure most likely injured during a mitral valve repair when sutures are placed at the 2:00-3:00 region of the mitral annulus
What is the AV node/bundle of His (or conduction bundle)?
This paraneoplastic syndrome most commonly associated with lung adenocarcinoma is characterized by painful swollen joints and digital clubbing
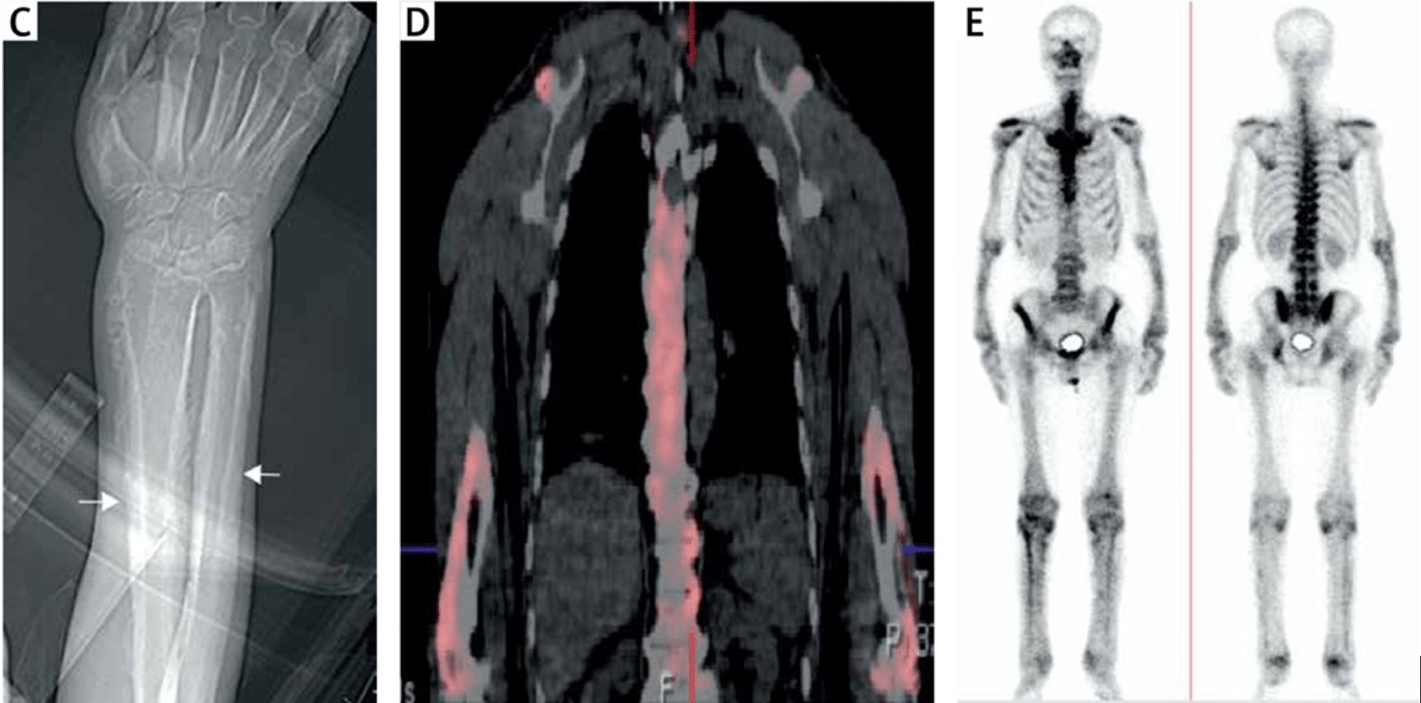
What is hypertrophic (pulmonary) osteoarthropathy?
Digital clubbing, increased periosteal activity of the tubular bones, arthralgias, and joint effusion. Lung adenocarcinoma accounts for 90% cases.
The thoracic duct is located between these two vascular structures in the chest
What is the aorta and the azygous vein
The most common cause of mortality in lung transplant recipients after the 1st year of transplantation
What is chronic lung allograft dysfunction?