Sutures, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis belongs to this type of structural joint.
What is fibrous?
Explanation: Fibrous joints are a structural type of joint. Sutures can be found in the skull. Syndesmoses can be found in ligaments. Gomphoses can be found in the tooth and socket complex.

Three basic types of movements at synovial joints.
What are gliding, angular movements, and rotation?
Explanation: These three basic movements allow our bones to move in all three planes or axes (sagittal, frontal, transverse) as a collective unit.

A joint that moves in one axis is ___ and a joint that moves in all three axes is ___.
What is uniaxial; multiaxial?
Explanation: Uniaxial joints can only move in one direction (typically only flexion/extension or only rotation). Multiaxial joints can move in the sagittal, frontal, and transverse plane (only ball and socket joints).
Skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles share this characteristic while smooth muscles don't.
What are striations?
Explanation: Skeletal muscle and cardiac muscles have striations that can be seen under a light microscope. Smooth muscles are not striated (hence the name smooth).
These specialized contractile organelles make up more than 80% of the sarcoplasm and create light and dark striations under the light microscope.
What are myofibrils?
Explanation: Myofibrils are the reason you see light and dark striations. Myo (muscle) fibrils (fiber) is another way to think about and breakdown the word.
These structures monitor the amount of stretch and detect pain in synovial joints.
What are nerves?
Explanation: Nerves are found in synovial joints to monitor stretch and pain, helping you maintain posture and telling your body to relax from movements that may damage a joint.

___ decreases the angle between bones while ___ increases the angle between bones.
What is flexion; extension?
Explanation: When thinking about flexion, think about movements that make your bones move anteriorly. When extension occurs, think about movements that make your bones move posteriorly.

All synovial joints are functionally classified as ___.
What is diarthrotic?
Explanation: Synovial joints can all move freely due to the shape of their articulating surfaces.

The endomysium is ___ to the sarcolemma in a muscle cell (directional term)
What is superficial?
Explanation: The endomysium is the membrane layer that covers muscle fibers while the sarcolemma is the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber. I like to think of a cell and its plasma membrane. The plasma membrane plays a role in acting as a barrier, preventing certain things from coming into the cell. The endomysium on the other hand is a layer that is there to protect it.

This region of the sarcomere is where thin and thick filaments overlap.
What is the A band?
Explanation: The A band is the thick and thin filament overlap that allows for muscles to contract through the sliding filament theory.
Symphysis joints and syndesmotic joints are functionally classified as ___.
What is amphiarthrosis/amphiarthrotic?
Explanation: Amphiarthrosis is a functional classification that means it is slightly moveable. The other two functional classifications consist of synarthrosis (immovable) and diarthrosis (freely moveable)
 At the top of this glute bridge exercise, this movement is occurring at the hips.
At the top of this glute bridge exercise, this movement is occurring at the hips.
What is extension?
Explanation: When looking at the hips at the top position, it extends backward. You can think of it as sitting down and standing up. When you stand up, your hips are extended (moves posteriorly). When sitting down, your hips are flexed (moves anteriorly).
The elbow joints and the atlantoaxial joint are functionally described as this type of synovial joint based on the shape of its articulating surfaces.
What is uniaxial?
Explanation: These joints can only move in one plane or axis. The elbow is a hinge joint (flexion/extension) while the atlantoaxial joint is a pivot joint (rotation).

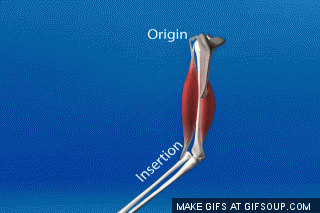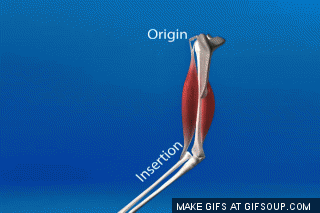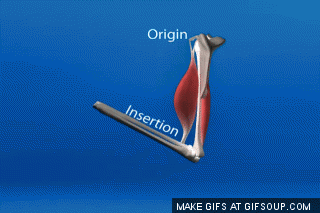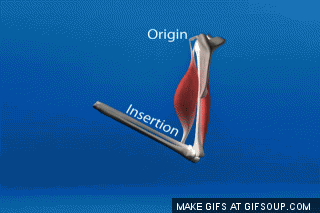
The less moveable bone that a muscle attaches to is the ___ and the more moveable bone that a muscle attaches to is the ____.
What is origin; insertion?
Explanation: The origin is where a muscle starts from and the insertion is where it attaches to. I like to think of origin almost like looking at an evolutionary tree. The origin is the ancestor, branching into its insertions.
This springlike molecule extends from the Z disc to the thick filament and runs within the thick filament and attaches to the M line.
What is Titin?
Explanation: Titin is sort of like an elastic structure that helps prevent a muscle from stretching too far. It is almost like a rubber band. When you pull a rubber band too far, it starts to resist your stretch and when you release it, it coils up.

Overlapping of nerves and vessels in synovial joints play a role in ____ to keep joints nourished if one were to be compressed. (Two words)
What is functional redundancy?
Explanation: Functional redundancy plays a huge role in nourishing and monitoring stretch and pain in synovial joints. There are typically many branches of blood vessels and nerves around a single joint because, during movement, we can compress a blood vessel, not allowing proper diffusion of nutrients to a joint. The extra branches allow for a different blood vessel that is not compressed to supply the nutrients.

The head of the radius crosses over the ulna to form an X during this special movement.
What is pronation?
Explanation: Pronation is the special movement that occurs at the elbow (particularly, the proximal radioulnar joint). Your palms would be facing posteriorly in this position.

Out of the 3 factors that help influence the stability of a synovial joint, this particular factor plays the least significant role in stabilization.
What are articular surfaces?
Explanation: Articulating surfaces don't play the biggest role in stabilizing joints. The other two factors - number & position of ligaments and muscle tone play a much more important role in stabilizing joints. This is why we need to protect our ligaments from injury and exercise to keep our joints from becoming delicate as we get older.

List the organizational levels of skeletal muscles from deepest to most superficial.
What is myofilament (actin/myosin), sarcomere, myofibril, Muscle fiber (cell), Fascicle, Muscle?
Explanation: This organizational level is good to remember for upcoming midterms and quizzes.
This type of contraction is a movement that resists gravity. It is not the same as a muscle that is passively relaxing.
What is an eccentric contraction?
Explanation: Eccentric contraction is the active movement of resisting gravity. For example, when you curl your arms to pick up groceries, slowly letting go of the bag to place it on the floor is considered eccentric contraction. Relaxing a muscle is like going from sitting to lying down. When you're sitting, your hips are flexed which means it's working. When you lie down, you extend your hips to a neutral position, allowing them to relax passively.

Synovial joints have an outer ____ layer made of ___ connective tissue and an inner ___ layer made of ___ connective tissue
What is fibrous; dense irregular; synovial membrane; loose
Explanation: The outer fibrous layer is continuous with the periosteum and it plays a role in protection, strength, and stabilization. The inner synovial membrane functions mainly to supply synovial fluid to joints which lubricate joints to reduce friction during movement and nourish articular cartilage (which is avascular).

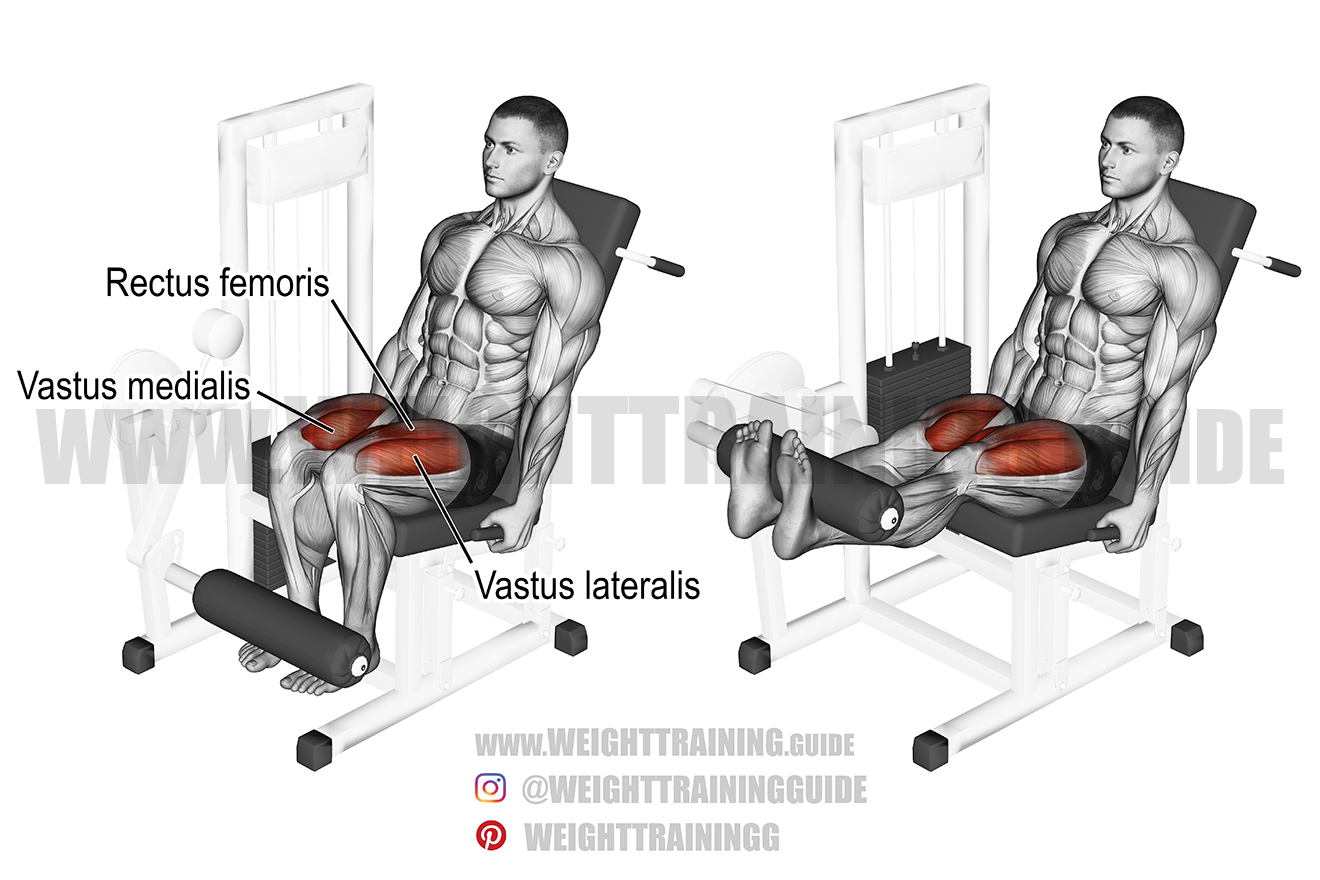 From left to right of this image, this person moves his leg from a ___ position to an ___ position.
From left to right of this image, this person moves his leg from a ___ position to an ___ position.
What is flexed; extended
Explanation: The person's leg in the left image is flexed (moves posteriorly). When the person moves his leg in the right image, he extends his leg (moves anteriorly).
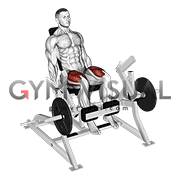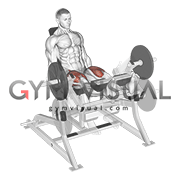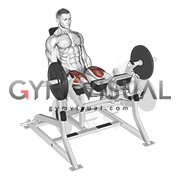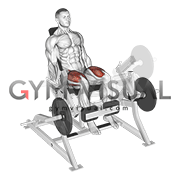
The temporomandibular joint (temporal bone + mandible), sternoclavicular joint (sternum + clavicle), acromioclavicular joint (acromion and clavicle), distal radioulnar joint (radius + ulna), and tibiofemoral (tibia + femur) joint, contain this structure because its poorly designed articular surfaces, helping improve the fit of the joints.
What are articular discs/meniscus?
Explanation: All of these joints have articular discs which are made of fibrocartilage. These joints also don't fit well together. Looking at the tibia and femur, they articulate at the condyles which are like two wheels rolling on top of each other. Typically, joints should fit complementary to each other, like a lock and key. These discs help improve the fit, minimize wear and tear, and distribute compressive forces more evenly.


The white part of this muscle is considered an indirect attachment and it resembles a flat sheet called ____.
What is aponeurosis?
Explanation: An aponeurosis is a huge sheet or thick layer of indirect attachment. They are typically white in color and are bigger than raphes.
During a concentric contraction, the __ region moves closer together, the ___ region shortens, and the ___ region disappears completely while the ___ bands stay the same length.
What is Z disc; I bands; H zone; and A bands?
Explanation: A bands do not move during contraction because the length of thick filaments does not shorten or lengthen. However, Z discs move closer together, which creates more overlap between thick and thin filaments. The I bands become shorter because there is more overlap. H zones disappear because the filaments start moving towards the center and filling in the empty space.

