List 4 causes of burns

What are the 3 layers of the skin?
Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis/Subcutis/Subcutaneous
List 3 appendages of the skin
Hair, nails, glands
What is the most abundant cell type in the epidermis?
Keratinocytes
Which layer of the epidermis are dividing cells found and how do they divide?
Basal layer
Mitosis
What are the 3 main types of burns?
1st degree (superficial), 2nd degree (superficial/deep partial thickness), 3rd degree (full thickness)
Describe the histology of the epidermis
Stratified squamous epithelium
What are the 3 sweat glands?
Sebaceous, eccrine and apocrine glands
The degree of keratinisation decreases with increasing differentiation. True or false?
Cell-cell junctions called ________ link ________ filaments to adjacent cells.
Cell-cell junctions called desmosomes link keratin filaments to adjacent cells.
How do superficial wounds heal?
Epidermis regenerates from the basal layer.
What are 2 differences between thick and thin skin (namely regarding stratum corneum and stratum lucidium)?
Thick skin has defined stratum corneum, thin skin has less prominent stratum corneum.
The epidermis of thick skin has stratum lucidium, the epidermis of thin skin does not.
List 4 physiological functions of the skin?
Thermoregulation, sensation, vitamin D synthesis, immune defence, protection against UV radiation
What shape are Melanocytes?
Where do they arise from in development?
Dendritic
Neural crest
The stratum corneum is rich in _______ and insoluble _______ which form a hydro-_______ layer.
The stratum corneum is rich in lipids and insoluble proteins which form a hydrophobic layer.
What are the 3 zones of burns? Which of these is classified by irreversible tissue loss?
Zone of Coagulation, Stasis, Hyperaemia.
Zone of Coagulation = irreversible tissue loss
The dermis is divided into which two areas?
Which is the thicker layer?
Which consists of loose connective tissue?
How does the dermis contribute to strength and flexibility of the skin?
Papillary dermis and reticular dermis
Reticular dermis = thicker layer
Papillary dermis = loose connective tissue
Fibroblasts produce collagen and elastin fibres which contribute to strength and flexibility
How does the skin regulate heat?
Heat --> dilate blood vessels --> blood circulates near surface of skin --> heat released
Sweating causes heat loss by evaporation
Where are Merkel cells found and what are they responsible for?
In the basal layer in association with nerve fibres
They are responsible for fine touch sensation
What are the 3 phases of hair growth?

• Haemostasis: formation of fibrin clot --> no blood loss
• Inflammation: removal of bacteria and damaged tissue
• Fibroplasia: fibroblasts lay down new collagen
• Epithelialisation: migration and mitosis of keratinocytes from wound edges --> new basal layer
• Remodelling: initial new tissue replaced through turnover --> stronger structure
What are the 4 layers of the epidermis?
Which of these layers is a single cell layer and which is several cells thick?
Which layer contains keratohyalin granules? What are they and what is their role?
Stratum basale (single cell), spinosum (several cells), granulosum, corneum.
Granular layer contains keratohyalin granules. They are proteins which bind and aggregate keratin filaments.
Describe the process of vitamin D synthesis and activation. Which cell type in the skin carries out vitamin D synthesis?
Keratinocytes carry out vitamin D synthesis in the presence of UV light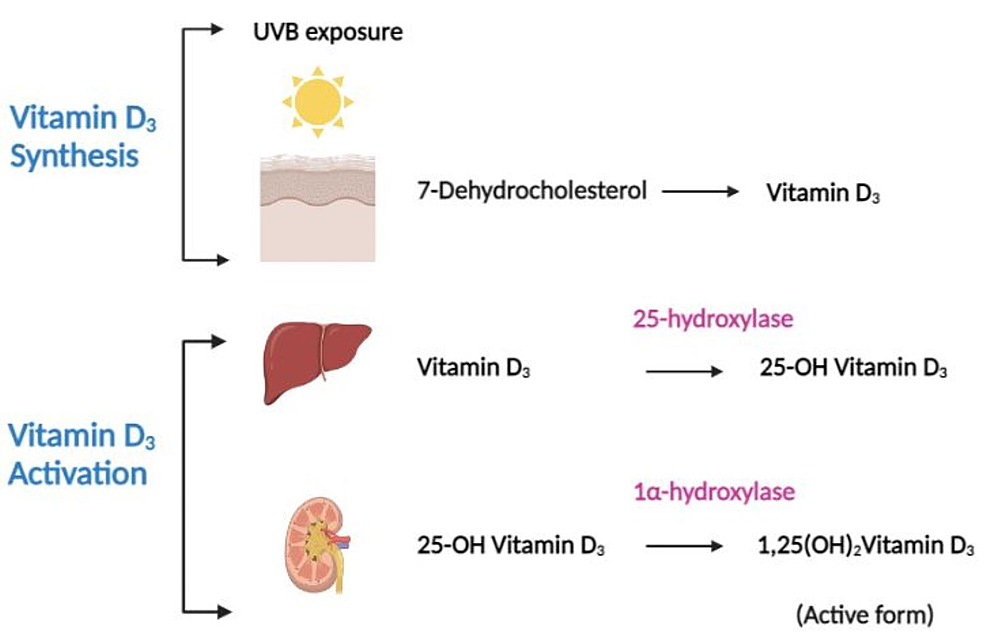
What 3 cell types can be found in the dermis? What are their roles?
Fibroblasts, immune cells (e.g. mast cells, macrophages, lymphocytes) and adipocytes
Fibroblasts: connective tissue and ECM
Immune cells: immune defence
Adipocytes: follicle growth and wound healing
What is the shape of sebaceous, eccrine and apocrine glands? What part of the dermis can you find eccrine and apocrine glands?
Sebaceous = branched acinar
Eccrine and apocrine = coiled tubular. Found in deep reticular dermis
