Fundamental unit of length in the SI.
The rate of doing work.
What is power?
An electrostatic attraction that forms bettween atoms when they share or transfer valence electrons.
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
What is matter?
Spherical regions located at fixed distances from the nucleus.
Fundamental unit of mass in the SI.
What is the kilogram?
Basic mechanical devices that change the magnitude,direction, or distance traveled of the force used when doing work.
What are simple machines?
Atoms are generally most stable when they have full eight electrons in their valence energy level.
What is the octet rule?
Material made of only one kind of element.
What is a pure substance?
DAILY DOUBLE
Atoms do not travel randomly.
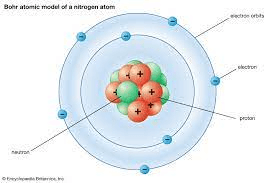
What is the Bohr Model?
A system of moral values or theory of proper conduct.
What is Ethics?
The measure of the change in input needed to do a certain amount of work when using a simple machine.
Molecules made of two atoms.
What are diatomic molecules?
Anything about a substance that can be observed or measured without altering the substance's chemical composition.
What is a physical property?
Carries no electrical charge.
What is the Neutron?
A model that explains a related set of phenomena.
What is a theory?
Effectiveness of a machine or process at converting energy from one form to another.
What is efficiency?
The name we use for unequal distribution of electric charge.
What is polarity?
A substance changes in the presence of another substance.
What is a chemical property?
The unique number of protons in the atoms of each element.
What is Atomic Number?
The degree of exactness of the measurements.
What is precision?
DAILY DOUBLE
A simple machine, rigid bar that turns around a pivot point, the point it turns at is called the fulcrum.
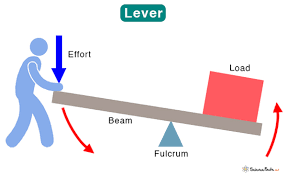
What is a lever?
Bonds sharing two pairs of electrons.
What is a double covalent bond?
Matter can neither be created nor destroyed, but only change forms.
What does the Law of Conservation of Matter state?
Atoms of the same element but differing numbers of neutrons.
What are Isotopes?