Cellular reproduction with 5 phases that results in identical diploid daughter cells.
Mitosis
A type of organic macromolecule that can be an enzyme or part of the plasma membrane.
Protein.
Traits partially BLENDED during a cross:
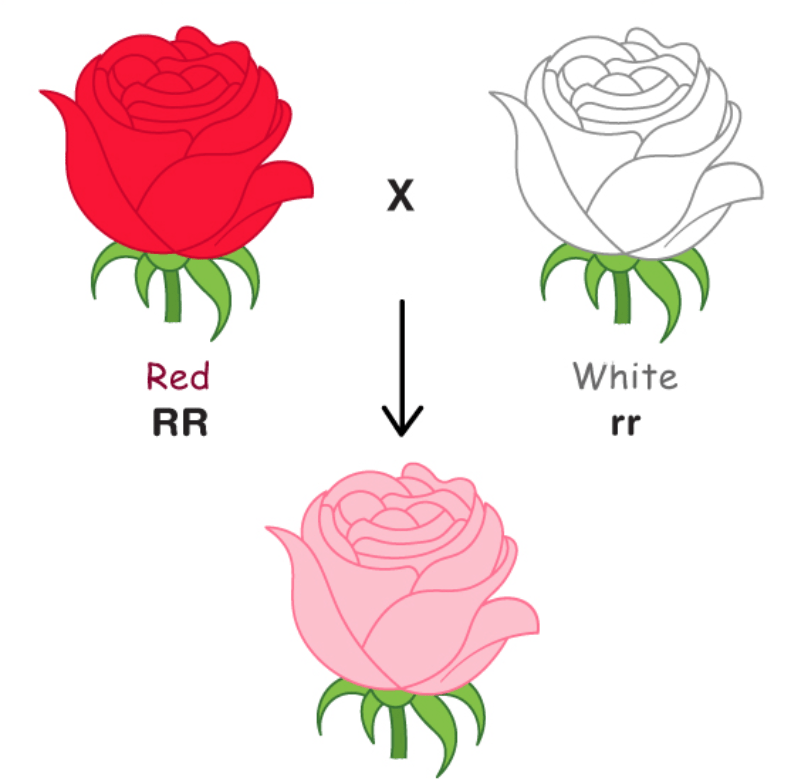
Incomplete dominance
Remnant, impression, or trace of an animal or plant of a past geologic age that has been preserved in Earth’s crust.
Fossil
Organisms make their own food using sunlight or chemical energy.
Producer
A section of a chromosome that controls a particular trait.
Gene
One of two steps during protein synthesis in which mRNA codons are used to assemble long chains of amino acids on the ribosomes.
Translation
The genetic sequence of an organism.
Genotype
Anatomical structures that show similar evolutionary history:
Homologous
Organisms that must get their energy from other organisms.
Consumers
Double helix strand of nucleic acid found in the nucleus of the cell.
DNA
Name of nucleic acid that transfers amino acids to the ribosome for translation into proteins.
tRNA
The characteristic that results in partial expression ALONGSIDE another trait:
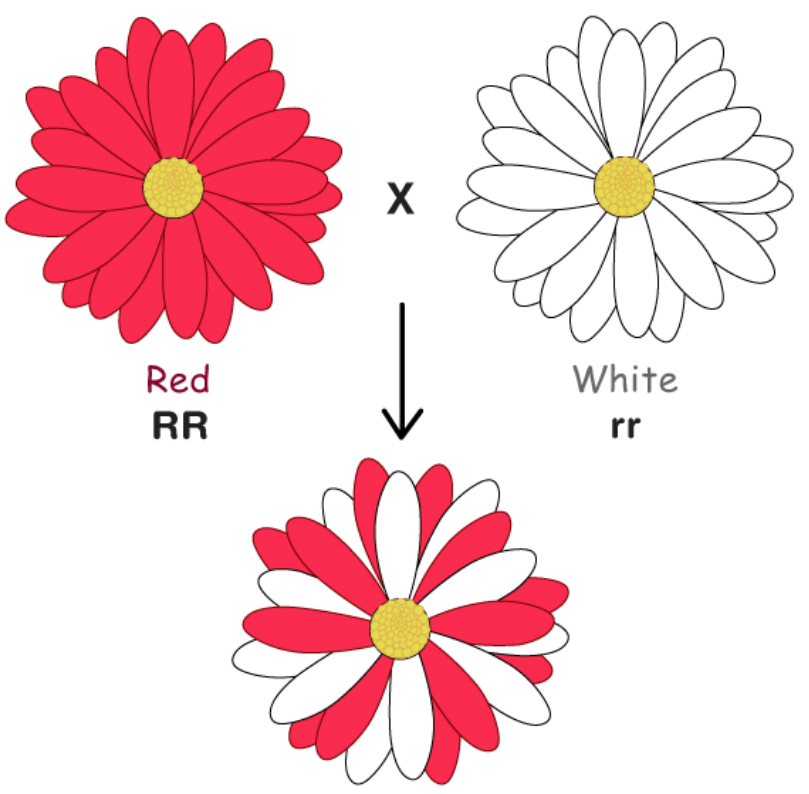
Co-dominance.
Comparative study of organisms from early stages to adult.
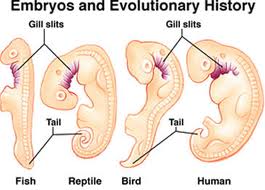
Embryology
Factors that refer to all living organisms within an ecosystem, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Biotic
Single-stranded nucleic acid that has A, U, G and C as its nitrogen bases.
RNA
* DAILY DOUBLE*
One of two steps in protein synthesis in which DNA's genetic sequence is copied to make a strand of mRNA.
Transcription
The physical appearance of an organism.
Phenotype
Evolutionary principle that emphasizes the advantage of a trait and its increased expression over time.
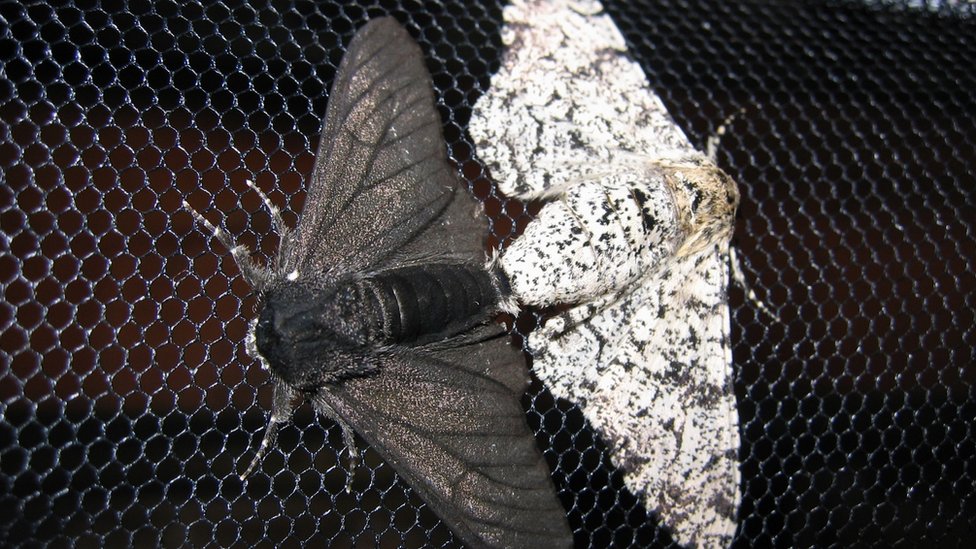

Natural selection
*DAILY DOUBLE *
Factors encompass all nonliving elements that influence ecosystems, such as landforms, water, air, sunlight, and climate
Abiotic
Cellular reproduction that results in 4 haploid daughter cells, each with half of the genetic information of the parent cell.
Meiosis
A type of mutation that occurs when a single nitrogen base is missing or replaced and can result in an altered protein.
Gene mutation.
The three types of gene mutations that involves the addition, deletion, or swapping of a single nucleic acid.
Missense, nonsense, silent.
Process in which a preferred gene is inserted into a plasmid DNA ring in order to make a desired protein.
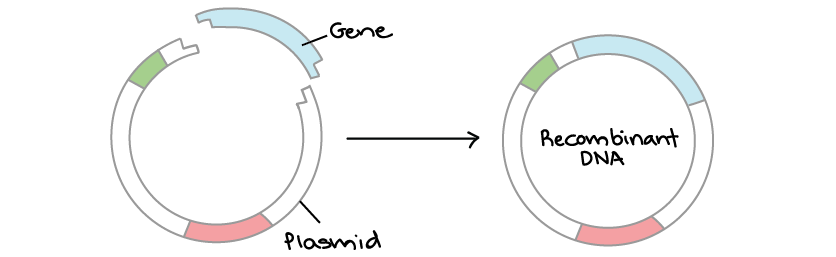
Genetic engineering (or recombinant DNA).
A factor is anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing such as food, mates, and competition with other organisms for resources
Limiting