Most important fitness variable
intensity
The body's main source of energy during moderate-high intensity prolonged endurance exercise...
carbohydrates
Acronym used to prescribe exercise and what it means?
FITT-VP
frequency, intensity, time, type, volume, progress/pattern
Kinetics is the study of...
How can burnout or entrapment be prevented?
adding variety and new challenges, rest days
What is the disadvantage of field work?
What is the advantage of field work?
less control over research variables
better simulates real world situations
What macronutrient is the primary fuel source at rest and during low-intensity exercise?
fats
What is the best and easiest way to measure exercise intensity in novice individulas when resources are limited?
talk test
Kinematics is the study of
types of motion (speed, acceleration, velocity)
What is the difference between stress & anxiety?
•Anxiety: a negative response to a stressful situation characterized by apprehension and feelings of threat
•Stress: when individuals perceive an imbalance between their capabilities and the demands of the situation
How does sleep deprivation affect exercise performance?
increased fatigue, decreased cognition, reduced recovery, impaired carb metabolism, suppressed immune function
How does sweat loss during exercise affect the heart?
decreases plasma volume, increased blood viscosity, increased blood pressure & heart rate, increased core body temperature
Minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week vs. moderate-intnesity?
75-150
150-300
What are the 3 risk factors for osteoarthritis?
obesity
previous knee injury
time spent doing high-impact, quick-stop activities
What does flow mean when discussing intrinsic exercise?
an optimal mental state characterized by total absorption in a task.
What is the difference between the heart rate in trained and untrained individuals at rest and during submaximal exercise?
lower in trained, higher in untrained
The difference between basal metabolic rate (BMR) and energy expenditure (EE) represents...
What is the difference between repetition-volume and load-volume?
What are four applications of biomechanics?
•techniques for sport performance and motor skill acquisition •Improve equipment •Prevent injury •Guide rehabilitation and treatment
No set of personality traits exists for athletes, but... consistent exercisers are more self-motivated/confident than sedentary people. Trained athletes use more productive coping strategies than less trained individuals. Successful athletes possess more positive self-perceptions than less successful athletes.
What are the major topics studies in Exercise Physiology?
hormonal/endocrine changes during exercise; skeletal muscle fiber types; physiological adaptations to exercise training; cardiorespiratory responses to exercise; energy systems; brain & spinal cord changes
Bailey exercises at a MET level of 10 for 30 minutes, 4 times per week. What is her MET-mins this week?
NO CALCULATOR
1200 MET-mins
What are the definitions of the 5 resistance training principles?
•Progressive overload – stress must be gradually increased on the body for improvements to be made
•Specificity – exercises match the techniques, movements, energy systems used in sport
•Reversibility – when you stop overloading the body, training adaptation is lost
•Variation – variety needs to be regulated for adaptation to continue & for overtraining to be avoided
•Individuality – every person responds differently to a given exercise stimulus
Give examples of internal vs. external forces?
External: gravity, ground reaction force, friction, drag, spring
Internal: muscle forces, tension, compression
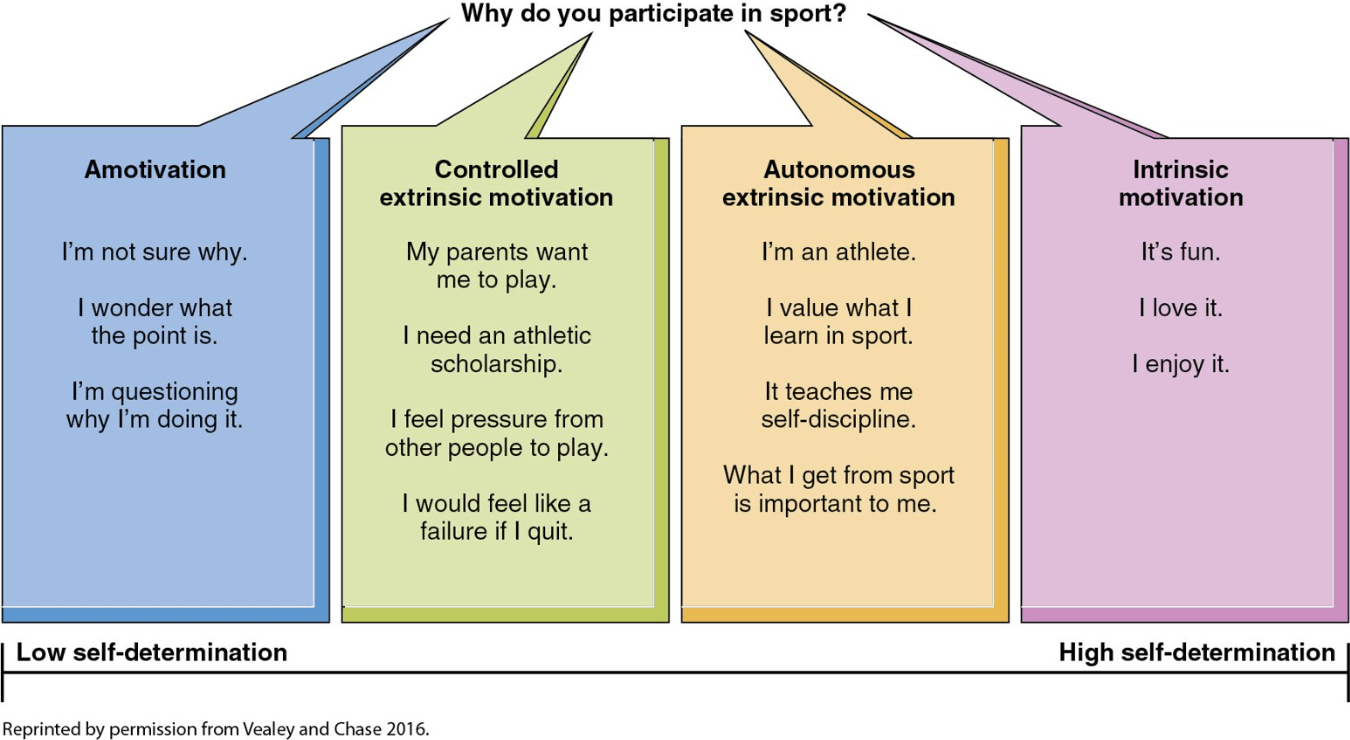
What are the 4 types of motivation? Provide an example of each