Resumes)
Resumes)
Interviews)
Flex
Bones
Name some essential personal information that should be on your cover letter/resume.
name, address, phone number, etc.
How do you secure a job interview?
apply
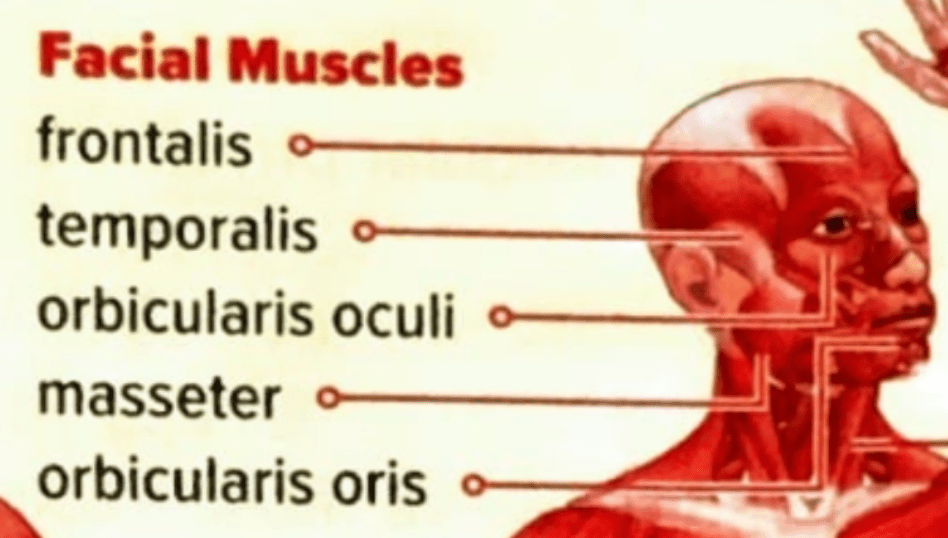
Name a muscle.
come on.
Name a bone.
okay.
How long should your resume be?
one page
What is something that most people don't do, but greatly increases your chances of securing an interview?
follow-up
An extensor muscle opens a joint, and a _______ muscle closes it.
flexor
How do you strengthen your bones?
Dietary Calcium: Consume foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach, broccoli), tofu, almonds, and fortified foods. Calcium is essential for bone strength and density.
Vitamin D: Ensure an adequate intake of vitamin D, which helps the body absorb calcium. Sources of vitamin D include sunlight exposure, fatty fish (salmon, tuna), fortified foods (milk, orange juice, cereals), and supplements if needed.
Regular Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises regularly. Weight-bearing activities like walking, jogging, dancing, and resistance exercises help stimulate bone formation and maintain bone density.
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Limit alcohol consumption and reduce intake of caffeine-containing beverages, as excessive alcohol and caffeine can interfere with calcium absorption and affect bone health.
Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quit smoking. Smoking has been linked to decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintain a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Being underweight or overweight can negatively impact bone health.
Limit Soda and Sugary Drinks: Limit consumption of sugary sodas and drinks, as they may displace calcium-rich beverages and contribute to bone loss.
Get Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor bone health and discuss any concerns or risk factors for osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions.
Supplements if Necessary: Consider calcium and vitamin D supplements if you are unable to meet your daily requirements through diet alone or if advised by your healthcare provider.
Fall Prevention: Take steps to prevent falls and reduce the risk of fractures, especially in older adults. This may include removing tripping hazards, improving lighting, using assistive devices, and participating in balance and strength training exercises.
find a template, one page, choose a font, change font sizes, color schemes, etc.
What aspects of the job should you research before the interview?
Company Overview: Understand the company's mission, values, products or services, history, culture, and recent news or developments.
Job Description: Review the job posting carefully to understand the responsibilities, qualifications, and expectations for the role.
Company Culture: Gain insights into the company's culture, work environment, and values to assess if it aligns with your preferences and work style.
Industry Trends: Stay updated on relevant industry trends, challenges, and opportunities that may impact the company and the role you're applying for.
Competitors: Familiarize yourself with the company's main competitors, market position, and how it differentiates itself in the industry.
Interviewer(s): If possible, learn about the background and role of the interviewer(s) you'll be meeting with to tailor your responses accordingly.
Recent Projects or Initiatives: Research any recent projects, initiatives, or accomplishments of the company that you can discuss during the interview to demonstrate your interest and knowledge.
Company's Online Presence: Explore the company's website, social media profiles, and online reviews to gather additional insights and information.
What are the three types of muscles?
Skeletal Muscle: Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and are responsible for voluntary movements of the body, such as walking, running, and lifting objects. They are striated in appearance due to the arrangement of muscle fibers and are under conscious control.
Smooth Muscle: Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, and other structures throughout the body. They are responsible for involuntary movements and functions, such as peristalsis (contractions of the digestive tract) and regulation of blood flow. Smooth muscles are not striated and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Cardiac Muscle: Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is striated like skeletal muscle but is involuntary like smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle cells are interconnected and coordinated to produce rhythmic contractions that maintain the heartbeat.
The skeletal system is comprised of bones and WHAT?
Connective tissue
What should the cover letter accomplish that the resume does not?
The cover letter complements the resume by providing context, personalization, and a persuasive argument for why you're the ideal candidate. It allows you to showcase your enthusiasm, personality, and alignment with the company's values and needs.
What are some common mistakes people make when interviewing?
Lack of preparation: Failing to research the company, the role, and the interviewer(s) can convey disinterest and lack of commitment.
Not listening actively: Interrupting the interviewer, not fully answering questions, or veering off-topic can give the impression of poor communication skills or lack of focus.
Overlooking body language: Slouching, avoiding eye contact, or fidgeting can signal nervousness or lack of confidence.
Speaking negatively about past experiences: Criticizing previous employers or colleagues can raise concerns about your professionalism and interpersonal skills.
Being unprofessional: Arriving late, dressing inappropriately, or using unprofessional language can create a negative impression.
Failing to ask questions: Not asking thoughtful questions about the company, the role, or the team can suggest a lack of interest or initiative.
Overemphasis on salary: Focusing solely on salary and benefits during the interview can make you appear more concerned about compensation than the job itself.
What is tendonitis?
Tendonitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon, commonly caused by overuse or injury. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and weakness in the affected area. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, NSAIDs, and physical therapy. Severe cases may require corticosteroid injections, PRP therapy, or surgery.
What are THREE FUNCTIONS of the skeletal system?
Support: The skeleton provides structural support for the body, giving it shape and rigidity. It forms the framework that supports and holds the body's soft tissues and organs in place.
Protection: The bones of the skeleton protect vital organs and tissues from injury. For example, the skull protects the brain, the rib cage protects the heart and lungs, and the vertebral column protects the spinal cord.
Movement: The skeletal system works in conjunction with muscles to allow movement of the body. Muscles attach to bones via tendons, and when muscles contract, they pull on the bones, causing movement at the joints.
Mineral Storage: Bones serve as a reservoir for essential minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are stored in the bone matrix and can be released into the bloodstream as needed to maintain mineral balance in the body.
Blood Cell Production: Within the bone marrow, specialized cells called hematopoietic stem cells produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets through a process called hematopoiesis. This function is crucial for the body's immune system and oxygen transport.
Energy Storage: In addition to minerals, bones also store fat in the form of yellow bone marrow. This fat serves as an energy reserve for the body and can be mobilized during times of energy demand.
Hormone Regulation: Bones produce and regulate several hormones involved in metabolism, including osteocalcin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels, and osteopontin, which plays a role in immune response and inflammation.
In the "work experience" part of your resume, what should you focus on?
Accomplishments
What is the most important part of the job interview process?
PREPARATION
Name two muscles in your face.
What are the different types of connective tissue in the skeletal system?
Cartilage: Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body, including the joints, rib cage, and nose. It consists of chondrocyte cells embedded in a matrix of collagen fibers and proteoglycans. Cartilage provides cushioning and support to the joints, allowing for smooth movement, and also helps maintain the shape of certain structures, such as the nose and ears.
Tendons: Tendons are fibrous connective tissues that connect muscle to bone. They are composed primarily of collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles. Tendons transmit the force generated by muscles to the bones, allowing for movement of the skeletal system.
Ligaments: Ligaments are fibrous connective tissues that connect bone to bone, providing stability and support to the joints. Like tendons, ligaments are primarily composed of collagen fibers, but they are more elastic and flexible to allow for joint movement while preventing excessive motion.
Periosteum: The periosteum is a dense layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of bones. It consists of fibrous and cellular layers containing blood vessels, nerves, and osteogenic cells. The periosteum plays a crucial role in bone growth, repair, and nutrition.
Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue): Bone tissue is the primary structural component of the skeletal system. It is composed of cells called osteocytes embedded within a matrix of collagen fibers and mineral salts, primarily calcium and phosphorus. Bone tissue provides strength, support, and protection to the body and serves as a reservoir for minerals.
What is a CV and what does it stand for?
A CV stands for "curriculum vitae," which is a Latin term that translates to "course of life." In professional contexts, a CV refers to a detailed document that outlines an individual's educational background, work experience, skills, accomplishments, and other relevant qualifications. Unlike a resume, which is typically concise and tailored for specific job applications, a CV is more comprehensive and provides a comprehensive overview of a person's academic and professional achievements. CVs are commonly used in academic, scientific, research, and medical fields, as well as for certain international job applications.
Tell the class about a job interview you had and why you did/didn't get the job.
?
What is this muscle?
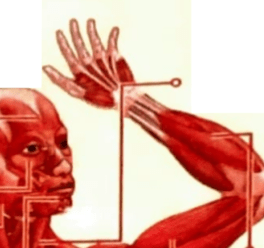
sternocleidomastoid
Name FIVE bones in your body. Hurry. You have 10 seconds.