Which compound is formed from its elements by an exothermic reaction at 298 K and 101.3 kPa?
(1) C2H4(g) (3) H2O(g)
(2) HI(g) (4) NO2(g)
What is
(3) H2O(g)
Given the equation and potential energy diagram representing a reaction:
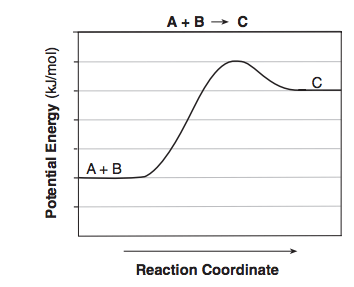
If each interval on the axis labeled “Potential Energy (kJ/mol)” represents 10. kJ/mol, what is the heat of reaction?
(1) +60. kJ/mol (3) +30. kJ/mol
(2) +20. kJ/mol (4) +40. kJ/mol
What is
(3) +30. kJ/mol?
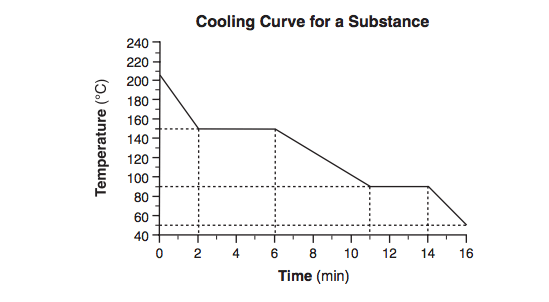
Starting as a gas at 206°C, a sample of a substance is allowed to cool for 16 minutes. This process is represented by the cooling curve below.
What is the melting point of this substance?
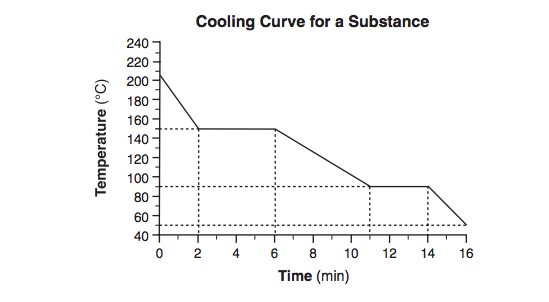
What is
90°C ± 2°C?
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
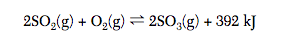 Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the pressure of the gases in the
cylinder increases the rate of the forward reaction.
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the pressure of the gases in the
cylinder increases the rate of the forward reaction.
What is...
When the pressure in the cylinder is increased, the SO2(g) molecules and O2(g) molecules collide more frequently, producing more SO3(g).
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
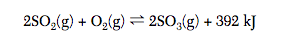
State, in terms of the concentration of SO3(g), what occurs when more O2(g) is added to the reaction at equilibrium.
What is
The concentration of SO3(g) increases.
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
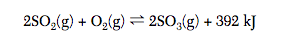
Determine the amount of heat released by the production of 1.0 mole of SO3(g).
What is
196 kJ?
Given the formula for a compound:
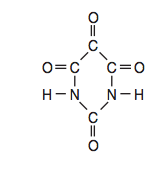
Which molecular formula and empirical formula represent this compound?
(1) C2HNO2 and CHNO (2) C2HNO2 and C2HNO2
(3) C4H2N2O4 and CHNO (4) C4H2N2O4 and C2HNO2
What is
(4) C4H2N2O4 and C2HNO2
Starting as a gas at 206°C, a sample of a substance is allowed to cool for 16 minutes.
This process is represented by the cooling curve below.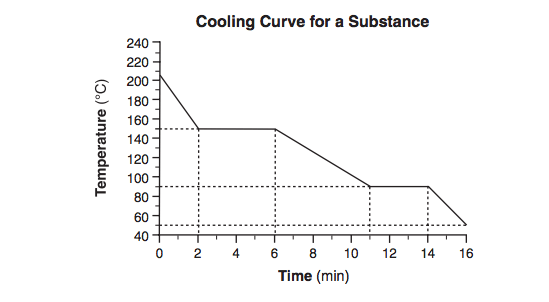 At what time do the particles of this sample have the lowest average kinetic energy?
At what time do the particles of this sample have the lowest average kinetic energy?
What is
at 16 minutes?
Given the diagram representing a heating curve for a substance:
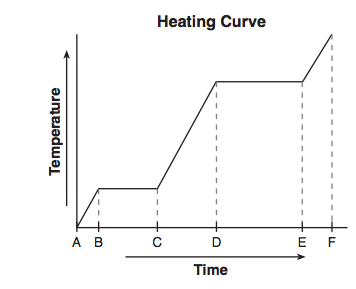
During which time interval is the average kinetic energy of the particles of the substance constant while the potential energy of the particles increases?
(1) AC (2) CD (3) BC (4) DF
What is...
(3) BC
Given the diagram representing a closed system at constant temperature:
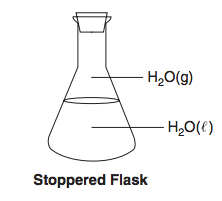
Which statement describes this system at equilibrium? (1) The mass of H2O(ℓ) equals the mass of H2O(g).
(2) The volume of H2O(ℓ) equals the volume of H2O(g).
(3) The number of moles of H2O(ℓ) equals the number of moles of H2O(g).
(4) The rate of evaporation of H2O(ℓ) equals the rate of condensation of H2O(g).
What is...
(4) The rate of evaporation of H2O(ℓ) equals the rate of condensation of H2O(g)?
At 101.3 kPa and 298 K, what is the total amount of heat released when one mole of aluminum oxide, Al2O3(s), is formed from its elements?
(1) 393.5 kJ (3) 1676 kJ
(2) 837.8 kJ (4) 3351 kJ
What is
(3) 1676 kJ
Given the potential energy diagram representing a reversible reaction:
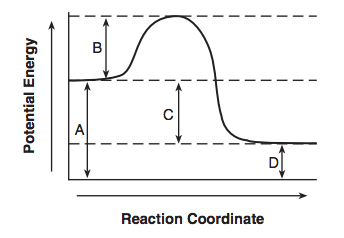
The activation energy for the reverse reaction is represented by
(1) A + B (3) B + D
(2) B + C (4) C + D
What is
(2) B + C
Starting as a gas at 206°C, a sample of a substance is allowed to cool for 16 minutes. This process is represented by the cooling curve below.
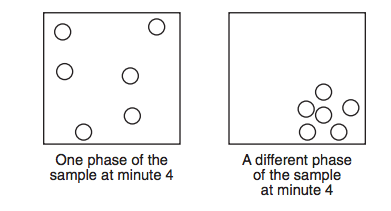
Using the key shown below, draw two particle diagrams to represent the two phases of the sample at minute 4. Your response must include at least six particles for each diagram.
What is
Which statement describes a chemical reaction at equilibrium?
(1) The products are completely consumed in the reaction.
(2) The reactants are completely consumed in the reaction.
(3) The concentrations of the products and reactants are equal.
(4) The concentrations of the products and reactants are constant.
What is..
(4) The concentrations of the products and reactants are constant.
The potential energy diagram and balanced equation shown below represent a reaction between solid carbon and hydrogen gas to produce 1 mole of C2H4(g) at 101.3 kPa and 298 K.
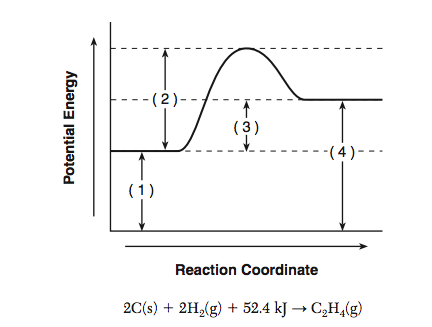
State what interval 3 represents.
What is
Interval 3 represents the heat of reaction, +52.4 kJ.
The potential energy diagram and balanced equation shown below represent a reaction between solid carbon and hydrogen gas to produce 1 mole of C2H4(g) at 101.3 kPa and 298 K.

Determine the net amount of energy absorbed when 2.00 moles of C2H4(g) are produced.
What is
104.8 kJ.
The potential energy diagram and balanced equation shown below represent a reaction between solid carbon and hydrogen gas to produce 1 mole of C2H4(g) at 101.3 kPa and 298 K.

Identify one change in the reaction conditions, other than adding a catalyst, that can increase the rate of this reaction.
What is...
Increase the temperature.
Increase the pressure.
Increase the concentration of H2(g).
Increase the surface area of the carbon.