Ligament
This small, triangular bone, also known as the kneecap, protects the knee joint and aids in leg extension.
Patella
This important ligament in the knee helps prevent the tibia from sliding forward relative to the femur and is commonly injured in sports
ACL - Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Direct blow or valgus force from lateral direction or lateral tibial rotation
MCL Sprain
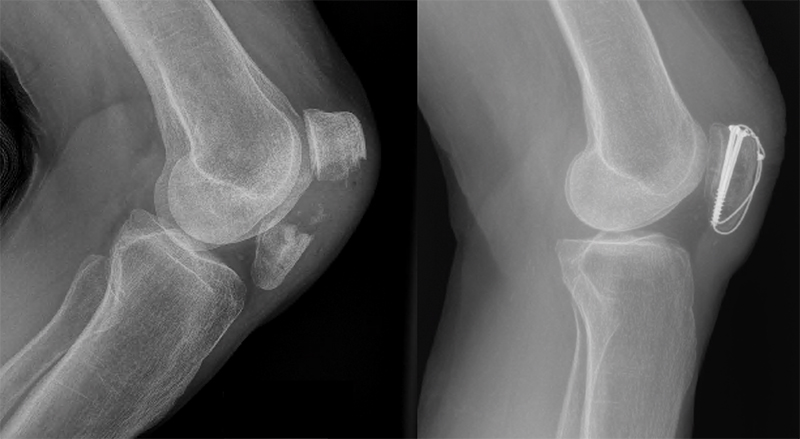
Patella Fracture
Structure 3
ACL
This slender bone runs parallel to the tibia and provides support and stability to the lower leg
Fibula
This C-shaped cartilage in the knee acts as a shock absorber between the femur and tibia.
Meniscus
Direct blow or varus force from medial direction or internal tibial rotation
LCL Sprain
Knee extension to help reduce dislocation
Immobilized 4 weeks - isometric exercises
May need horseshoe brace for protection
Patella Dislocation / Subluxation
Structure 4
MCL
This bone is the longest and strongest bone in the human body, connecting the hip to the knee.
Femur
This ligament, located behind the ACL, prevents the tibia from moving backward relative to the femur
PCL - posterior cruciate ligament
Weight bearing combined with rotary force, or sudden, strong internal rotation of femur with flexed knee
Meniscus Tear
Jumping, running, repetitive forceful extension of knee, plyometrics causes this
Patella Tendonitis
Structure 8
Lateral Meniscus
This bone, also known as the shinbone, is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the lower leg
Tibia
This ligament runs along the outer side of the knee, providing stability and preventing excessive side-to-side movement
LCL - lateral collateral ligament
decelerating from jump or forward running; combination of multiple plane forces acting at the knee, most commonly knee extension, valgus force, anterior shear & internal rotation of tibia
ACL Sprain
tibial displacement with respect to the femur: anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, and rotary
Knee dislocations
Structure 7 
Fibula
The knee is classified as this type of synovial joint, allowing movement primarily in one direction like a door
Hinge
This ligament on the inner side of the knee helps stabilize the joint and prevent excessive inward movement
MCL - Medial collateral ligament
Most at risk when knee flexed to 90 degrees: fall with full weight on anterior aspect of bent knee w/foot in plantar flexion, hard blow to front of bent knee (dashboard injury)
PCL Sprain
Very common to feel & hear pop
Disability, unstable, feels like knee is “shifting”
Mild to severe swelling
Positive Anterior Drawer test, positive Lachman’s sig
ACL Sprain
Structure 5
Patella Tendon