True/False: The antebrachial region is distal to the brachial region.
True
Define homeostasis
A state of balance among all the body systems needed for the body to survive and function correctly.
What are the 4 groups of tissues?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What is the largest organ of this system?
Skin
What are the two subdivisions of the nervous system called?
Central (CNS) and Peripheral (PNS)
Your ankle is refered to as the ________ region.
tarsal
What organ is usually the integrator for most feedback loops?
Brain/Spinal Cord
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue and name their locations in the body.
cardiac (heart), skeletal (attached to bones), smooth (internal organs)
What substances do eccrine/apocrine and sebaceous glands produce?
Sweat (salty water) and Sebum (oily substance)
What are the two major organs of the CNS?
Brain and Spinal Cord
Your neck is refered to as your _________ region.
cervical
Draw a graph of a negative feedback system vs a positive feedback system with axes and a line (no labels)
How do the 2 types of nervous tissue work together to function?
Neurons send messages for communication while neuroglia support these larger cells by nourishing, insulating, and oxygenating them.
What is the difference between the eccrine and appocrine glands?
Eccrine- thermoregulation and go straight to the skin surface
Appocrine- activated during puberty and stink (because of bacteria) and are attached to hair follicles rather than directly to the skin.
What is the 5 step pathway of a reflex arc?
1. Stimulus, 2. Sensory neuron, 3. Interneuron in the CNS processes info, 4. Motor neuron causes muscle gland etc to change, 5. Response to stimulus occurs
List the following locations from most superior to most inferior by using their correct atomical region names: belly button, shoulder, and knee cap
acromial, umbilical, patellar
Describe the feedback mechanism associated with childbirth contractions.
Positive feedback- head pushes on cervix, nerve impulse tells the proan to activate the pituitary gland to release oxytocin, this hormose causes the uterus to contract and move baby down and out- will continue until baby has exited (head no longer pushing on cervix)
What is the structure of epithelial tissues? Explain the words that are used to describe layering and cell shape.
Layers: simple (1) vs. stratified (many)
Cell Shape: squamous (squished footballs), cuboidal (same height as width), and columnar (taller than they are wide)
Explain how the 3 types of burns work
1st- epidermis from sun/ temp
2nd- dermis and hurts, causes blisters, from boiling water, fire exposure, oven, etc.
3rd- down to hypodermis causing lethery skin, no pain because burned off nerves
Name the 4 major regions of the cerebrum and their functions
Frontal lobe: higher level executive functions
Occipital lobe: vision
Temporal lobe: hearing and processing memories
Parietal lobe: sensory perception and integration, including the management of taste, hearing, sight, touch, and smell
If a midsaggital cut was made through a body, name 3 regions that would be damaged.
cranial, nasal, oral, mental, cervical, thoracic, umbilical, pelvic, pubic
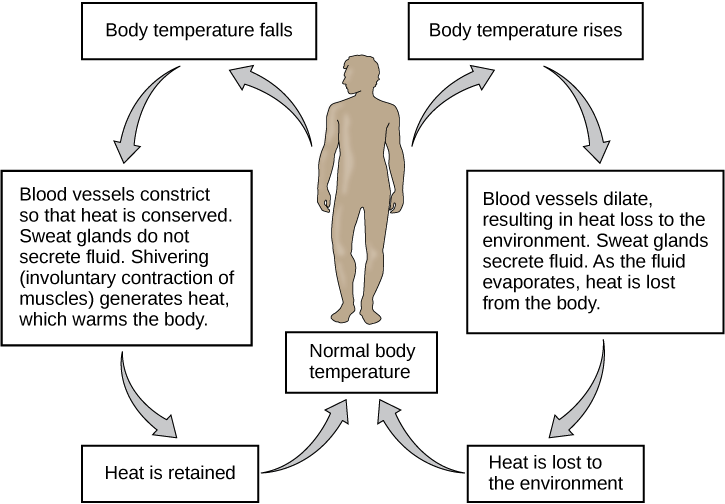
Describe how thermoregulation works (body heat).
What is the type and name of the tissue that lines the esophagus? What structures does it have that help it function?
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: has cilia that help it catch debris and invaders from entering into the digestive and respiritory tracts when we breathe in.
Name the 8 layers that make up the skin in order from superficial to deep (5E, 2D, 1H)
Stratum Corneum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum Basale, Papillary Layer, Reticular Layer, Adipose Tissue (subcutaneous layer)
Name the 3 parts of the brainstem and explain their functions.
Midbrain: motor control, particularly eye movements and processing of vision and hearing
Pons: coordinates face and eye movements, facial sensations, hearing and balance
Medulla Oblongata: breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure and swallowing