What is ONE difference between RNA and DNA?
** not the R and D
DNA - stays in the nucleus, double stranded, A-T and C-G
RNA - made in nucleus but goes to ribosome, single stranded, A-U and C-G
Where does Transcription occur in the cell?
The nucleus
What is a mutagen?

causes mutation to occur
x-rays
gamma rays
UV light
chemicals
radioactive materials
Using the metabolic pathway diagram below - identify how many different products are made?

3
What does DNA stand for?
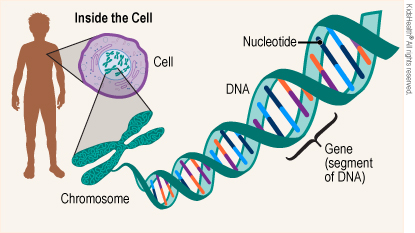
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
How many hydrogen bonds are there between A and T/U and C and G?

A-T/U = 2 hydrogen bonds
C-G = 3 hydrogen bonds
Where does Translation occur in the cell?
Ribosome
Define this mutation
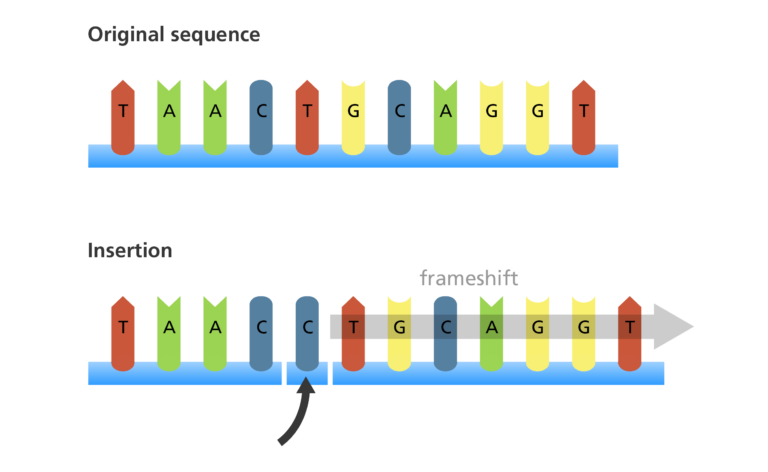
Insertion
What is the definition of a metabolic pathway?
A series of enzyme controlled reactions where the product from one reaction becomes the substrate for the next reaction
Why is blood red?
Because of the iron found in the haemoglobin protein that is contained in red blood cells. That’s why your blood tastes a bit like rust.
Why does the DNA need to stay inside the nucleus?
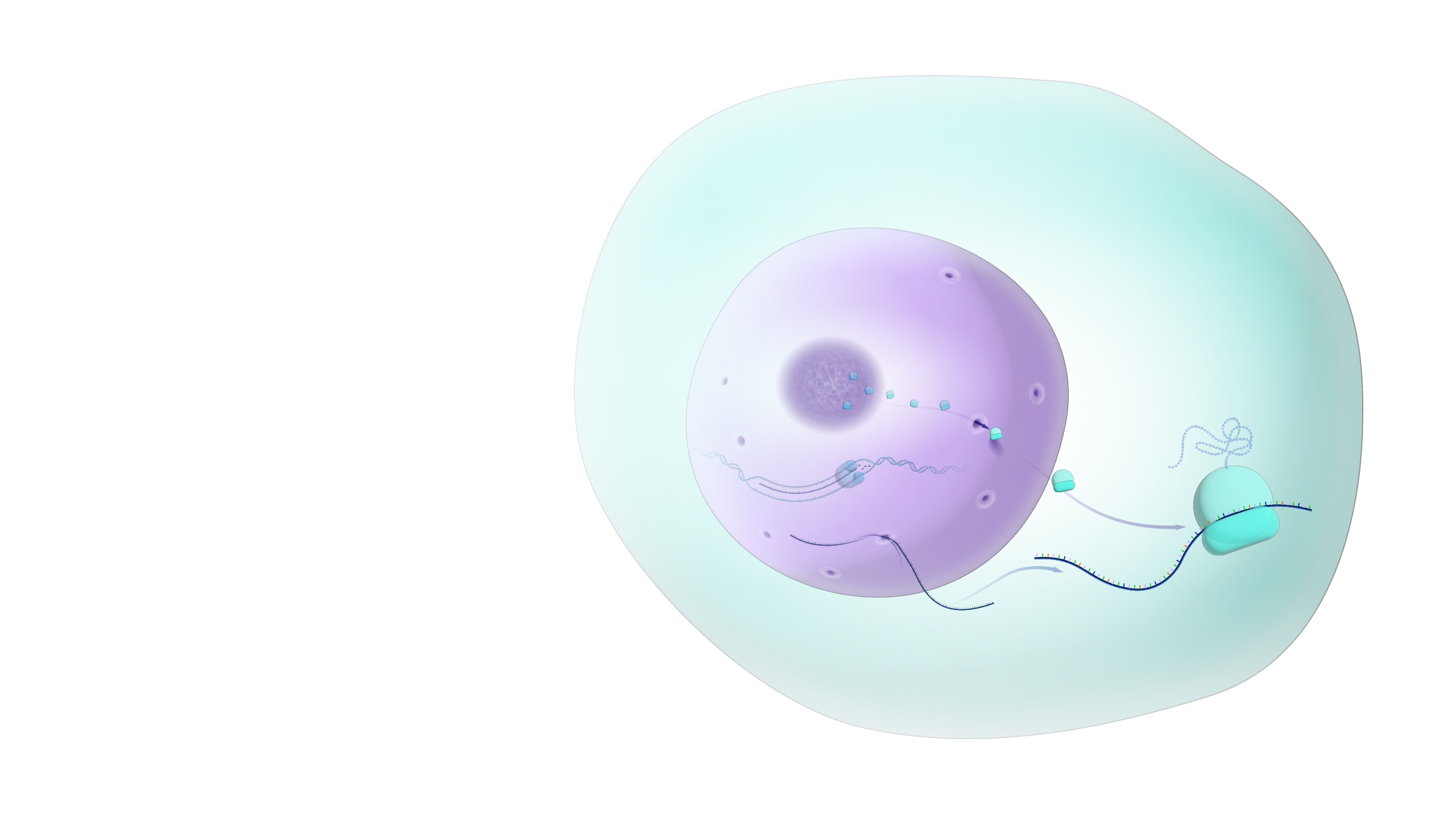
Too big to leave the nucleus
Needs to be protected as it has all of the instructions
What is the role of tRNA?

To transfer amino acids to the ribosome to make a polypeptide chain
Name this mutation
subsitution
In the diagram below - how many intermediaries are made?

2
When is your brain most active?
During the night
What is the difference between a triplet, a codon and a anticodon?
triplet - DNA
codon - mRNA
anticodon - tRNA
What is the role of the mRNA?

to act as a messenger taking the information for a specific gene to the ribosome to be translated into a protein/polypeptide chain
What is a frameshift mutation?
These are caused by insertion and deletion mutations
Using the metabolic pathway diagram below, what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene that encodes for Enzyme 3?

There would be no final product (Melanin) produced
What is the largest organ in the human body?
Skin
What is the connection between a codon, a anticodon and an amino acid?
the codon on mRNA and anticodon on tRNA complementary base pair together and the tRNA brings the corresponding amino acid to join the polypeptide chain. You use the codon to determine which amino acid
Using the codon chart below - identify the amino acid sequence
AUG - CAC - AGG - UGU - CUA - UAG

Met - His - Arg - Cys - Leu - STOP
What is the effect of this mutation on the final protein?

deletion mutation causes a frameshift. This no longer encodes for the same animo acid sequence so the resulting protein does not fold correctly and would not be able to carry out the same function
Using the metabolic pathway diagram below - describe how we produce product C

Enzyme 1 catalyses the starting molecule to produce product B. Enzyme 2 catalyses product B to become product C
What 2 parts of the human body never stop growing?
Nose and ears