What are the key differences between management and leadership?
"Management is a set of processes that keep an organisation functioning. They make it work today – they make it hit this quarter's numbers. The processes are about planning, budgeting, staffing, clarifying jobs, measuring performance, and problem-solving when results did not go to plan."
Leadership is very different. "It is about aligning people to the vision, that means buy-in and communication, motivation and inspiration."
What is the difference between scientific decision-making and intuitive decision-making?
Scientific decision-making relies on data analysis, logic, and evidence, while intuitive decision-making leverages experience, gut feelings, and quick judgment.
Scientific decision-making aims to reduce uncertainty and risk through systematic analysis, while intuitive decision-making can be faster and more flexible but may lack the same level of rigor.
Define the term 'stakeholder' and name 3 internal and 3 external stakeholders
A stakeholder is someone who has an interest in a business.
Internal: Employees, Shareholders, Managers
External: Competitors, Suppliers, Customers, Government, Interest Groups, Pressure Groups
State 3 roles of a manager
setting objectives, organising, motivating, communicating, measuring performance (reviewing) and developing employees
What is the definition of the term opportunity cost?
The next best alternative foregone when a decision is made
The managers of a business propose to retain all of its profit to finance automation of its production. This is most likely to cause conflict with:
a. Employees and lenders
b. Employees and shareholders
c. Lenders and suppliers
d. Shareholders and suppliers
Competitors
When might an increase in a company's sales NOT result in increased market share?
If their competitors' sales increase at a faster rate.
If the market grows at a faster rate than the company's sales grow.
Put the following stages of the Tannenbaum-Schmidt Leadership Continuum in the correct order:
Joins
Sells
Suggests
Delegates
Tells
Consults
Abdicates
Tells
Sells
Suggests
Consults
Joins
Delegates
Abdicates
In a decision tree there are four possible outcomes of an action.
The probabilities of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd outcomes are 0.4, 0.32 and 0.24 respectively.
The probability of the 4th outcome is:
0.04
Explain how an organisation might benefit from using stakeholder mapping
Stakeholder mapping offers significant benefits for businesses by facilitating better communication, risk management, and decision-making. It helps identify and understand key stakeholders, their level of interest and power (influence), allowing businesses to tailor engagement strategies and build stronger relationships. This, in turn, can lead to improved project success, increased support, and reduced conflicts.
Names 3 factors that might influence a company to set a marketing objective of achieving 15% market share in 3 years
- Ambitions of the leader
- Past success of the business
- Financial performance of the business (budget/liquidity)
- Dynamic market
Explain one situation where a laissez-faire style of management would be inappropriate and explain your reasoning.
Laissez-faire leadership, where leaders offer minimal guidance and allow teams to make their own decisions, is generally inappropriate in situations where there's a lack of experience, a need for clear direction, or when a lack of leadership could jeopardise safety or productivity. This is because...
It can also be unsuitable when strong leadership is needed to address conflict or ensure adherence to deadlines...this is because...
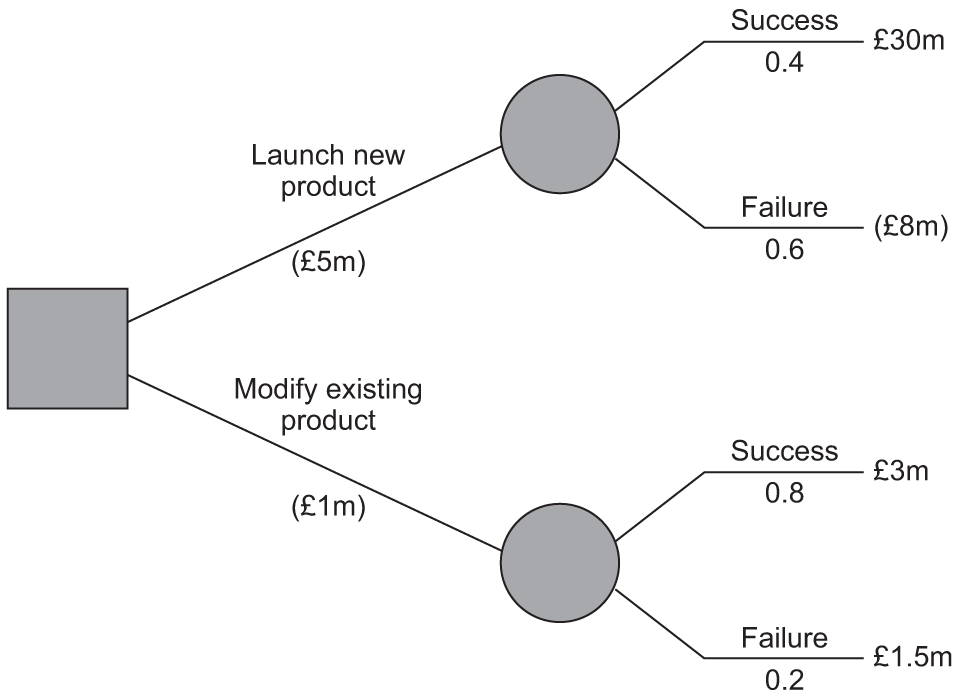
Calculate the following for each option:
a) Expected value
b) Net gain
Make a decision on which option the business should choose
- The Expected Value (EV) shows the weighted average of a given choice; to calculate this multiply the probability of each given outcome by its expected value and add them together e.g. EV Launch new product = [0.4 x 30] + [0.6 x -8] = 12 - 4.8 = £7.2m.
- EV of modifying existing product = [0.8 x 3] + [0.2 x 1.5] = 2.4 + 0.3 = £2.7m.
- The Expected Value is the average outcome if this decision was made many times.
- The Net Gain is the Expected Value minus the initial cost of a given choice.
- Net Gain of launching new product = £7.2m - £5m= £2.2m.
- Net Gain of Modify existing product = [0.8 x 3] + [0.2 x 1.5] = 2.7 -1 = £1.7m.
- Decision based on choice with highest net gain which is to launch new product [£2.2m as against £1.7m].
Shares of Elon Musk's electric vehicle maker have fallen for seven straight weeks, the longest losing streak since the company floated on the stock market 15 years ago.
Explain the impact of this on two of Tesla's stakeholders.
Employees - Reduced Market Capitalisation: A lower share price translates to a lower overall market valuation of the company, which can impact its perception and standing in the market. This can negatively impact employee morale, as stock options and other company-related benefits may become less valuable, and future demand and labour requirements are more uncertain (job security).
Shareholders- Reduced Investment Value: The most immediate impact is a decrease in the value of Tesla stock held by shareholders. This can lead to financial losses for individuals and institutions holding the stock, including pension funds.
Managers - Difficulty Raising Capital: A decline in the share price can make it more difficult and expensive for Tesla to raise additional capital through future stock offerings or other financing methods. This may inhibit the ability of senior management to meet their aggressive growth targets (which could be linked to pay).
Company X has a 40% market share. The market size declines by 20%. There are no other changes. Company X's market share now is:
One method
(40/100) *100 = 40%
0.8 x 100 = 80
(40/80) *100 = 50%
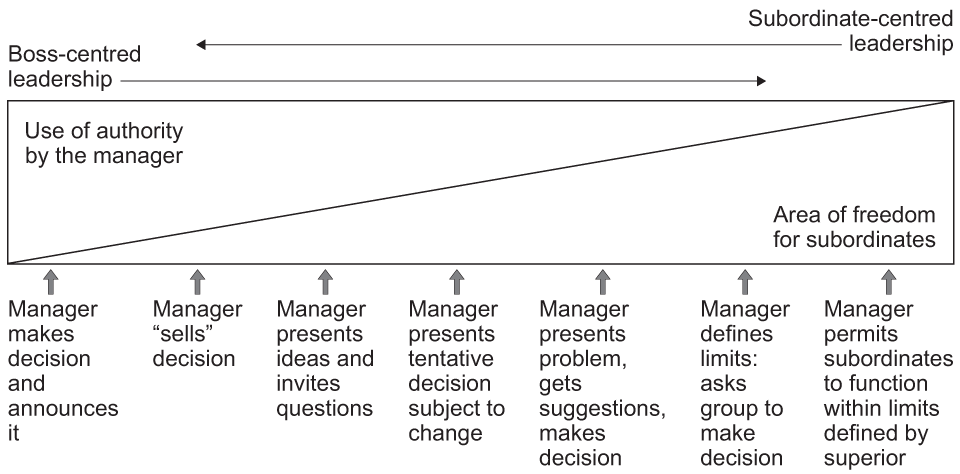
Managers' leadership style in a business is shown by the Tannenbaum and Schmidt diagram above. The managers change their leadership style from point A (sells) to point B (defines limits).
Explain one benefit of this change to the business.
The demands of the question are:
- Explain one benefit to a business of changing the style of management from manager centred to subordinate centred.
Indicative content:
- The employees are given a greater level of responsibility which may make them feel more trusted in the business which may lead to greater levels of motivation.
- The subordinate employees within the business have more control over the decision and therefore gain experience and learn to develop allowing productivity and/or quality to improve.
- The business may benefit from the manager getting more consultation with those staff who are dealing with issues day to day and therefore the manager is better informed in the decision making.
NB: Valid lines of argument should be linked to benefit to the business.
This indicative content is not exhaustive; other creditworthy material should be awarded marks as appropriate.
[4 marks]
Fully explain 2 limitations of managers relying on decision trees in their decision-making process.
1. Reliance on Quantitative Data:
- Decision trees primarily use numerical data to calculate expected values and probabilities, ignoring qualitative aspects of a decision like human resources, customer satisfaction, or employee morale.
- This can lead to overlooking crucial factors that could impact the success or failure of a decision.
2. Potential for Bias:
- The assignment of probabilities can be subjective and influenced by personal biases, leading to inaccurate predictions.
- Managers might subconsciously favor certain outcomes, leading to biased calculations that don't reflect the true risks and rewards of a decision.
3. Inaccurate Predictions due to Time Lags:
- Decision-making can be a time-consuming process, and the information used to build the tree might become outdated by the time a decision is implemented.
- Changes in external factors like economic conditions, market trends, or competitor actions can render the initial analysis unreliable.
4. Limited Scope of Options:
- Decision trees might only consider a limited set of potential options, potentially excluding other viable choices that could be more advantageous.
- This can lead to a narrow focus and the overlooking of alternative strategies.
5. Difficulty in Handling Uncertainty:
- Decision trees can struggle to accurately reflect uncertainty and unforeseen circumstances.
- The dynamic nature of businesses and external factors can make it difficult to predict outcomes with certainty
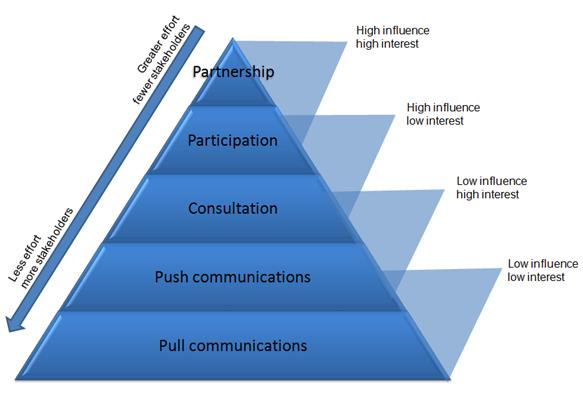
Draw and label the pyramid which shows the different methods of stakeholder engagement a business might use as a result of stakeholder mapping.
Explain the reason why falling labour productivity rates may result in falling market share
Falling labour productivity rates may result in increased unit labour costs which MIGHT be increasing faster than competitors.
This may result into them having to charge higher prices than their competitors.
If demand for their products is price elastic, consumers may purchased from competitors instead, resulting in competitors' sales increasing relative to this company's, resulting in lower market share.