What mask is the highest flow besides a non-rebreather (NRB)?
Oxymask
How often can you give Ketorolac?
Every 6 hours (Q6) or PRN
What are the goals of therapeutic communication?
Building trust, fostering a trusting relationship; Achieving better health outcomes and satisfaction
What P waves would you see for Atrial Flutter?
Sawtooth
What is the purpose for Therapeutic Communication?
Overcoming emotional or psychological distress
Do not start an IV on this site
Lymphedema
What does PCA stand for?
Patient controlled analgesic
What is the highest liter flow you can run on a nasal cannula?
6 Liters
What class of medications would you give in a PCA?
Opioids
What are the 3 phases of the Nurse-Client relationship?
Orientation Phase, Working Phase, Termination Phase
What are the hallmark signs for Atrial Fibrillation?
Irregular and No P waves
What is the Artial heart rate for Atrial Flutter?
250-400
How many bottles do you need for 1 set (2 bottles) of blood cultures?
2 sets (4 bottles)
For preoperative nursing, what are the 3 phases that are covered
Preoperative, Intraoperative, Postoperative
Which mask delivers a precise % of oxygen?
Venturi mask
Name 3 NSAID's
Ketorolac (Toradol), Ibuprofen, Celebrex (Celecoxib)
What are examples of nontherapeutic communication? Name at least 5.
Reassuring, giving approval, rejecting, approving/disapproving, agreeing/disagreeing, advising, probing, challenging/arguing
What rhythm is this?
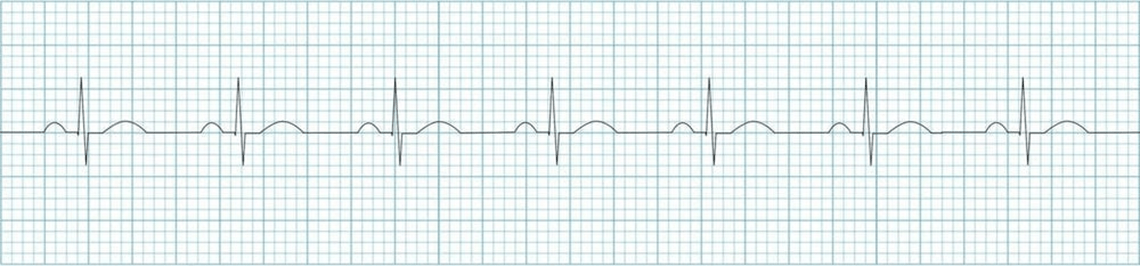
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
What rhythm is this?

Atrial Flutter
If the patient is on a PCA machine, what would you monitor?
O2 saturations
What medications would be held prior to surgery? How long before?
NSAIDs, herbs/supplements- 2 weeks priors; Anticoagulants- 5 days prior
What mask do you put on a person with labored breathing?
Non-rebreather
What is the max dose for Tylenol in 24 hours?
4,000 or 3,500
**Some medications are combined with Tylenol
What are the characterisics for the working phase?
Supports the development of healthy problem-solving, Encourages patient to prepare for the future, Countertransference
What is the purpose of a 12-lead ECG?
It views the heart's electrical activity from different angles; Diagnostic tests (can diagnose an MI)
T or F: Atrial Flutter is treated the same as Atrial Fibrillation?
True
What color tube would you use for blood count? and for a patient at risk for bleeding?
What is the reason for post-op HTN?
Bladder retention, Hypoxia, pain
What do you use if your patient is not breathing?
Ambubag
What reverses morhine?
Naloxone (Narcan)
What are examples of therapeutic communication? Name at least 5.
Broad opening statements, Offering general leads, Exploring, Focusing, Silence, Accepting, Giving recognition, Offering self, Empathy, Reflection, Paraphrasing, Provide information, Clarification, Validation
What rhythm?
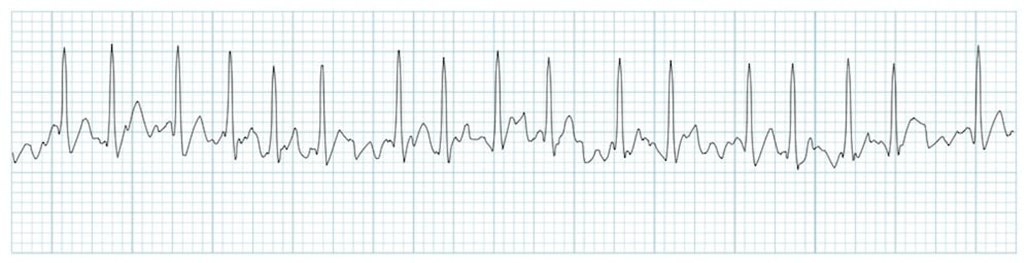
Arterial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
What are the characteristics of the Termination Phase?
Avoids returning to the patient’s initial problems, Encourages independence, Promotes positive family interactions, Help the patient acknowledge their emotions regarding feelings of sadness and anger regarding separation.
How would you give fluids in preop?
IV freeflow
How would you witness a phone consent?
With another nurse (two RN verifications). Make sure to verify the information, write the name of the person giving the consent, relationship, and phone number
What are the indications for room air?
O2 saturations maintain >92% when ambulating and resting
What are non-pharmacological pain treatments?
Ice, heat, deep breathing, guided imagery
What is the Characteristics of the Orientation Phase? Name at least 4
Actively listens, Establishes boundaries of the relationship, Clarifies expectations, Identifies countertransference issues, Uses empathy, Establishes rapport, Sets up a contract with the patient
What would you measure on the rhythm strip each shift?
PR, QRS, QT
Who does not get NSAIDs?
Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and GI (think may bleed)
What IV fluids do anesthesiologists like?
LR, electrolytes including K+, Both isotonics
List safety mechanisms for PCA?
Time outs- lock outs, set dose, only patient can press the buttons
What is a COPD persons drive to breathe?
Low O2
What reverse Midazolam?
Flumazenil
Non-Therapeutic: What are some phrases to avoid?
“You should……”; “You‘ll have to…..”; “You can’t …”; “if it were me, I’d…?"; “Why don’t you…?"; “I think you ……”; “It’s the policy on this unit?"; “Don’t worry?"; “Everyone does that…”; “Why..?”; “Just a second..”; “I know…”
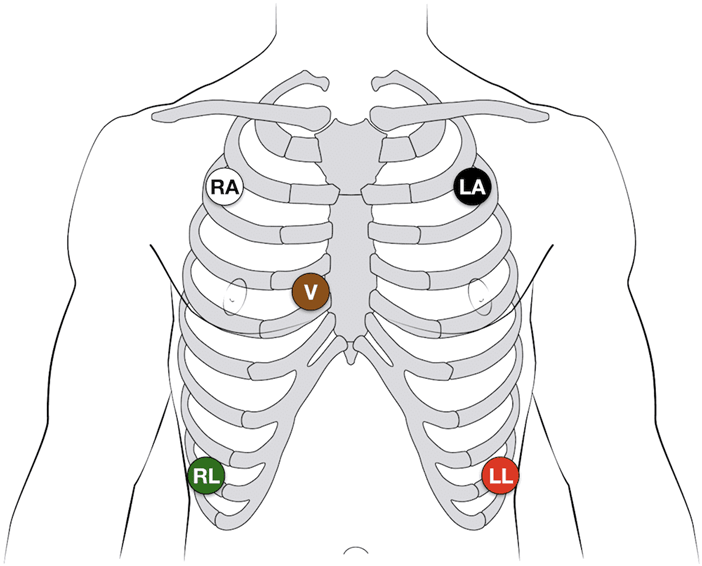
What are the cardiac monitor placements for a 5-lead?
White over right, Snow over grass; smoke over fire. The V lead (brown) is placed at the 4th intercostal space of the right border
Where is Tylenol processed/eliminated?
The liver
What are the IV catheter gauges?
22, 20, 18
(think blue-22, pink-20, green-18)
When should a surgery person's teaching begin?
Pre-op
Name the different types of oxygen devices?
Nasal Cannula (0.5-6 liters), Simple Face Mask (5-8 liters), Oxymask (1-15 liters), Venturi Mask (can give more precise O2), Trach Collar (1-10 liters), Non-Rebreather Mask (10-15 liters)
What are some reasons medication errors still happen?
Provider could order a medication on the wrong patient, Shortages of medications (new medication you don’t normally use now ordered), Labeling and packaging changes (i.e. you are used to seeing a vial with a certain color top), Nurse fatigue, Understaffing
Name 3 defense mechanisms
Denial, Regression, Reaction formation, Acting out, Repression, Suppression, Displacement, Compensation, Identification
**Mature defense mechanisms are:Repression; Rationalization; Intellectualization; Compensation; Substitution; Sublimation; Identification.
**Immature defense mechanisms are: Denial, Projection; Regression; Conversion; Fixation; Withdrawal, or Dissociation.
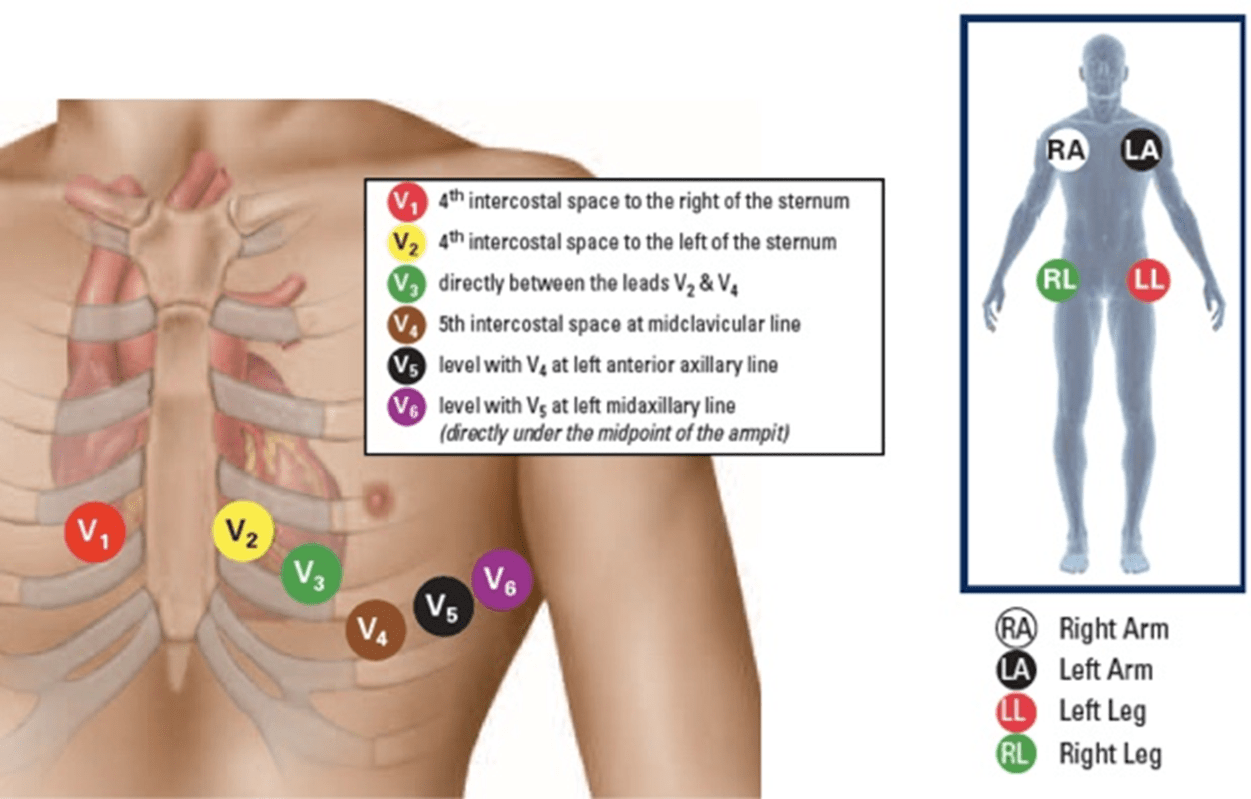
What is the placement for a 12-lead ECG?
Which IV narcotic is the strongest?
Hydromorphine
What do you look for when evaluating an IV on a patient?
Phlebitis, Infiltration, Extravastion
When would surgery be cancelled?
Not NPO, medications, sometimes high BP's