Name 3 sites you can safely administer an IM injection.
deltoid, vastus lateralis, ventrogluteal
This is the minimum hourly urine output (in mL) required to indicate adequate renal perfusion in an average adult
30 mL/hr
Which vital sign is concerning to you about Mr. Johnson?
1. SPO2 96
2. Temperature 38.8 C
3. HR 62 BPM
4. BP 128/88
2
38.8 C = 101.8 F
fever!
To assess a patient's fluid balance and the kidneys' ability to concentrate urine, the nurse monitors this value, which normally falls between 1.005 and 1.030.
Urine specific gravity (highly concentrated is greater than 1.030, highly dilute is less than 1.005)
What tool should you use to make sure your suctioning and/or oxygen therapy is effective for your patient?

These terms are all seven rights of medication administration.
What are Right Patient, Right Medication, Right Dose, Right Time, Right Route, Right Reason, and Right Documentation?
This is the most common and effective nursing intervention used to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia in a post-operative patient by encouraging deep breathing and visual feedback.
incentive spirometer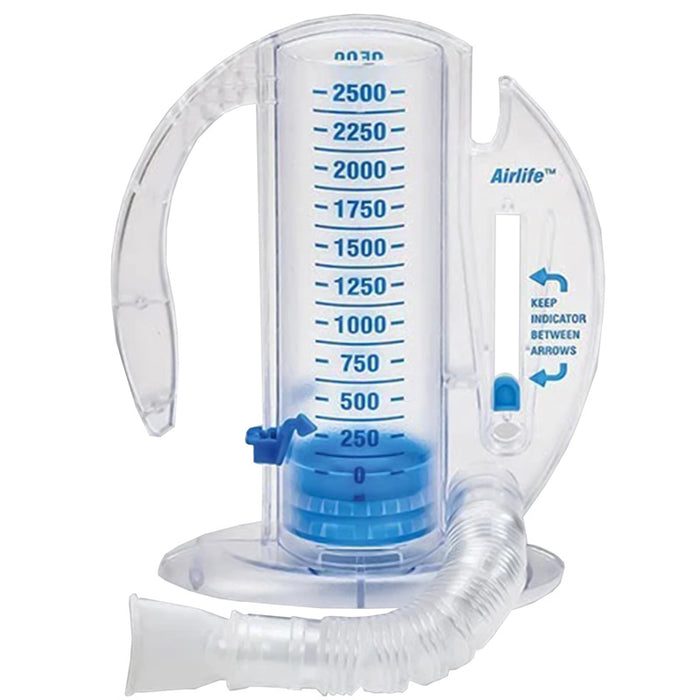
Mr. Johnson is in bed. His vital signs are 88 bpm, respirs are even and unlabored 20 min, BP 128/88, pulse ox 86%. He gets up to pee, and when he stands to use the bathroom, he takes a few steps and hits the floor. His vitals signs are now 96 bpm, respirs 16 bpm, BP 92/40, pulse ox 94%. What did Mr. Johnson experience?
orthostatic hypotension
This is the expected normal range for a fasting blood glucose level in a healthy adult.
70-110
To prevent hypoxia, a single suction pass should never exceed this maximum amount of time.
10-15 seconds
Name 3 sites you can safely administer a subQ injection.
Back of arm, belly, fatty part of thigh
Name 3 tasks that you need to wear sterile gloves for.
Trach suctioning, inserting a foley/straight cath, central line care, many tasks in the OR, wound care, performing vaginal exams in labor and delivery
You are the triage nurse. Which of these four patients must you see first?
- Mr. A: BP 150/94, reporting a mild headache.
- Ms. B: RR 28, SpO2 90% on room air, appearing restless.
- Mr. C: Pulse 52, history of being a marathon runner, no symptoms.
- Ms. D: Temp 101.2°F, reporting body aches and chills
Ms. B - ABC's - showing signs of hypoxia
This lab value—typically ranging from 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL—is a more specific indicator of kidney filtration and function.
Creatinine
 What is this and what is it used for?
What is this and what is it used for?
Nasopharyngeal airway - used to help keep airway open.
If you have questions about a medication, what are three resources you have as a nurse?
Look it up in your drug resource, call the pharmacist, ask the doctor.
A patient with Continuous Bladder Irrigation (CBI) following a TURP has a total output of 3,000 mL for the shift. If 2,400 mL of irrigant was infused, this is the patient's actual urine output.
600 mL
When a nurse notes a blood pressure of 88/50 mmHg paired with a heart rate of 120 bpm, they should immediately suspect this condition, characterized by low circulating volume.
Hypovolemic shock
ABG
7.2 pH
50 CO2
30 HCO3
What's going on?
Partially compensated respiratory acidosis
This low-flow device can deliver oxygen concentrations between at flow rates of 0.5 to 6 (ish) liters per minute.
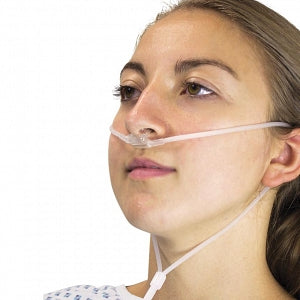
Nasal cannula
Before administering a medication through a nasogastric (NG) tube, the nurse must perform this priority action to ensure the tube has not migrated into the lungs.
Verify tube placement
This is the specific term for the "crunching" or "popping" sensation felt under the skin—resembling Rice Krispies—which indicates that air has escaped into the subcutaneous tissue, often near a chest tube site.
crepitus or subcutaneous emphysema
A patient on oxygen with a tracheostomy suddenly becomes agitated and cyanotic. Their SpO2 has dropped from 98% to 84%. After ensuring the oxygen is connected, this is the immediate next nursing action.
What is suctioning the tracheostomy? (Agitation and a sudden drop in SpO2 often indicate a mucus plug obstructing the airway).
This lab value, typically ranging from 7 to 20 mg/dL, measures a waste product of protein metabolism but can be "falsely" elevated by dehydration, high protein intake, or GI bleeding.
BUN
This specific tool must always be kept at the bedside to guide the reinsertion of a tracheostomy tube in the event of accidental dislodgement
Obturator