Regular uterine contractions with cervical dilation of 6cm or more
What is active labor?
Naegle's Rule
What is subtracting 3 months and adding 7 days (in the next calendar year)?
This test analyzes placental DNA fragments
What is NIPT? (or NIPS or cffDNA)
This is the strongest risk factor for preterm birth.
What is prior preterm birth?
Bonus: What is the baseline rate of PTB in the US?
This medication is contraindicated for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage for women with asthma.
Hemabate.
Bonus: Name the generic.
6 or more contractions in a 10-minutes period, averaged over a 30-minute window
What is tachysystole?
This lab (test and value) is the most sensitive predictor of iron deficiency.
What is serum ferritin < 30?
Bonus: what are the units?
The test you need to order to pick up a Robertsonian Translocation.
What is a karyotype?
This is the definition of a short cervix according to SMFM and ACOG.
What is 25 mm or less?
Hands and knees position to relieve an impacted fetal shoulder
A gradual decrease in the fetal heart rate that has a nadir coinciding with the peak of a contraction.
What is an early decel?
There are two ways to assess amniotic fluid volume. This is the recommended method.
What is deepest vertical pocket?
Preimplantation genetic testing replaces the need for aneuploidy screening in pregnancy. True / False
What is false?
Maternal treatment with magnesium sulfate reduces the risk for developing this disorder by 32%.
What is cerebral palsy?
Acute onset of severe hypotension (read: cardiovascular collapse) is the most common initial symptom of this obstetric emergency.
What is amniotic fluid embolism?
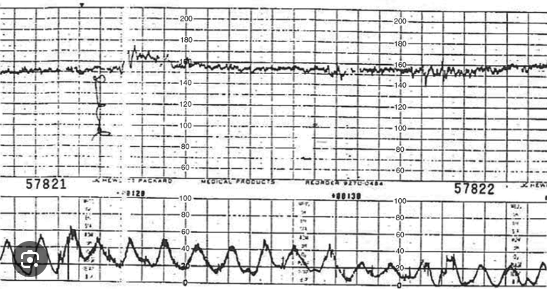
Describe the classic uterine contraction pattern in the setting of an abruption.
What is high frequency, low amplitude?
These are the biometric parameters used to diagnosed fetal growth restriction.
What are EFW and AC?
Amniocentesis can be performed during this gestational age time period (in weeks)
What is any time from 15 weeks on?
Indomethacin given after 32 weeks can have this consequence in the fetus.
What is premature closure of the ductus arteriosus?
Partial credit given for oligohydramnios.
BONUS: consequence in the newborn
This is the time at which to initiate a perimortem cesarean after maternal cardiac arrest.
What is 4 minutes?
This is the risk of uterine rupture during labor with a prior classical cesarean incision.
What is 4-9%
This is the critical antibody titer for Rh alloimmunization risk
What is 1:16?
Hemoglobin electrophoresis will not detect this particular hemoglobinopathy.
What is alpha thalassemia?
Bonus: why?
Pre-gestational diabetes or prior course of betamethasone
What are contraindications to betamethasone between 34w and 36w6d?
The application of pressure to the anterior shoulder to adduct and dislodge the shoulder