
Which nerve block would you use to anesthetize this wound?
Supraorbital nerve
A 3-year-old boy presents to the ED with an burn to the oral commisure after chewing on an electrical cord at home. What is the most serious complication associated with this injury?
Delayed hemorrhage from the labial artery after the eschar separates
T/F: You should repair any cartilage defects involved in lacs on the nose.
False. Suture the skin OVER the cartilage.
What is the importance of the potential space between the galea and the scalp periosteum?
Allows infections/hematomas to spread easily with scalp lacerations
What is the maximum dose of lidocaine with epi that may be used safely?
6-7 mg/kg
Injury to which nerve results in foot drop?
Common peroneal nerve
False - it increases infection risk and should not be done!
How would you close a flexor tendon laceration of the hand?
Describe the steps for draining a septal hematoma.
Incise (large) or aspirate (small) the clot. Pack the nose. Call ENT for OR if bilateral.
A 16 yo p/w a 50% subungual hematoma and intact nail folds. An X-ray shows a nondisplaced distal tuft fracture. What management is indicated?
Trephination, splinting, and follow up. Antibiotics are not indicated.
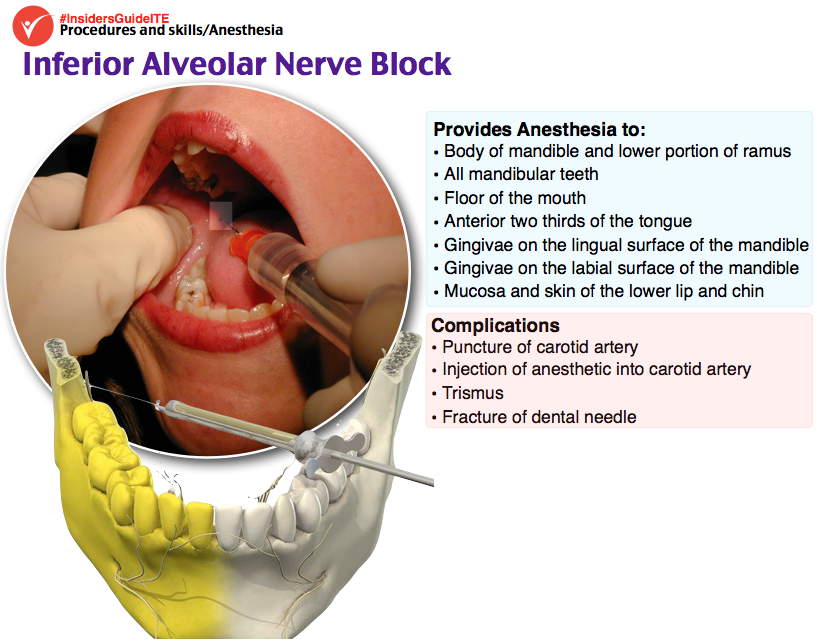
A 39-year-old woman presents to the ED with sharp pain of the right lower second premolar (tooth #29).Which nerve block may be appropriate for pain control?
inferior alveolar nerve block = all mandibular teeth to the midline, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and the floor of the oral cavity
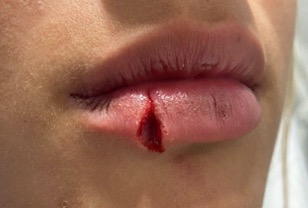
Where should you throw your first suture?
Vermillion border

When should you close an intraoral lac?
If flap interferes with chewing or lac large enough to trap food (usually not necessary if <1cm)
Describe the dressing to prevent an auricular hematoma for a patient with an ear lac.
Apply xeroform over repair site conforming to shape of ear
Fluff gauze to fill space between ear and scalp and in front to fill interior contours
Wrap head and ear with gauze and ACE wrap
Recheck in 24 hours
May bupivacaine be safely administered to a patient with a lidocaine allergy?
No - this patient has an amide allergy so may receive the ester class of local anesthesia but not other amides.

Describe how you would perform a nerve block to anesthetize this laceration?
Mental nerve block = Retract the lower lip and inject parallel to the premolar at about 1 cm depth
Name at least 4 indications for antibiotic prophylaxis for hand lacs.
Mammilian bite
>12 hours old
Co-morbidities affecting wound healing (DM, ESRD)
Contaminated wound
Exposed bones
Burns
Macerated soft tissue
List at least 3 indications for re-implantation of digit amputation.
Children
Multiple digits
Thumb
Proximal to insertion of flexor digitorum superficialis
Name some complications of an untreated septal hematoma.
Saddle nose deformity, septal perforation, +/- airway obstruction
Describe where you would test for sensation in the hand for the radial, median, and ulnar nerves?
Radial - first dorsal webspace
Median - volar aspect of index finger
Ulnar - volar aspect fifth finger
Where would you inject for a regional block to repair this laceration?
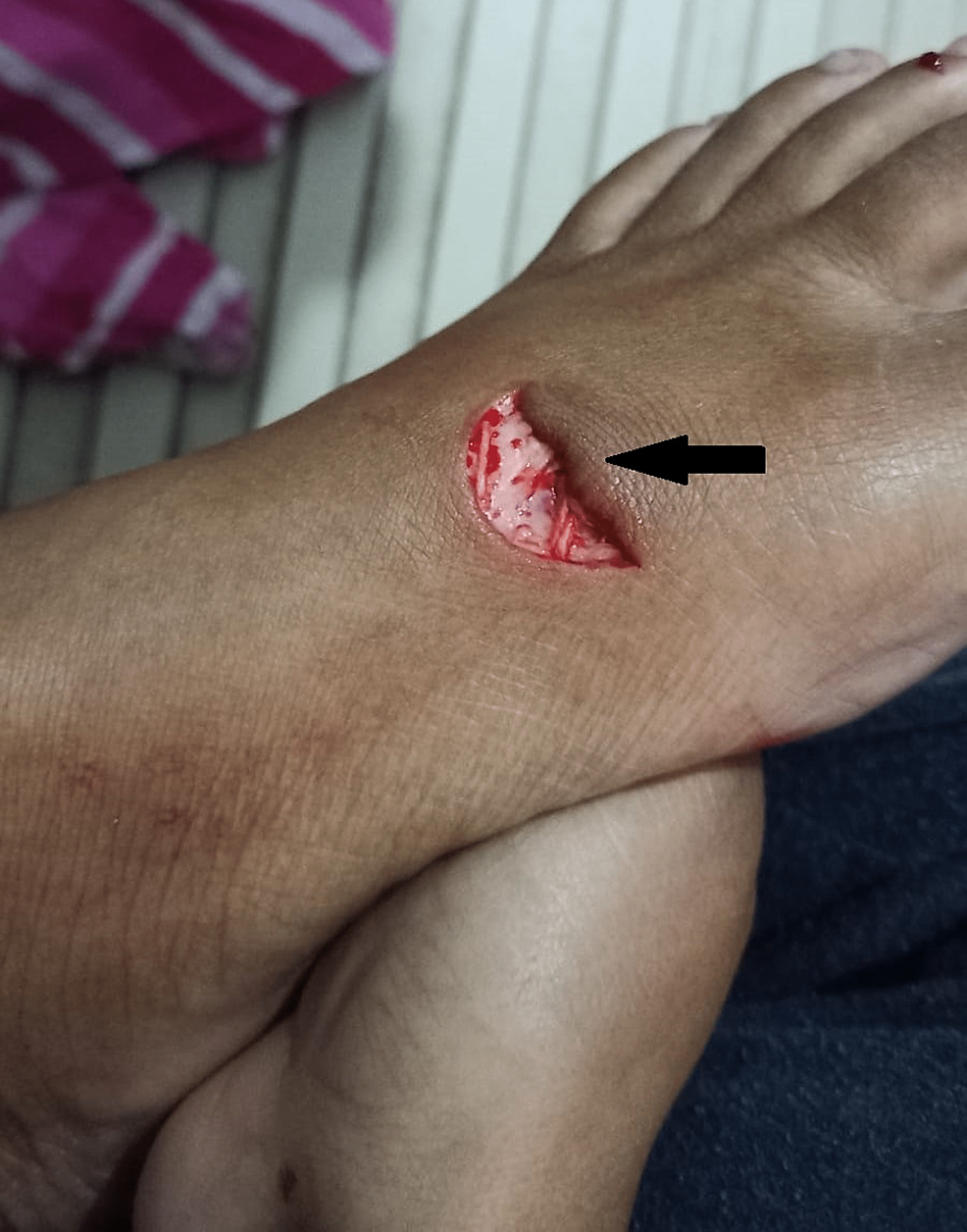
Superficial peroneal nerve = between superior portion of lateral mal and tibialis anterior tendon
Have pt dorsiflex and invert foot to help ID this tendon
Name the landmarks for identifying possible parotid gland injury with a face lac.
Suspect parotid duct injury when the wound crosses a line from the tragus to the frenulum and is posterior to a vertical line downward from the lateral canthus.
Name the 5 reasons to consult ophtho for an eyelid laceration.
Involvement of tarsal plate
Involvement of lacrimal system
Through eyelid margin
Inner surface of eyelid
Associated with ptosis
Describe mallet finger, swan neck, and Boutonniere deformities of the digits.
Mallet - hyperflexion of DIP
Swan neck - hyperextension of PIP, hyperflexion of DIP
Boutonniere - hyperflexion of PIP, hyperextension of DIP
What is the maximum volume of 1% lidocaine with epi that can safely be administered to a 35 kg patient?
21-24.5 mLs
(1% lido - 10mg/mL. Max dose = 6-7 mg/kg. 6*35 = 210 mg. 210mg/10mg/mL= 21-24.5 mLs.)