Culture
Culture
What is the right to “digital disconnection”?

The right to not answer messages or be available outside of working hours.
True or false: we all manage stress in the same way.

False
What is a “micro break” and how does it help productivity?

They are short breaks during the workday; they help relax the mind, prevent fatigue, and improve concentration.
True or false: stress is negative.

False
Myth or reality: “Work-life balance means splitting 50% of the time for personal life and 50% for work.”

Myth. Balance depends on quality, not the exact amount of time.
Mention one practice that companies can implement to support work-life balance.

Flexible schedules, remote work, active breaks, wellness programs, Lean In Circles, etc.
Mention 2 types/areas of self-care

Spiritual, physical, emotional, cognitive.
What is the difference between working hard and working smart?
Working hard involves more effort and longer hours; working smart means prioritizing, using tools and time management techniques to achieve better results with less strain.
Mention 2 physical symptoms caused by excessive stress:

Rapid heartbeat, fast breathing, sweating, trembling, muscle tension, headache, and fatigue.
Myth or reality: “Working more hours always means greater productivity.”
Myth. More hours do not mean better results; productivity depends on focus and breaks.
True or False: An “always on” culture (always available) improves performance in the long term.

False. It causes burnout and decreases productivity.
Mention the 3 aspects of the “Work-Life Triangle.”
Self-care, work (career), relationships.
What is more effective for productivity: multitasking or monotasking?

It allows greater focus and quality in the task.
It is a healthy stress that motivates us to achieve goals, such as performing well in a presentation or avoiding danger, and is essential for personal growth.

Eustress
Myth or reality: an employee with high work engagement is not at risk of burnout. 
Myth. Even the most committed employees can burn out if they don’t set boundaries; engagement alone does not protect against exhaustion.
What cultural practices within a company foster a greater sense of belonging and support for work-life balance?

Recognition of performance, flexible schedules, inclusion policies, open communication, wellness programs, and leaders who model balance.
Which hormone is associated with stress and can affect physical health if it remains elevated?
Cortisol
What is the time management technique called that alternates 25 minutes of work with 5 minutes of rest?

Pomodoro Technique.
What is burnout?

Syndrome of physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion caused by chronic workplace stress.
Myth or reality: remote work always improves employees’ work-life balance.

Myth. It can improve flexibility, but it can also blur the boundaries between work and personal life, increasing the risk of overload.
Why is organizational culture key to preventing burnout among employees?

It sets norms and expectations about workload, fosters respect for working hours, promotes spaces for support and care, and creates an environment where well-being is a priority, thus reducing the risk of chronic burnout.
What is the ability to say “no” without feeling guilty called?

Assertiveness
What is the 80/20 rule in productivity (Pareto Principle)?
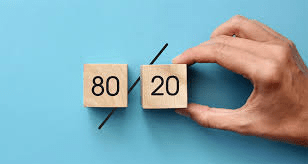
20% of the actions generate 80% of the results.
What is the difference between work-related stress and burnout?

Stress is temporary and manageable; burnout is chronic, with extreme exhaustion, lack of motivation, and decreased performance.
Myth or reality: a leader who models self-care and disconnection habits has more influence on the culture of balance than a policy.
Reality. The practical example set by the leader directly impacts team behaviors more than a formal policy.