Terms
This Lean manufacturing technique organizes machines, workstations, and resources into self-contained units to improve workflow, efficiency, and production by minimizing movement and waste.
What is Cellular Layouts?
Benefits of Cellular Layouts
This type of waste refers to:
❌ Either producing more than downstream operation requested or sooner than it’s prepared to accept.
❌ It's considered the most harmful type of waste because it causes all the others.
What is Overproduction?
According to the first Lean principle, this key stakeholder determines what is truly valuable in a product or service.
Who is the Customer?
The Japanese word meaning change for the better or continuous improvement.
This mindset engages workers at all levels to surface problems, experiment, and make incremental improvements to their work each day.
What is Kaizen?
This metric refers to the actual time it takes to complete each step of the process. This represents the process’s capacity.
What is Cycle Time?
The Toyota Production System is focused on the complete elimination of this.
What is Waste (Muda)?

This lean fundamental refers to visual, worker developed documents that display the current best way to effectively, safely, and timely complete the tasks within a process. It eliminates variation, ensures process stability, and set a baseline for all improvement.
What is Standard Work?

The most effective standard work is collaboratively developed by those responsible for performing the work; consists of clear, concise visuals; and is easily accessible at the point-of-use.
This is the term for a group of related products that pass through similar process segments and use common equipment; serves as the scope for value stream mapping exercises.
What is Product Family?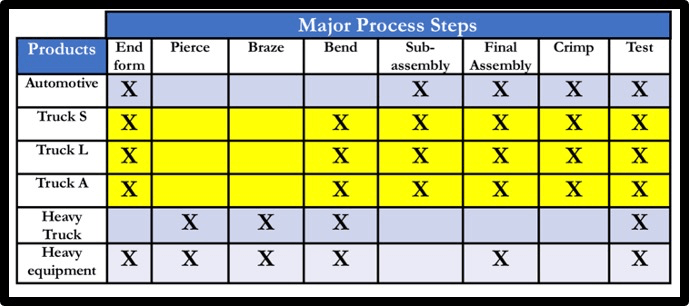
These are the two pillars of a Lean Culture. Name and Define them.
What are Continuous Improvement and Respect for People? 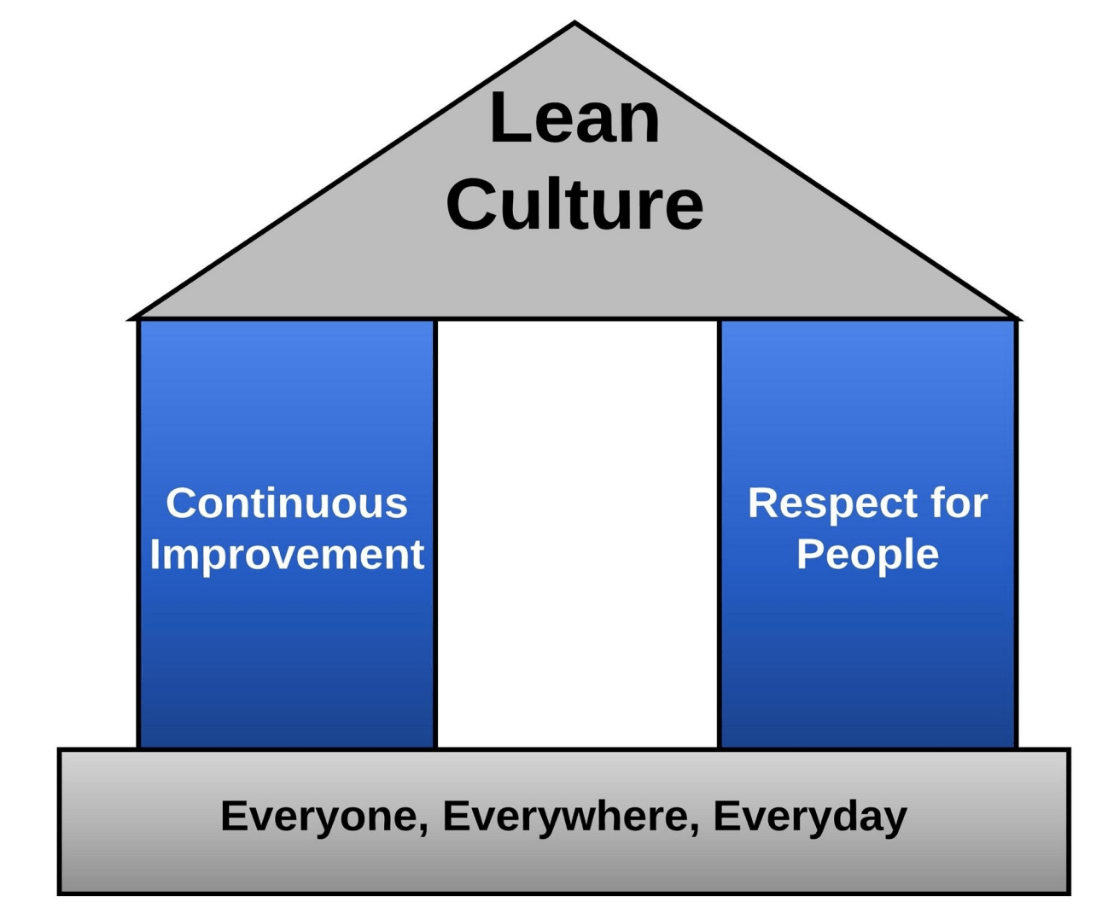
The Japanese term for actual place, often used for the shop floor or anywhere value-creating work occurs. Examples: shop floor, office, emergency room, kitchen, hotel lobby, call center, construction site, etc.
What is the Gemba?

This metric refers to the the total time it takes a product or service to travel through a value stream; Cycle time plus all waiting/delays.
What is Lead Time?
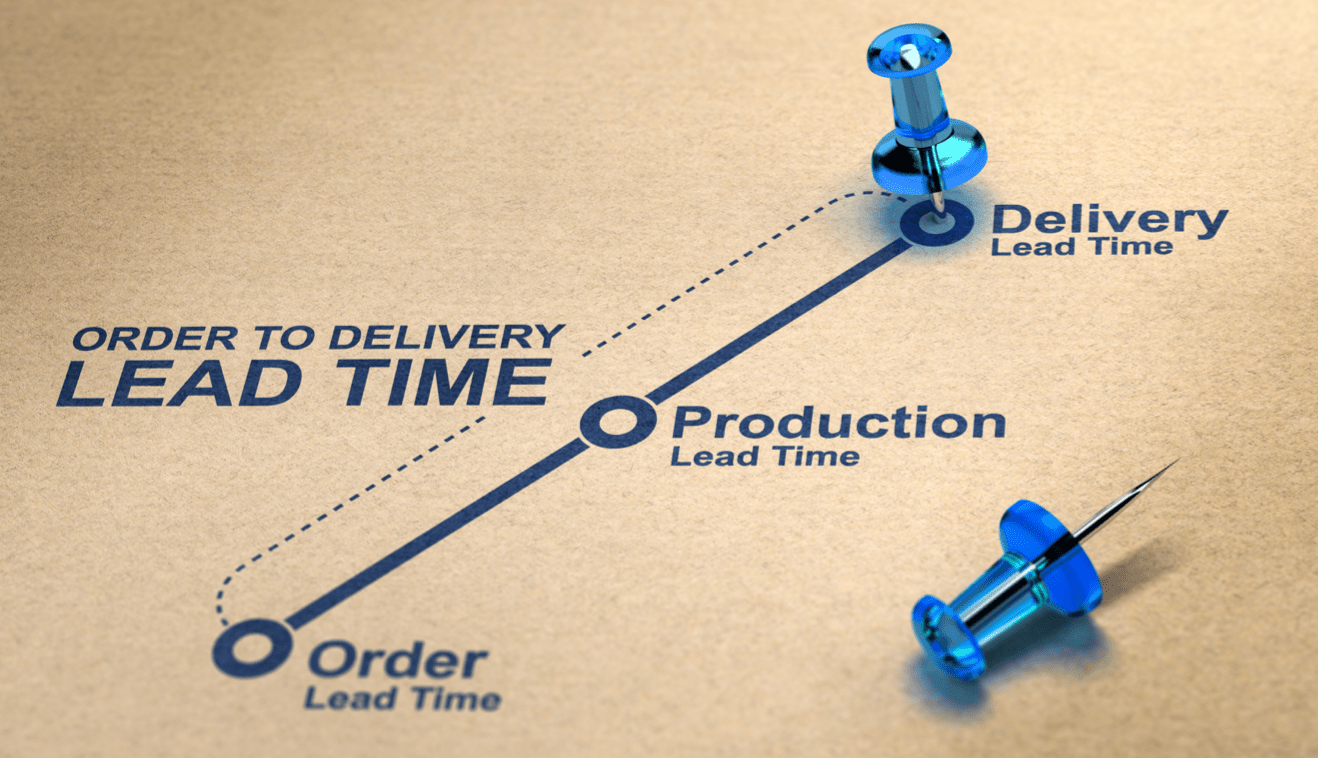
Lead Time is regarded as the most important metric to improve in value stream mapping efforts, since it forces problems to the surface so we can eliminate waste in the process to deliver customer value.
The man pictured below is known as the architect of The Toyota Production System.

Who is Taiichi Ohno?


This Lean fundamental with 5-6 pillars helps workers establish and maintain an orderly, clean, safe, and effective work environment through disciplined daily routines and visual management.
What is 6S Workplace Organization?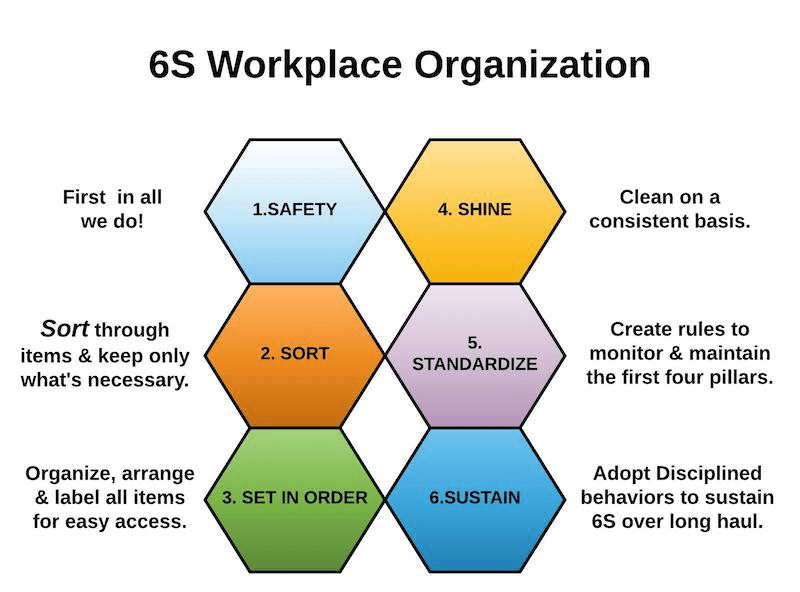
This refers to the practice of maintaining precise production and conveyance sequence by ensuring that the first part to enter a process or storage location is the first part to exit.
What is FIFO?
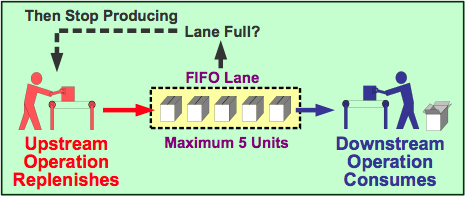
This Lean principle (#3) emphasizes the importance of ensuring that each step in a value stream moves smoothly without interruptions, delays, or bottlenecks. It is often considered the prime goal of a Lean enterprise.
What is Create Flow?
Benefits of Flow
✅ Improved customer value.
✅Shorter lead time.
✅ Removes unnecessary burden on operators and machines.
✅ Reduced wait time.
✅ Easier to identify and eliminate defects.
✅ Less rework.
✅ Less WIP inventory.
✅ Level workflow.
✅ Improved communication.
✅ Flexibility to adapt to changes in customer demand.
✅ Reduced opportunity for errors.
✅ Lower costs.
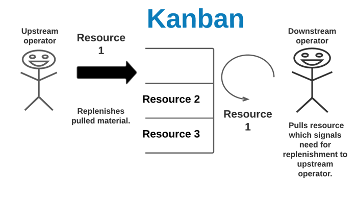
This Japanese term refers to any signaling device (often a card) used in pull production systems that authorizes and instructs workers to produce or withdraw materials or information.
What is Kanban?
This auto manufacturer has led the industry in sales 18 times since 2000, including 2020-2024.
What is Toyota?

The man pictured below was a a pioneer in industrial engineering and manufacturing and greatly significantly contributed to the success of the Toyota Production System through his consulting work for the company. He's especially well regarded for his revolutionary work in poka yoke (mistake proofing), and set up reduction (single minute exchange of dies).

Who is Shigeo Shingo?
This acronym describes the process for changing over production equipment from one part number to another in as little time as possible--to the target of reducing changeover times to a single digit, or less than 10 minutes.
What is Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)?
The primary objective of setup reduction is to convert equipment shutdown time due to product changes into value-added time.

Mass production technique in which batched orders are pushed from a central production authority based on a pre-determined schedule, whether or not the customer placed an order or if the downstream operation is ready for it.
What is a Push System? 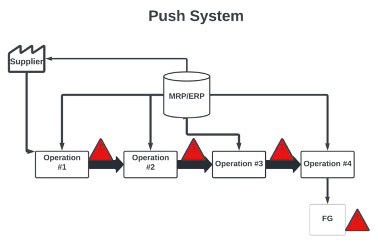
This Lean principle (#4) describes a production method where work advances only when the next in line customer is ready, triggered by a request (usually a visual signal) from the downstream operator, helping to prevent overproduction and minimize excess inventory.
What is Establish Pull?
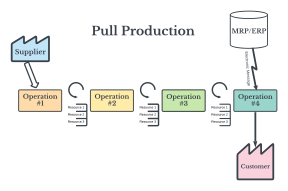
Pull Benefits
The Japanese term for visual management; it provides the operator with "stop the line authority" any time an abnormal condition is observed. It is often used in the form of cord operators can pull or stacked lights: green means all is good; yellow is a request for supervisor assistance; red means there’s problem and the line stops until the problem is resolved.
What is Andon?
This metric defines the the rate at which products must be processed to meet customer demand--the steady beat of production.
What is Takt Time?

This Toyota method refers to a visual management device that empowers operators to signal the occurrence of an abnormality in the production process. It enables operators to stop the production line and address problems immediately at their source, ensuring that defects are not passed to the next downstream operation.
What is Andon cord?
Also known as Built-in Quality; practice of controlling variables within a process, securing quality at one’s own process, not passing on poor quality, and checking every piece.
What is Quality at the Source?

This type of pull production system refers to an inventory stocking system in which items are stored by the operation that produces them (upstream) until they are retrieved by the operation that needs them (downstream).
What is Supermarket Pull System (Type A)?
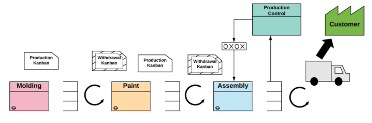
Any item that exists the supermarket signals the need for production or delivery. In a Supermarket Pull System, the segment at the end of a process contains a supermarket that holds an amount of each item it produces. Once the downstream process retrieves the items, the upstream process then produces to replenish what is withdrawn from its supermarket. This is often communicated by using kanban cards.
This Japanese term, also known as automation with a human touch, refers to smart machines that provide operators with the ability to build in quality at each process and separate themselves from machines, consequently, freeing them up to complete value-added work while the machine is running.
What is Jidoka?

This is the formula for calculating takt time.
What is Time Available to Work (per day)/Customer Demand (per day)?

Example: 27,600 seconds/460 Widgets = Takt Time of 60 seconds.
This is the Toyota-pioneered problem-solving practice of gathering the problem, the analysis, the corrective-actions, and the action plan down on a single piece (11 by 17) of paper.
What is A3 Thinking?
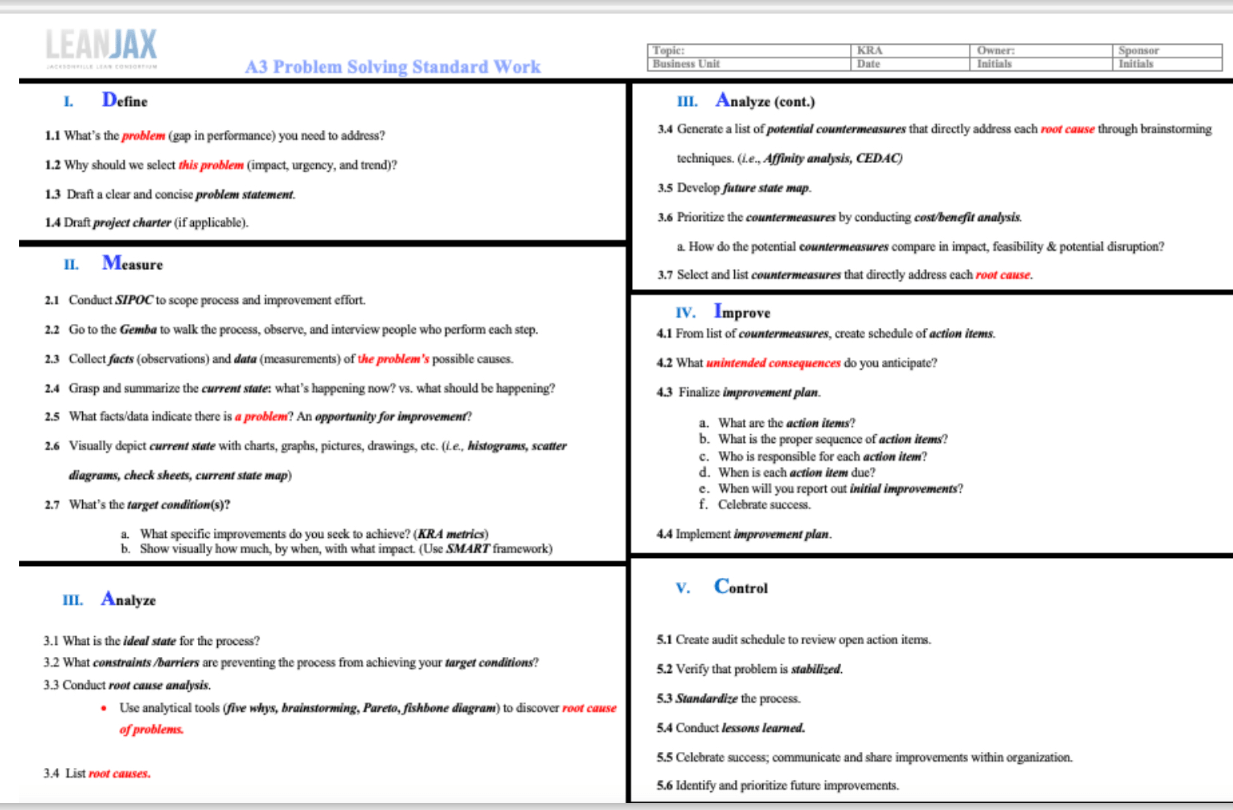
A3 Thinking Benefits
1. Visual roadmap for all Lean/continuous improvement efforts; tracks improvement work through visual story-telling approach.
2. Provides standard work process for a root cause analysis based problem solving approach.
3. Communicate facts in a logical, commonly understood format.
4. Helps get the right people to develop a healthy dissatisfaction with their work processes, develop a shared realistic vision for the future state and to develop an impactful action plan.
5. Enables individuals to observe reality, present facts, propose working countermeasures, and achieve desirable target conditions.
6. Creates a knowledge sharing database throughout organization.
7. Drives a balance of incremental and breakthrough improvements.
This refers to a proactive approach to detecting or preventing defects by designing and implementing creative devices and procedures.
Also known by the Japanese term Poka Yoke.
What is Mistake Proofing?
Name and define the three elements of a standard work document.
What are: 1. Takt time, which is the rate at which products must be made in a process to meet customer demand.
2. The precise work sequence in which an operator performs tasks within takt time.
3. The standard inventory, including units in machines, required to keep the process operating smoothly?
Japanese term for leveling or smoothing the production schedule, achieved by averaging out both the volume and mix of products throughout the production line.This method enables the operation to adapt promptly to fluctuations in customer demand, by evenly producing various kinds of products each day in a small amount.
Additionally, it allows for timely responses to variations in customer orders without relying on sizable inventories.
What is Heijunka (leveling)?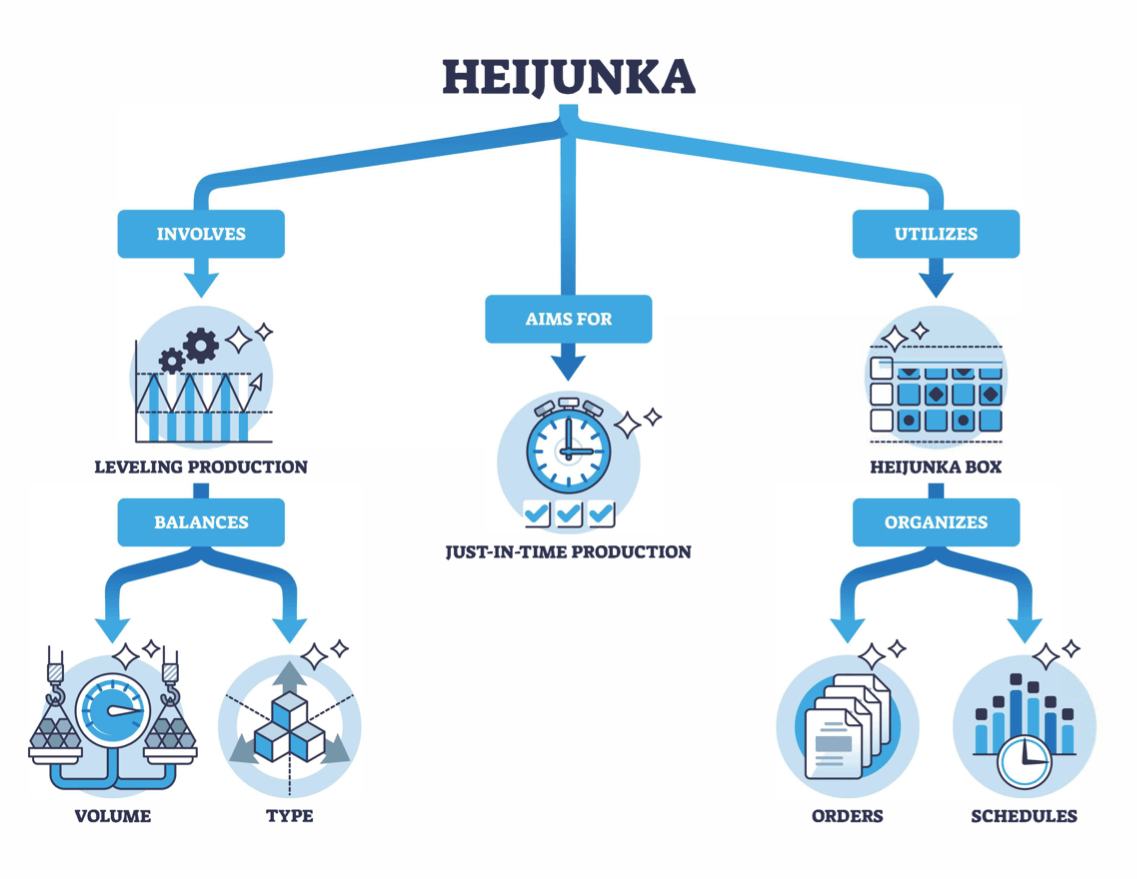 Heijunka
Heijunka
This is the formula known as Little's Law--a calculation used to understand and optimize the flow of work through a process.
What is WIP=Throughput×Cycle Time?
Relevance of Little's Law
This concept, one of the two pillars of the Toyota Production System, emphasizes the importance of producing only what is needed, when it is needed, in the quantity needed to minimize waste and reduce inventory.
What is Just-in-Time?