What is the reptilian brain? What is it made of?
The set of brain structures in charge of coordinating primitive autonomic functions and keeping the body alive. .
Brain stem (midbrain, pons and medulla) and basal ganglia.
Illustrate the 3 anatomical planes

Karl Lashley´s failed "Engram" hypothesis proposed that:
Memories left a physical trace or mark in specific neurons, suggesting that if those neurons were damaged, entire memories could simply vanish.
Disproved by Donald Hebb
What is the difference between Heuristics and Schemas (schemata)?
Schemata are mental structures like folders that allow for the accommodation of long-term memories.
Is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information, in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment.
Mention 5 structures that are part of the limbic system
Hippocampus, amygdala, nucleus accumbens, hypothalamus, thalamus, limbic lobe, etc.
Name 5 types of Neuro imaging techniques
MRI, FMRI, EEG, DTI, CT, PET, etc.
What does this mean?
Supramodal: that doesn´t rely on a single structure or pathway but instead is constructed by many.
Multi-channel: Like experience, it depends on the complex interaction of several senses and input forms.
Neurocognitive: That depends on both structural and functional processes within the CNS.
What are Schemata?
Mental structures that allow for the filtering and organization of long-term memory. They allocate new information through categories, associations and significance.
What is cognition?
"Cognitions are mental processes that deal with knowledge. They encompass psychological activities that acquire, store, retrieve, transform, or apply information. Cognitions are a pervasive part of mental life, helping individuals understand and interact with the world. "
Describe the differences between neurotransmitters, hormones and pheromones. Where are they all located?
Neurotransmitter: Substance that allows communication between neural cells (CNS & PNS)
Hormone: Substance that allows communication with cells via the bloodstream.
Pheromone: Substance that allows communication between members of the same species. They go in through the olfactory nerve in humans*
What is the historic importance of post-mortem examinations?
They allowed studying brain structures and even identifying the role of regions and functions before the digital era.
What did Donald Hebb say about memory?
Reverberating circuits, Multi-channel experiences codify better (Neurons fire together), supramodal functions.
Describe the 3 types of basic learning
Conditioning (Classical and operant) and observational
Describe 2 ways in which Emotional Significance plays a role in cognition.
In perception, it filters information subjectively.
In memory, it mediates association of information and build a complex narrative around episodic memories.
In decision making, subcortical processes can overtake cortical ones and affect judgement.
Etc.
Meaning chamber in greek (Thalami), it is a subcortical structure that connects several regions of the brain, filtering and allocating signals for the corresponding regions. It is key in attention, cognition and working memory. It doesn´t filter out information from the Cranial nerve 1 (Olfactory).
Positron-Emitting Tomography
Describe ways in which short-term memory consolidates into long-term.
Bonus: where are they located structurally?
Information from short-term memory (subcortical, hippocampus) gets filtered through significance, and either proven useful or lost. Sleeping and dreams play key roles in its consolidation into long-term memory (Cortical areas)
Describe Piaget´s cognitive learning theory.
Assimilation: The process of integrating new information into existing schemas without changing the schema itself.
Accommodation: The process of modifying existing schemas or creating new ones when new information cannot be explained by current schemas.
Repetition of system 2 tasks allow for eventual automation of processes and decrease the cognitive mental effort, to the point where now system 1 operations can complete the same tasks.
--> Cognitive load is filtered better and the effort is optimized.
Explain the HPA axis
In the presence of danger awareness, Hypothalamus secretes noradrenaline/norepinephrine into the Pituitary, which then secretes adrenaline/epinephrine to the bloodstream and, reaching the adrenal glands, they are instructed to release cortisol into the bloodstream to increase stress and sympathetic response.
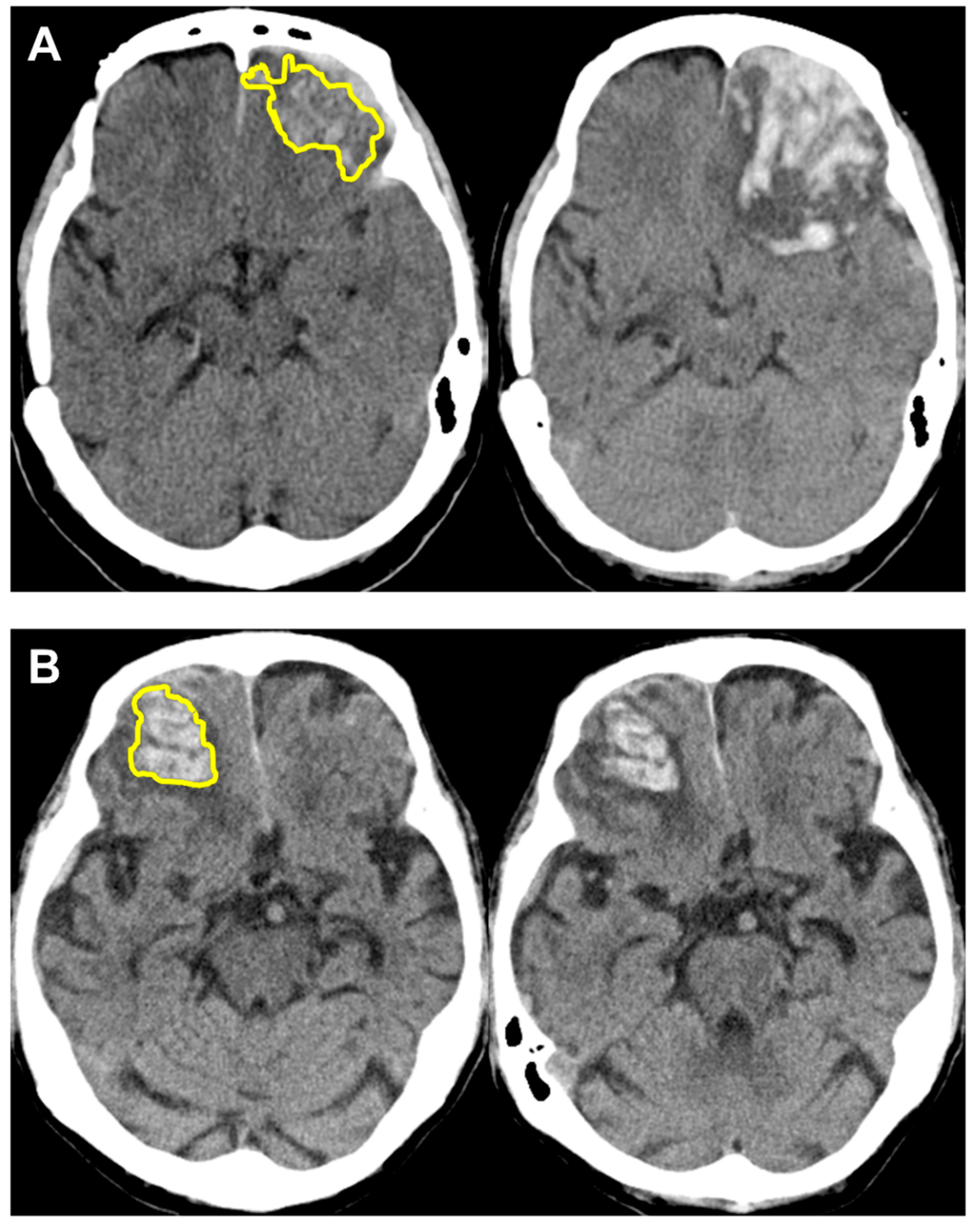
What behavioral alterations would this patient show?
The patient shows a subdural hemorrhage in the frontal lobe.
Pre-frontal cortex is damaged, resulting in alterations in behavior monitoring, impulse control, reasoning, planing and excecutive functions.
There are two types of long term memory.
Describe two types of each category.
Declarative (Explicit): Semantic, episodic, autobiographical, spatial.
Non-declarative (Implicit): Emotional, procedural, priming, conditioning.
Tip: Observational learning, schematas and heuristics
:D
I knew you could do it
Describe the dual processing model and give an example of system overtake.
E.G. "Is that a new haircut?"