A type of learning that involves stimulus-response connections.
Conditioning
Learned avoidance of a particular food.

Taste aversion
Did I tell you that you are one of my favorite students? So, you get 100 points.
Yay!
The reinforcement of the behavior occurs every time the behavior occurs.
Continuous reinforcement
Learning that remains hidden until it is needed.
Latent learning
A stimulus that causes a response that is automatic, not learned.
"Meat" - Pavlov's dogs
"Clanging of the steel bars" - The little Albert Experiment
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
In this method, a person is exposed to the harmless stimulus until fear responses to that stimulus are extinguished.
Flooding
Reinforcers that function due to the biological makeup of an organism.
Primary reinforcers
You are one of my favorite students. You get 200 points!
Yahoo!
You are so lucky today! 200 points are yours!
Yeah!
Learned stimulus.
"Bell" - Pavlov's dog
"Rat" - The little Albert experiment
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
What occurs when the conditioned stimulus (CS) is disconnected from the unconditioned stimulus (US), and as a result, the conditioned stimulus (CS) no longer causes the conditioned response (CR) to occur.
Extinction
Reinforcers that increase the frequency of the behavior they follow when they are applied.
Positive reinforcers
The way of teaching complex behaviors in which one first reinforces small steps in the total activity.
Shaping
Studying something regularly, so the learning is distributed over several days or weeks.
Distributed learning
Automatic response.
"Salivation" - Pavlov's dog
"Fear" - The little Albert experiment
Unconditioned response (UR)
In this method, people are taught relaxation techniques, and then, while they are relaxed, they are exposed gradually to the stimulus they fear.
Systematic desensitization
These reinforcers initially acquire their value through being paired with established reinforcers.
Secondary reinforcers
A behavior is not reinforced every time it occurs.
Partial reinforcement
Trying to learn something all at once.
Massed Learning
Learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral, or meaningless.
"Salivation" - Pavlov's dog
"Fear" - The little Albert experiment
Conditioned response (CR)
The act of responding in the same ways to stimuli that seem to be similar.
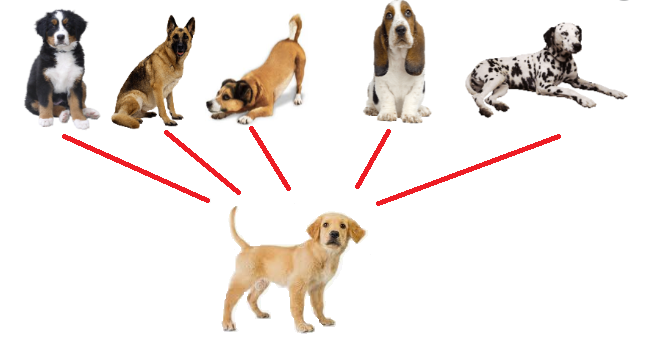
Generalization
Reinforcers that increase the frequency of the behavior that follows when they are removed.
Negative reinforcers
Each step of the sequence must be learned and must lead to the next until the final action is achieved.

Chaining
Learning in which people acquire knowledge and skills by watching others.
Observational Learning