What is a cell?
The smallest unit of life that performs all life functions.
Who named cells after looking at cork?
Robert Hooke
Do prokaryotes have a nucleus?
No they do not.
This organelle converts chemical energy from food into ATP through cellular respiration.
mitochondria
Mitosis ensures genetic consistency by producing these types of cells.
Identical daughter cells
What is cytoplasm?
This substance is found inside all cells and helps carry out functions.
Who saw tiny living things in pond water?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Give 4 examples of a eukaryote.
plant/animal/fungi/protist
Found only in certain eukaryotes, this double-membrane organelle contains thylakoids and its own DNA.
Chloroplast
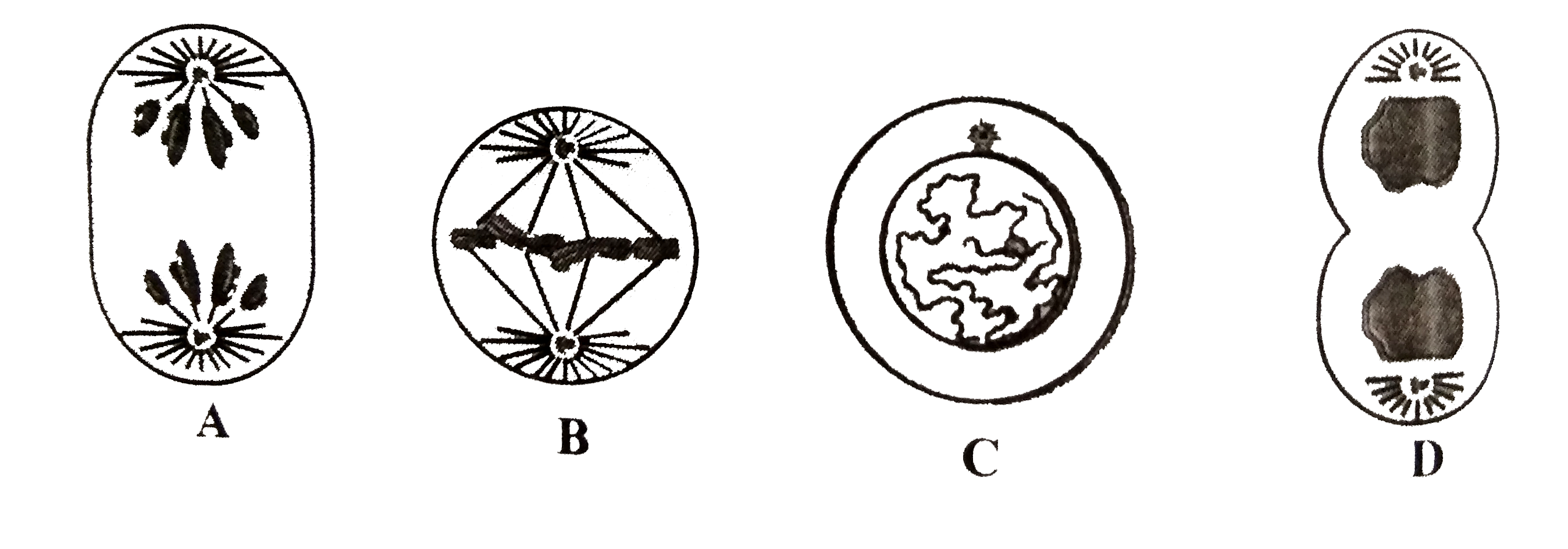
What stage of mitosis is B?
Metaphase
Name two life functions that cells perform.
metabolism, reproduction, homeostasis, response to stimuli, adaptation and growth.
Name one part of the cell theory.

These cells lack membrane-bound organelles and compartmentalization.
Prokaryotic cells
In plant cells, this structure regulates turgor pressure and stores pigments, toxins, and water.
Central vacuole
During this mitotic phase, sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles.
Anaphase
Name 3 things all cells have.
DNA, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
In what ways did the invention and improvement of the microscope directly influence the development of the cell theory? Name at least two scientists and their specific contributions.
1. Robert Hooke came up with the term “cell.”
2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a more powerful single-lens microscope to observe “animalcules” (bacteria and protozoa), becoming the first to see living cells which were foundational for developing the idea that all organisms are made of cells.
Are bacteria prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
prokaryotes
This organelle contains hydrolytic enzymes and is more prominent in animal cells than plant cells.
Lysosome
These cells are diploid and make up the majority of an organism’s body.
stomatic/body cells

What is C?
Mitochondria
What does the cell theory say about where cells come from?
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
These cells can carry out specialized functions due to their internal membrane system.
eukaryotic cells
This flattened organelle modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or membrane use.
Golgi apparatus/body
This diploid cell results from the fusion of two haploid gametes.
zygote