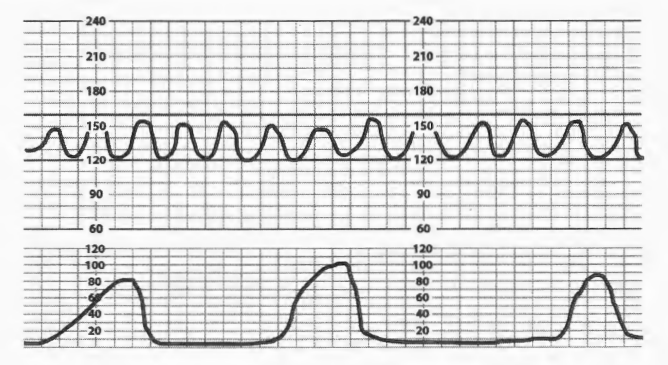
Abrupt increase in FHR that goes 15 bpm above baseline and lasts at least 15 secs in a baby that is greater than 32 weeks gestation.
What is an acceleration
Identify the FHR change in this picture.
What is an early deceleration?
This structure, which connects the fetus to the placenta, typically contains two arteries and one vein, and is responsible for transporting oxygenated blood to the fetus and deoxygenated blood away.
What is the normal umbilical cord?
Your monitor tracing shows fetal tachycardia. What should be your initial nursing intervention/assessment.
What is check maternal temperature.
These are congenital, flat, bluish-gray markings often found on the lower back or buttocks of newborns.
What are Mongolian spots?
This common condition in newborns involves the appearance of small, white bumps on the skin, usually on the face, due to clogged sebaceous glands.
What is milia?
Identify the periodic changes seen on this monitor strip. 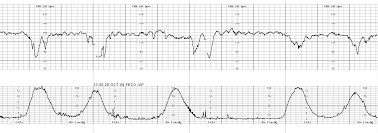
What are recurrent Variable decelerations?
This fluid, produced by the fetus and the placenta, serves several key roles during pregnancy, including cushioning the fetus, maintaining a stable temperature, allowing for fetal movement, and aiding in the development of the lungs and digestive system.
What is amniotic fluid?
This medication is administered to Rh-negative mothers within 72 hours after delivery of an Rh-positive baby to prevent sensitization during future pregnancies
What is RhoGAM?
What can cause decreased variability?
What is Narcotics, Cocaine, steroids- Betamethasone , Magnesium sulfate, fetal sleep pattern, Infections, Maternal fever, placental insufficiency
A decel that lasts > or = to 2 mins but less that 10 mins
What is a prolonged decel?
Is oxygen indicated for this tracing. 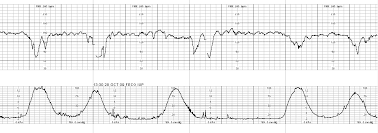
What is No. There is variability. Try other interventions first.
This condition occurs when the placenta is unable to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, often leading to fetal growth restriction, low amniotic fluid levels, and increased risk of preterm birth.
What is inadequate placental perfusion?
These interventions would be indicated for a Category III tracing.
What is reposition, O2, IVfluids, notify provider, prepare for imminent delivery.
This involves positioning the baby's mouth directly over the nipple and areola.
What is a proper latch during breastfeeding?
Irregular, painless contractions that do not result in cervical changes and usually subside with rest or hydration
What is false labor?
Here is your patient's current tracing. What do you chart in the medical Record?
Baseline- 125
Variability- Moderate
Acceleration- present
Decelerations- Absent
Category 1
Contractions- 6mins apart, 70-80 seconds, Intensity and resting tone- Can only be on palpation
This in the first trimester can disrupt fetal development, especially the formation of the brain and facial features, increasing the likelihood of lifelong cognitive and behavioral issues."
What is drinking alcohol?
This opioid antagonist is administered during delivery to reverse the effects of opioid-induced respiratory depression in a newborn, especially if the mother received opioids close to delivery
What is naloxone?
This stage of labor begins with regular contractions and ends when the cervix is fully dilated to 10 cm and is divided into three phases: latent, active, and transition."
What is the first stage of labor?
his term refers to the discharge of mucus mixed with blood from the cervix, often occurring as the cervix begins to dilate in preparation for labor
What is the bloody show?
What is this fetal tracing?

Sinusoidal
After delivery, this intervention helps reduce swelling and discomfort in the perineum in the first 24 hours.
What is ice packs?
Before administering an epidural, it is essential to complete these assessments.
What is maternal vital signs, platelet count, and the absence of certain conditions like hypovolemia or infection at the insertion site?
This crucial first step in newborn resuscitation.
What is dry and stimulate?
This stage of labor begins when the cervix is fully dilated and ends with the birth of the baby
What is the second stage of labor?
This is the external device used to record tension changes in the abdomen resulting from uterine contractions.
What is a TOCO?
These are the forces responsible for moving the fetus through the birth canal, including uterine contractions and the maternal efforts of pushing during the second stage of labor.
What are the powers of labor?
This theory suggests that non-painful stimuli, such as touch or heat, can interfere with the transmission of pain signals to the brain by "closing the gate" in the spinal cord, helping to reduce the perception of pain during labor.
What is the gate control theory during labor?
This includes ensuring uterine tone through fundal massage and addressing any trauma or lacerations immediately after delivery.
How can postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) be prevented?