Define electronegativity
Hydrogen's valence shell is filled with how many electrons: 8 or 2?
2
What is the formula for calculating formal charge?
FC = valence electrons - bonds - lone pair electrons
CCl4

Ionic compounds contain a _______ and non-metal, where electrons are __________ between atoms.
metal
transferred
Carbon
Which pair, does NOT include an element that is often an exception to the octet rule: P & B, or O & F
O & F
When comparing potential Lewis structures, the more stable structure has atoms with FCs closest to _______ .
Zero
O2

A species with an ODD # of Electrons.
A significant difference in electronegativity between to elements in a bond causes this (also depicted below).
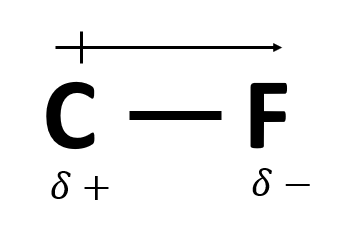
Dipole moment
When counting valence electrons for ClF4+ the positive charge means what; you've lost or gained an electron?
Calculate the highlighted atom's formal charge. 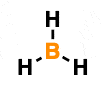
0
SF6

For ionic compounds, what increases with decreasing size of ions?
Lattice Energy
What is the least electronegative element? The most electronegative?
Francium
Fluorine
Which ionic compound will have a higher lattice energy: NaF or CaO?
CaO (greater charge)
Formal charge of highlighted atom 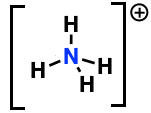
+1
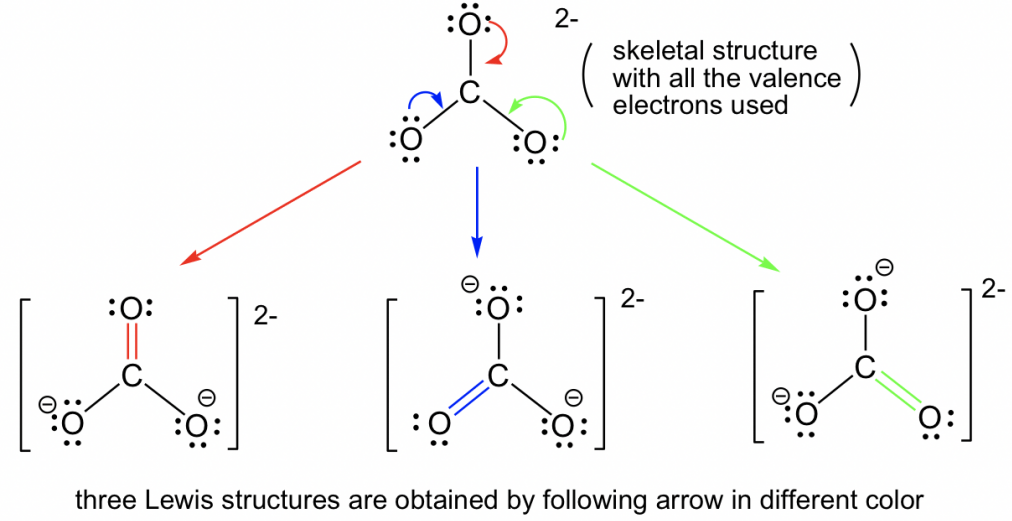
CO32-
Being large enough to have access to the same energy level d orbital allows an element to have this
Expanded Octet
What makes a bond polar covalent. (Rather than pure covalent)
Difference electronegativity of atoms in a molecule.
Which bond is stronger; ionic or covalent?
Ionic
Formal charge of highlighted atom 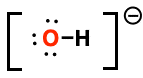
-1
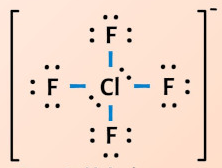
ClF4-
Resonance Structures