What are cells?
A: The Basic unit of life
B: Small things that are not living
A: The Basic unit of life
True or False: There are working structures that help the cell function like an entire organism.
True.
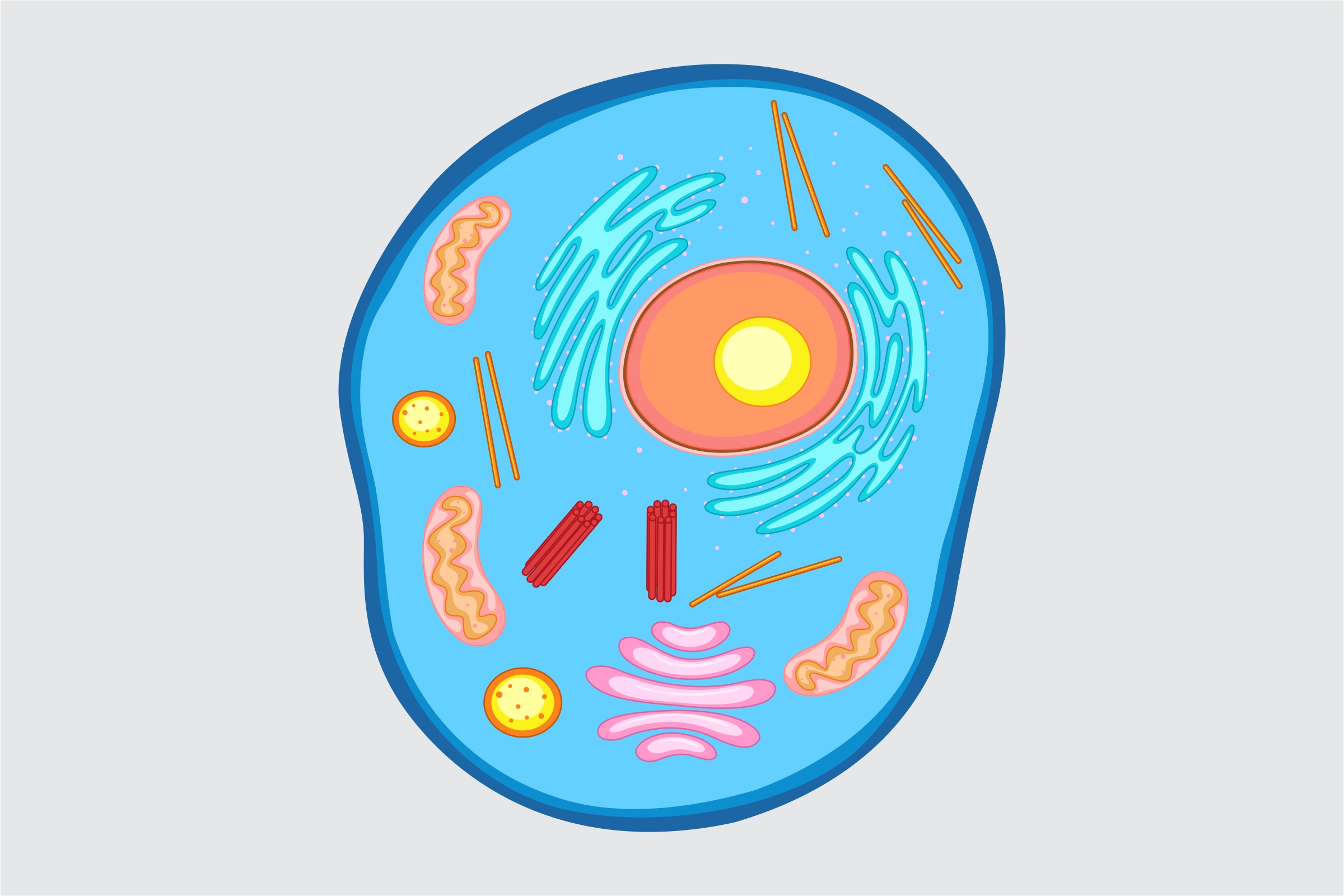

Fill in the blank.
Diffusion is the process in which molecules move from an area of ______ concentration to an area of _____ concentration.
higher, lower.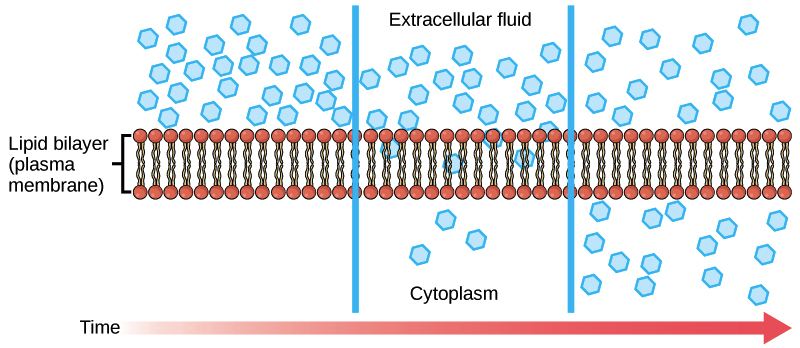
What is the cell cycle?
A: Liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates back to earth in the form of rain and snow.
B: The process a cell goes through each time it divides.
B: The process a cell goes through each time it divides.
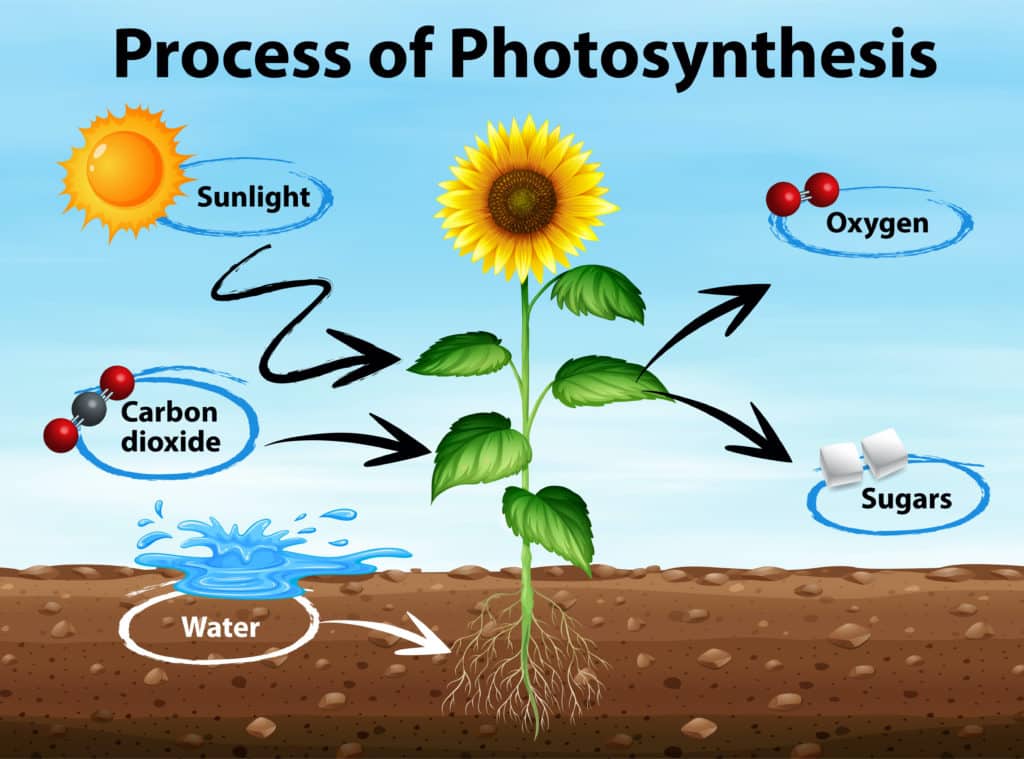
What is photosynthesis?
A: Cells capture energy from the sun and use it to make food.
B: Cell capture water from the ocean and turn that into food.
A: Cells capture energy from the sun and use it to make food.
What is NOT a part of the Cell Theory?
A: All living things are made of cells.
B: Cells are the Basic units of structure and function in living things.
C: All new cells are produced from existing cells.
D: Cells can be seen by the naked eye.
D: Cells can be seen by the naked eye.

What does the nucleus contain?
A: Oxygen
B: Tetrafluoromethane
C: Narotralification
D: Genetic Material (DNA)
D: Genetic Material (DNA)

What does selectively permeable mean?
A: No substances can cross the membrane.
B: Every substance can cross the membrane.
C: Some substances can cross the membrane.
C: Some substances can cross the membrane.

What is the longest phase in the cell cycle?
A: Interphase
B: Cytokinesis
C: Prophase
D: Extrogenostrophase
A: Interphase

What is another word for autotrophs and give an example.
Producers. Grass, trees, plants, ect.
Which are 3 functions of all cells?
1. Obtaining energy.
2. Bringing in water and nutrients.
3. Getting rid of wastes.

Fill in the blank.
The ____ __________ is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds a cell and controls what substances pass into and out of a cell.
Cell membrane.

What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water molecules across selectively permeable membranes.
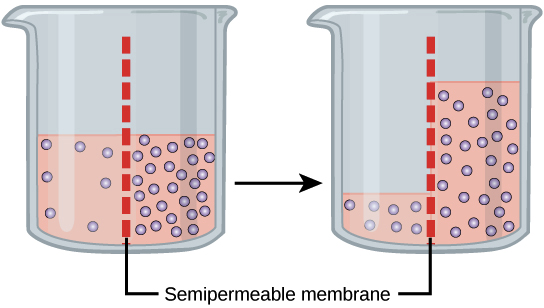
Fill in the blank.
The cell cycle splits into two ______ cells right after Cytokinesis.
daughter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cancer_cell_mitosis-2-af352aead7f549a6a5f2ba8b0e5bd779.jpg)
What is another name for a heterotroph and give an example.
Consumer. Fox, lion, cat, ect.

Who was the first person to observe cells through a microscope?
A: Robert Hooke
B: Anton van Leeuwenhoek
C: Matthias Schleiden
D: Theodor Schwann
B: Anton van Leeuwenhoek

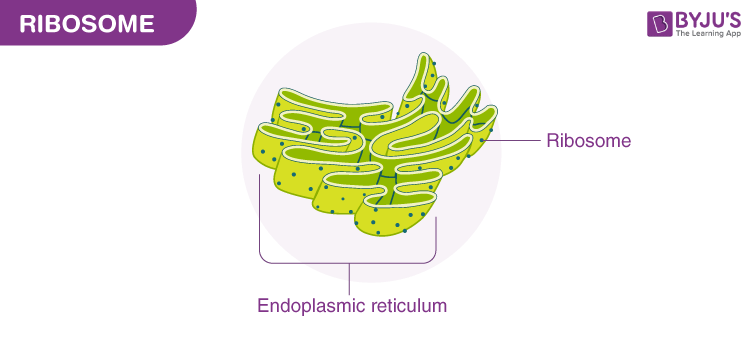
What do Ribosomes produce?
Protein.
Fill in the blank:
In the process called endocytosis, the cell membrane takes______ into the cell by changing shape and engulfing the ______.
particles, particles.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)
Why is it important for cells to go through the cell cycle?
In order for our bodies to grow and develop, they must produce new cells and allow for the death of old cells. Cell division is also an essential component of injury repair. If our cells couldn't divide and create new cells, our bodies could never produce new skin cells to heal road rash, or grow a fingernail back.
What is the correct equation for photosynthesis?
A: Light energy+ 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O
B: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O + Light energy
C: 12CO2 + 2H2O → 06H12O6 + 6O
A: Light energy+ 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O

What is the total magnification of a microscope with eyepiece lens 10x and objective lens 4x?
40x total magnification
What do chloroplasts do?
It captures energy from sunlight and makes it into an energy form that cells can make into food.

What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Endocytosis is cells taking in substances from outside the cell into the cell while exocytosis is where cells shift materials, such as waste products, from inside the cell to the outside.
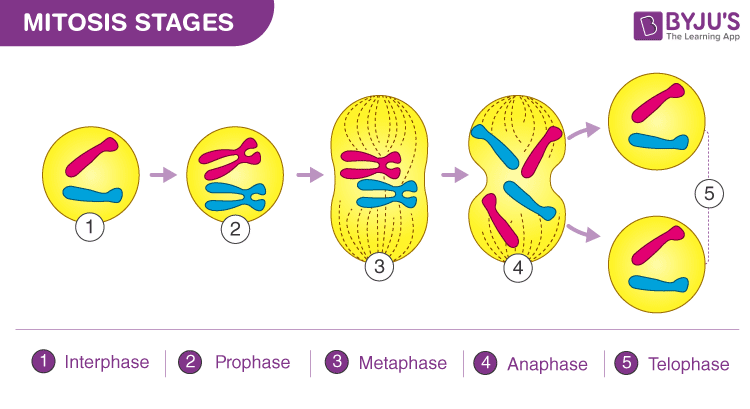
What happens during mitosis?
One cell, the mother, divides to produce two new cells, the daughters, that are genetically identical to itself.
What happens to glucose and oxygen that are produced by plants during photosynthesis?
The oxygen gets released and the glucose is used.