A structure or part of a cell that has a specific role or job.
What is an organelle?
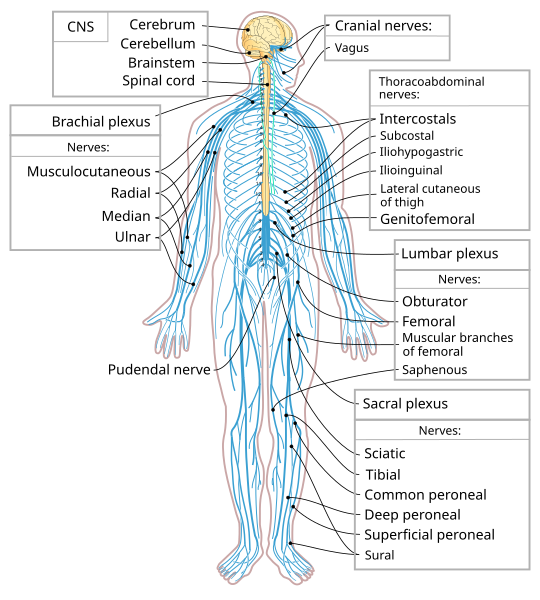
The system communicates information from the body to the brain and from the brain to the body.
What is the nervous system?
A fever of 101 degrees Fahrenheit disrupts the body's ability to digest and synthesize some proteins. Once a pathogen is destroyed body temperature returns to normal. The ability of the body to shift its temperature to restore health is known as
What is dynamic equilibrium/homeostasis?
Enzymes are made of this type of macromolecule.
What are proteins?
The common name for glucose is simple sugar. The scientific name for glucose is more complicated.
What is a monosaccharide?
The organelle that produces sugars from inorganic substances.
What is the chloroplast?
The powerhouse of the cell. makes energy in the form of ATP
What is the mitochondria?
 This body system made of up blood vessels, and the heart, transports vital nutrients throughout the body and collects waste for removal.
This body system made of up blood vessels, and the heart, transports vital nutrients throughout the body and collects waste for removal.
What is the circulatory/cardiovascular system.
The purpose of sweating is a way of maintaining homeostasis. The purpose of sweating does what to the body?
What is cooling down?
Enzymes fit together like these two objects meant to protect personal belongings.
What are lock and key/shape specific?
The building blocks for protein
This simple sugar produced by plants goes by simpler name.
What is glucose?
What is the nucleus?
This body system contains an organ that produces gastric juices (bile) that digest fat. It is the largest organ in the body?
What is the liver?
Blood sugar references the amount of glucose in a person's bloodstream. This hormone helps to regulate the amount of blood sugar in a persons bloodstream is called
What is insulin?
This factor will ruin an enzyme if it gets too hot or too cold.
What is temperature?
The building blocks of lipids are also called...
What are fatty acids/glycerol?
A pigment that reflects the color green.
what is chlorophyll?
This outer covering in animal cells is a barrier only allowing specific substances in or out.
What is the cell membrane?
This body system uses white blood cells and antibodies, to mark and destroy pathogens.
What is the immune system?
Cells cannot do their work without this 3 letter abbreviation for energy.
As long as there is enough ____________ enzymes continue to do their job.
What is substrate?
The building blocks to nucleic acids are called...
What are nucleotides?
This photosynthesis product allows animals to breathe.
What is oxygen?
Membranes with lots of folds. They help modify proteins with the help of ribosomes that are embedded in the membranes.
What is the rough ER?
This system removes waste through from the blood by filtering it though the kidneys. The waste removed is mostly urea and carbon dioxide.
What is the excretory system/urinary system?
This carbon-based waste product is transported by red blood cells to the lungs for excretion.
What is CO2?
It is what we call an enzyme that loses its shape.
What is denatured?
The scientific word that describes any type of building block to a macromolecule is known as a
What is monomer?
This molecule will suffocate animals if they breathe it but plants love this stuff.
What is CO2?