List two processes that increases variation within a population
Mutations, Meiosis (Crossing Over)
Identify the primary mechanism by which evolution occurs
Natural Selection
Define autotroph
An organism that can produce its own food.
True or False
BOTH plants and animals have a mitochondria
TRUE!
What organ helps deliver nutrients and oxygen from mother to fetus?
Placenta
Why do two proteins in the same cell perform different functions?
-Different shape
-Folded differently
-Different sequence of Amino Acids
Both the chicken and the human look very similar during the early stages of embryo development. In terms of evolution, what does this prove?
The chicken and the human have a common ancestor.
Which organism would receive the least amount of transferred solar energy?
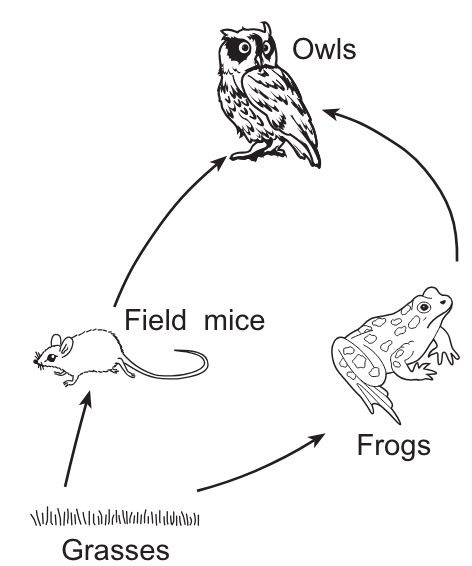
Owls
What term describes the diffusion of water down its concentration gradient?
Osmosis
The ability of the human body to keep blood sugar levels within a fairly narrow range, despite the intake of meals high in carbohydrates, is an example of
What is the name of the process that produces domestic animals and new varieties of plants with traits that are particularly desirable?
Selective breeding
List the 4 principles of natural selection
variation, competition, adaptation and overproduction of offspring
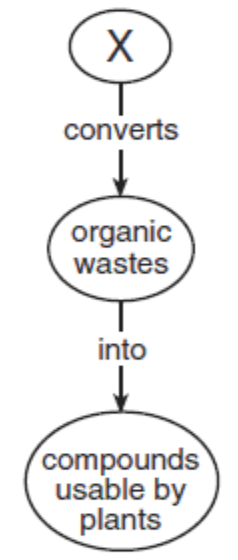
Decomposers
This organelle is only found in producers and allows producers to convert light energy into chemical energy.
Chloroplast
The substance labeled "catalyst" is also known as
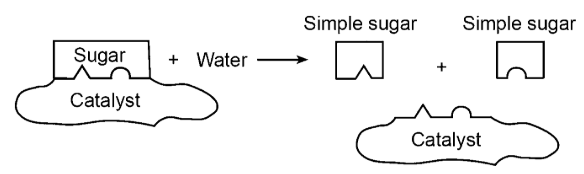
An enzyme
What is used to cut DNA at specific points into fragments
restriction enzymes
Name the 4 types of evidence that support the theory of evolution
Molecular similarities, comparative embryology, fossil records, homologous structures
Define and give an example of both abiotic and biotic factors
Abiotic: Non-living components of the environment (ex: rocks, water)
Biotic: Living components of the environment (Plants and animals)
Draw the relationship between cells, tissues, and organs in a complex multicellular organism
Cells -> Tissues -> Organs
Name all four macromolecules.
Proteins, nucleic acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids
Process in which you take genes from other organisms and insert them into the DNA of a bacterium
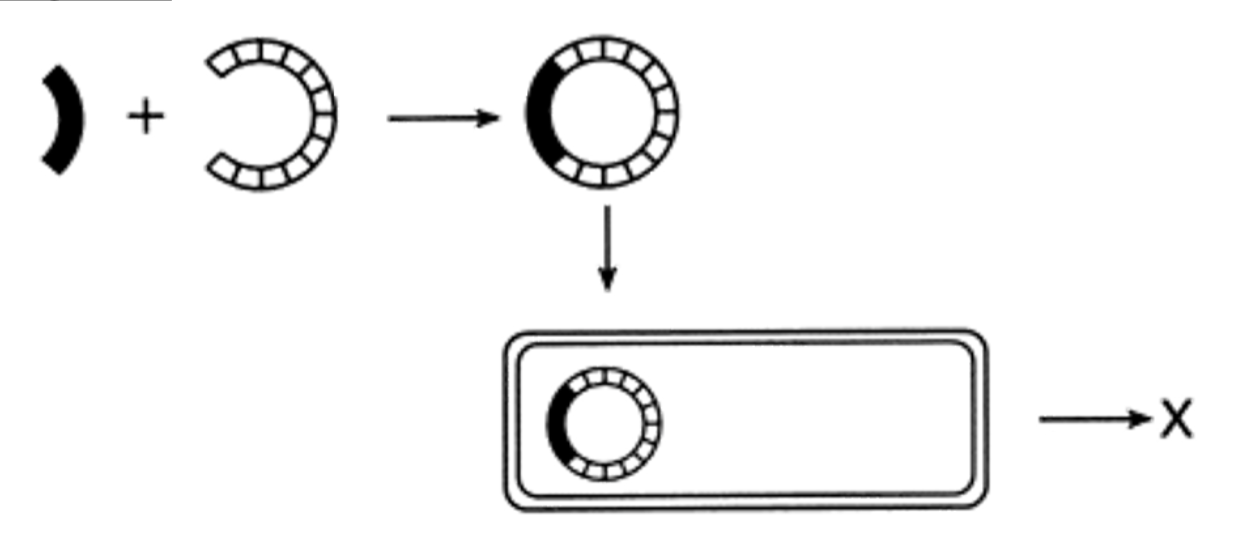
Genetic Engineering
Product: Recombinant DNA
How do bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
-Genetic mutations
-Transfer of resistant genes
-Misuse/Overuse of antibiotics
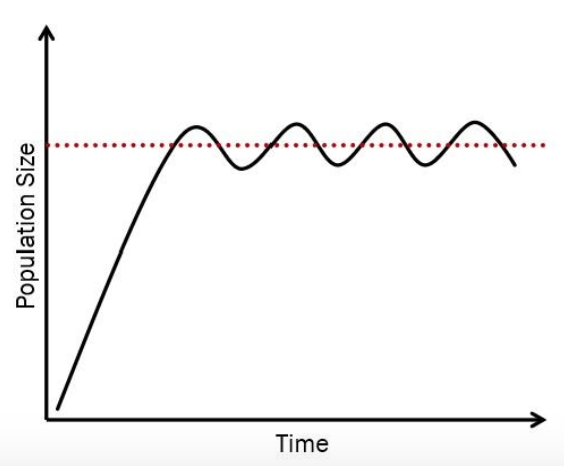
Draw a graph that shows carrying capacity in a population where there are limiting factors that maintain the stability of the ecosystem
Which process is shown below?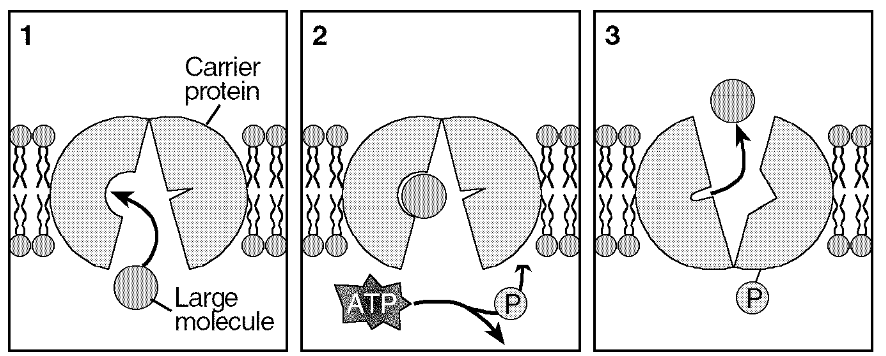
Active Transport
The cell labeled X is most likely what type of Leukocyte
What are Macrophages/phagocytes