Building block of Starch
What is a simple sugar or glucose?
Site of cellular respiration
What is mitochondria?
Three differences between RNA and DNA
What are
1. DNA is a double helix, RNA is single stranded
2. DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil
3. DNA cannot leave the nucleus and RNA can
All of the robins in the courtyard
What is a population?
What was the main objective of the Clothespin Lab?
The main goal was to show how traits that help survival can become more common in a population over time.
What did Darwin observe about the finches on the Galápagos Islands?
Darwin noticed that finches on different islands had different types of beaks, each suited to the food available on that island.
Building block of lipids
What is three fatty acids and a glycerol?
Three things a plant cell has that an animal cell does not
What are cell wall, one large vacuole, chloroplasts
Describe transcription and translation
What are
Transcription: copying the DNA into mRNA so it can go to the ribosome for protein synthesis
Translation: the ribosome reads the mRNA one codon at a time and the tRNA brings in the correct anticodon with the amino acid attached
The processes in the carbon cycle
What are photosynthesis and respiration?
Describe how the lab demonstrates the concept of natural selection.
The lab shows that the "fittest" survive and get passed on, just like animals with traits that help them survive in nature.
How do beak shapes relate to the diet of finches?
The shape of a finch’s beak helps it eat certain types of food. For example, big beaks help crack seeds, and small beaks help catch insects.
Name the parts of the nucleotide below.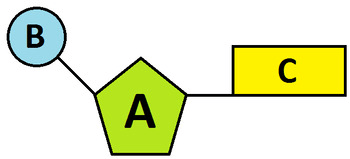
What is
A: 5 carbon sugar
B: phosphate group
C: Nitrogenous base
Reactants of photosynthesis
What are water and carbon dioxide?
The relationship between a honeybee and a flower
What is mutualism?
What variables did you control during the experiment?
We controlled things like how fast we picked up the clothespins and the distance, to make sure the results were fair.
What is the significance of the finches in the study of evolution?
The finches helped Darwin understand how species change over time, based on what traits help them survive in their environment.
Describe what happened in the image below
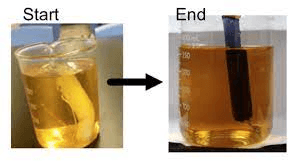
What is starch indicator moved into the cell causing the inside to turn black?
Describe one benefit of the process below and one drawback

What are
Benefit: all animals have the desired trait
Drawback: if one organism is susceptible to a disease, they all will be or you cannot mate the flock because they are all the same gender
Three causes of global warming
What are
1. Burning fossil fuels
2. Cow flatulence
3. Deforestation
How did the results support or challenge your hypothesis?
The results showed that the easiest-to-grab clothespins were picked more, supporting the idea that traits that make survival easier are more likely to be passed on.
Describe how environmental changes can affect finch populations.
Changes in the environment, like a drought, can change what food is available, so finches with beaks that can eat the available food are more likely to survive and have babies.
An enzyme only works on one substrate
What is "Lock and Key"?
Explain what happened to the cell below
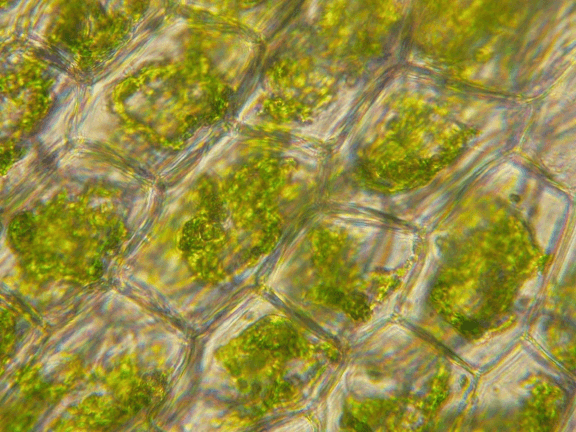

A saline solution was added which caused water to leave the cell so the cell membrane shrunk
The process used to diagnose chromosomal mutations during pregnancy
What are amniocentesis and karyotyping?
Which organism would be affected the most if toxins were released into the water supply and why?
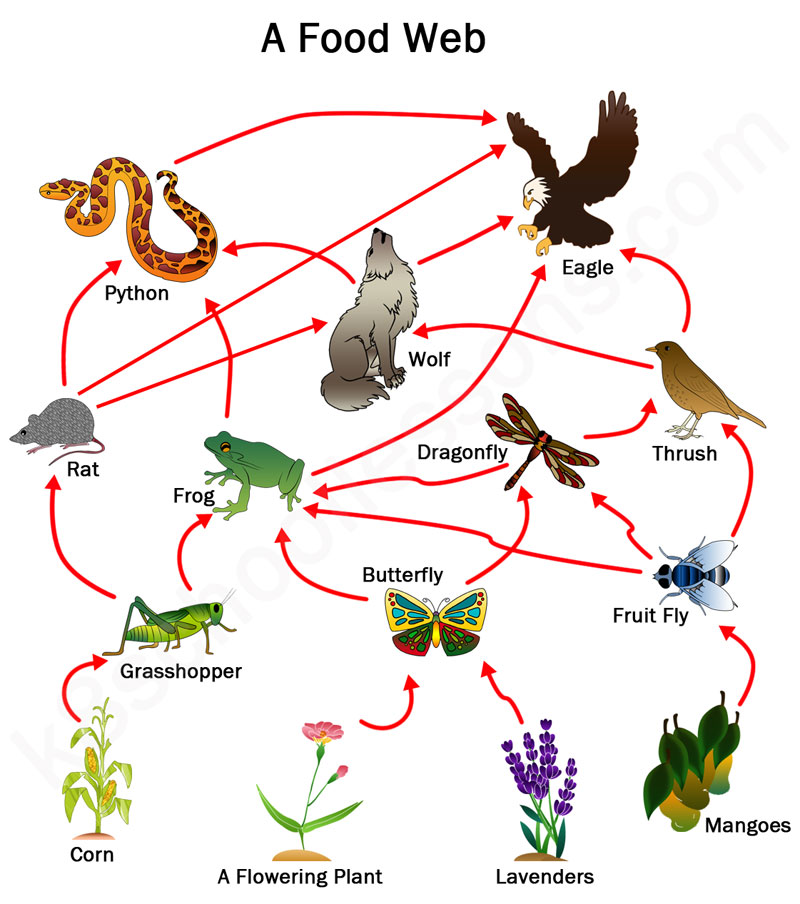
What is the eagle?
Top level consumers need to eat more to fulfill their energy needs so toxins build up in the bodies.
Discuss how this lab relates to real-world evolutionary concepts.
This lab relates to how animals with helpful traits survive better and have more babies, passing on those traits to the next generation, just like natural selection in the wild.
Explain how the beaks of finches provide evidence for natural selection.
Finches with the best beaks for their environment are more likely to survive and pass on those traits to their babies, showing how natural selection works.