What are the three parts of the cell theory?
1. All Cells come from other cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All living things are made of cells
Put the following terms in order from simplest to most complex:
Cell, Organelle, Organism, Tissue, Organ System, Organ
Organelle, Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism
What is the function of the chloroplast?
photosynthesis
The improvement in what type of technology led us to our understanding of the cell theory?
microscope technology
Which of the following explains why starch is not permeable to the cell membrane?
A. It is too large and complex.
B. It is negatively charged.
C. It is a waste product.
D. The concentration is always lower outside the cell.
A. It is too large and complex.
Explanation: A cell membrane is selectively permeable, meaning only small molecules can pass through. Starch is a large, complex molecule that cannot fit through the membrane's pores.
What is the function of the nucleus?
Store and regulate DNA
What is the function of the cell wall?
The primary function of a cell wall is to provide structural support, shape, and protection to the cell, acting as a rigid barrier that surrounds the cell membrane and helps the cell withstand mechanical stress and maintain its form; it's particularly important in plants, fungi, and most prokaryotes where it allows them to stand upright against gravity.
What types of cells in the human body would have a lot of Lysosome
white blood cells
What is the function of the cell membrane?
to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products.
Homeostasis in unicellular organisms depends on the proper functioning of
A. organelles
B. insulin
C. guard cells
D. antibodies
A. Organelles
Explanation: Since unicellular organisms only have one cell, their internal environment is maintained by the proper functioning of their organelles, which are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions.
What is the function of the Mitochondria?
Powerhouse of the Cell, ATP, Produces Energy
What is the function of the Golgi Body?
The Golgi body, also called the Golgi apparatus, functions as the cell's packaging center, receiving proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, further processing and modifying them, and then sorting and packaging them into vesicles to be transported to their final destinations within the cell or secreted outside the cell
What types of cells in the human body would have a lot of the Mitochondria
muscle cells, particularly heart muscle cells, liver cells, and nerve cells
What is the function of the Centriole
organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system
Damage to which structure will most directly disrupt water balance within a single-celled organism?
A. ribosome
B. cell membrane
C. nucleus
D. chloroplast
B. Cell Membrane
Explanation: The cell membrane acts as a barrier, controlling the movement of substances, including water, in and out of the cell through osmosis. Damage to the cell membrane would disrupt this regulation, leading to imbalances in water content within the organism.
Label the parts of the Animal cell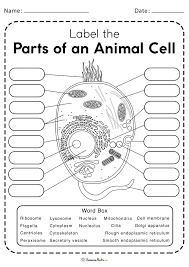
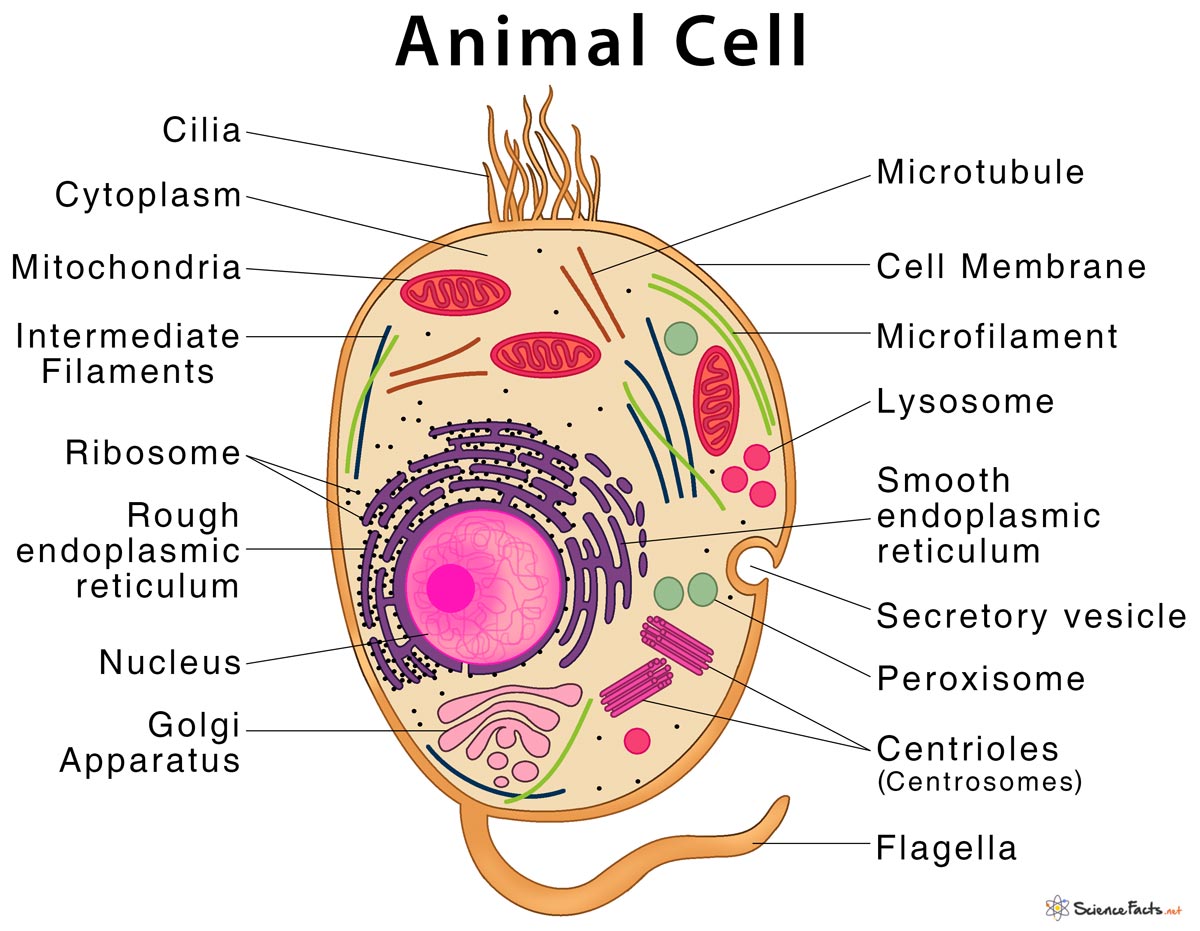
What is the function of cytoplasm?
to act as the gel-like fluid inside a cell, providing a medium for various cellular processes to occur, including storing necessary molecules, supporting organelles, maintaining cell shape, and facilitating the movement of materials within the cell.
what is in the plant cell that is not in the animal cell?
A plant cell contains a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, which are not present in an animal cell; these structures provide structural support and enable photosynthesis in plants, functions not needed by animal cells.
If you looked at a cell in focus under high power of the microscope, but still could not see very many details, list 2 things you could try to improve the image.
adjusting the condenser lens to optimize light intensity and staining the specimen with a suitable dye to enhance contrast
What is common to all cells?
B. All cells are photosynthetic.
C. All cells divide to form new cells.
D. All cells have a nucleus
The correct answer is C. All cells divide to form new cells.
Explanation: While not all cells have a cell wall (only plant cells do), nor are all cells photosynthetic, all cells share the ability to divide and create new cells; this is a fundamental characteristic of life.
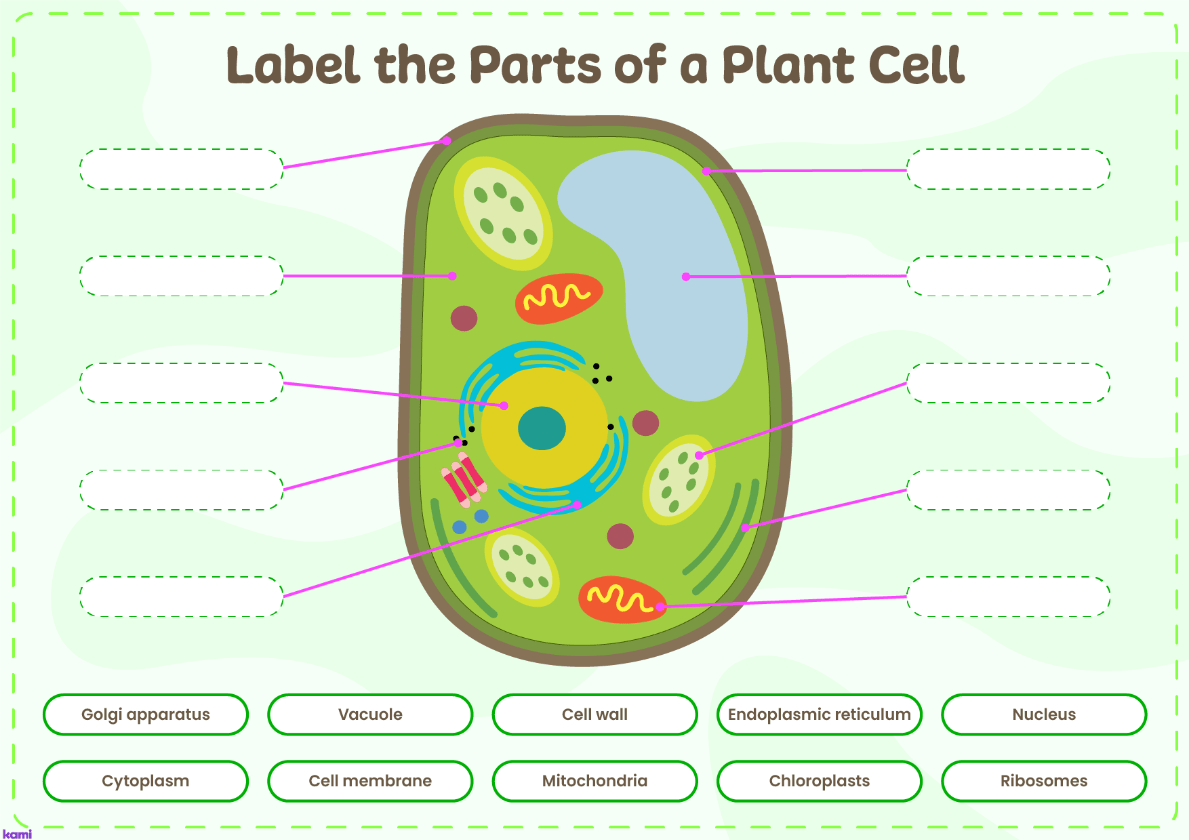
Label the parts of the Plant Cell

In multicellular organisms (like humans), we use organs and organ systems to carry out our life functions. Single celled organisms do not have organs and systems - what do they use instead?
Single-celled organisms use their individual cell organelles to carry out all life functions, as they only have one cell to perform all necessary tasks, unlike multicellular organisms which rely on specialized organs and systems made up of many cells.
Name the 5 ways that a plant cell and an animal cell are different and explain why.
A plant cell differs from an animal cell in the following ways:
What is the function of the vacuole
to store various substances within a cell, including water, waste products, nutrients, and pigments, while also helping maintain the cell's internal pressure and pH level
The organic compounds that scientist use to cut, copy, and move segments of DNA.
A. carbohydrates
B. enzymes
C. hormones
D. starches
The organic compounds scientists use to cut, copy, and move segments of DNA are enzymes.
Explanation: Enzymes like restriction enzymes are specifically designed to cut DNA at specific sequences, while other enzymes like DNA ligase can join DNA fragments together.