Parent education on conjunctivitis
take eye drops as prescribed
WARM wash cloths
clean everything
Why are cardiac defects not prevent in the unborn child?
Mom provided oxygenated blood for the baby
home care for strains and sprains
R est
I ce
C ompression
E levation
stridor is an indicator of what?
upper air way obstruction
could be epiglottitis, croup (barking cough), foreign body aspiration
How do you assess a post op tonsillectomy bleeding?
continuous swallowing

What is reyes syndrome?
liver and brain swelling due to aspirin or salicylate given during a viral infection
indicators infant needs a cardiac work up?
poor feeding
poor weight gain
cyanosis with crying
assessment for child abuse
T runk
E yes/ears
N eck
4 years and younger
bruising in various stages of healing or on 3 planes of the body
What does the pulmonary function test tell us?
lung volume
used with CF patients
most accurate for asthma diagnosis
Order: 1 mg valium for a child who is having an active seizure. The child weighs 99 pounds. The valium vial reads 4 mg/ml. How many milliliters would the nurse administer?
0.25 ml
what kind of isolation is used for RSV
contact/droplet
what is the best thing about babies?
Making them
What complication would your worry about with a injury to the epiphysis?
Growth impairment
diet for a cystic fibrosis patient
high fat, high calorie

what is this?
Retinoblastoma - tumor in the eye
what kind of medications would you give for this 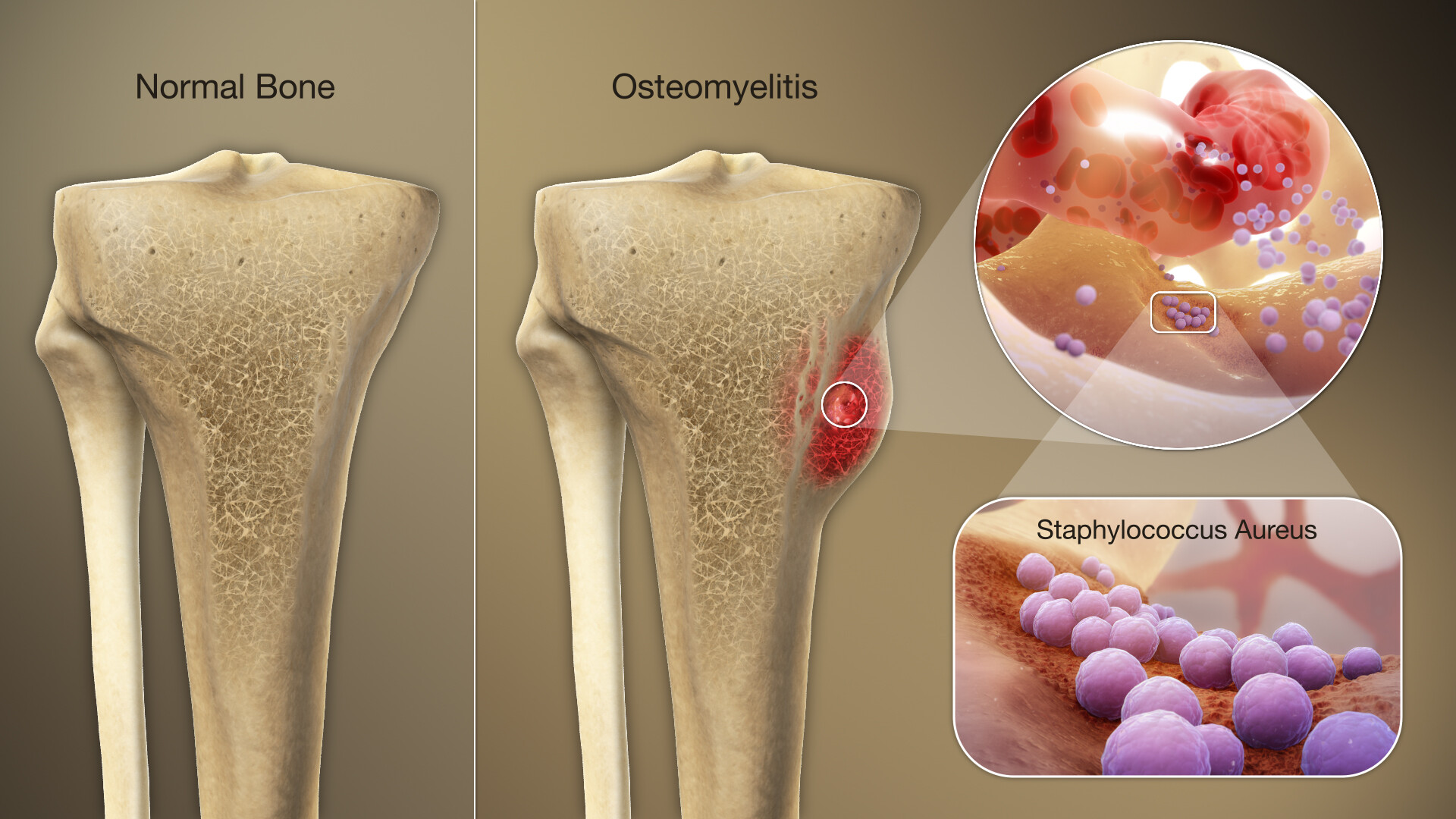
ABX
S/S of kawasaki disease?
high fever more than 5 days
strawberry tongue
peeling hands and feet
reddened eyes
cardiac involvement
s/s of cerebral palsy
mixed disorder!
includes musculoskeletal/mobility
seizures
feeding problems
delayed learning and physical milestones
What medication do you expect a status asthmaticus patient to be on?
albuterol / aminophylline
epinephrine
probably steroids also
what is most concerning with a head injury?
A. Bulging fontanels
B. Vomiting
C. Hypotension
D. Protruding tongue
A!
would be the first sign of increased intercranial pressure
s/s of meningitis
positive kernig and brudzinki
nuchal rigidity
Bulging fontanels
fever
Petechiae
how do you acquire heart disease?
happens after birth
drugs
sepsis
anemia - NO HIGH ALTITUDES
hypertension
nursing considerations for a patient in traction
weights should hang freely
no firm pressure on pressure points
skin should be well perfused
s/s of cystic fibrosis
steatorrhea
salty sweat
thick airway secretions
thick GI secretions
poor weight gain
Care for a patient post febrile seizure
tired/sleepy is normal in that post ictal phase
remember febrile seizure does not mean epilepsy