What ligament connects the laminae of adjacent vertebrae?
Ligamentum Flavum
If the inferior facet joints slide upward what motion will the lumbar spine be going in?
Flexion
Which of the following muscles is a primary flexor of the lumbar spine?
Rectus Abdominus
According to Skurkitt, what are the mechanical loading strategies?
Includes repeated movements and sustained postures
What nerve is innervating the iliacus?
Femoral Nerve (L2-3)
What is the job of the Interspinous ligament?
Helps connect the spinous processes of the adjacent vertebrae.
Describe what joint movement is occurring in the red arrow vs. the blue.
Red = Extension of the lumbar spine.
Blue = Flexion of the lumbar spine.
Name that muscle!
Multifidus
According to Werneke, how is the classification in MDT different than TBC?
MDT- classified into mechanical syndromes
TBC- classified on severity
Explain the centralization phenomenon.
Centralization is characterized by referred spinal symptoms that migrate in a distal-to-proximal direction.
1. Ventral band
2. Dorsal band
3. Sacral band
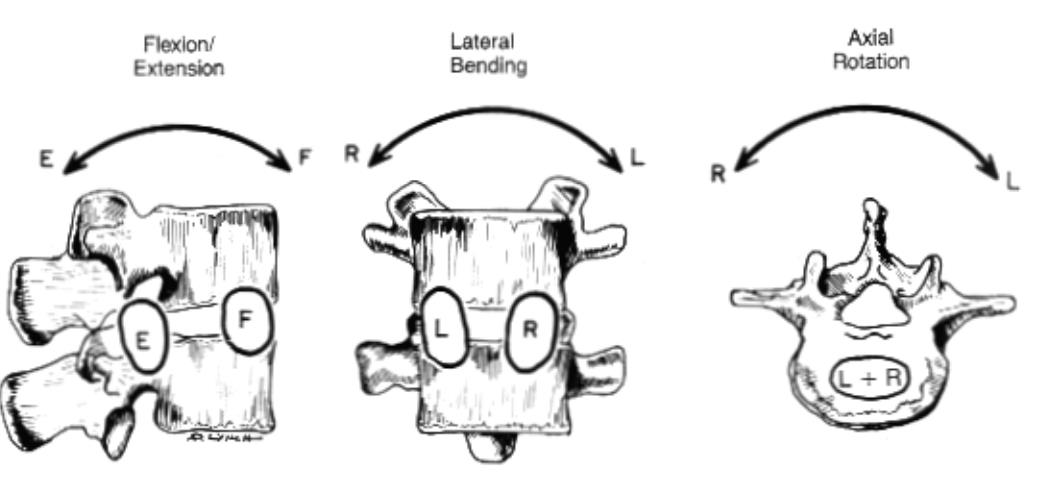
Describe coupled motion in terms of the lumbar spine.
Coupled motions are motions that are constrained to move together
What is the main function of the quadratus lumborum?
Pelvic hiking and side bending to the side.
According to Koh, what is more effective for initiating the abdominal muscles, and what was their reasoning behind it?
Bracing exercises is more effective than hollow exercises. Bracing exercises, can contract both deep and superficial muscles entirely, rather than performing hollowing exercises, which only contract deep muscles independently, is more effective for activating the abdominal muscles.
What innervates the zygoapophyseal joint?
Innervated by medial branch of dorsal rami ... "Spies"

Name that Ligament!
Iliolumbar ligament
Describe the motion that is going on with rotation at the lumbar spine.
Ipsilateral facets slide downward, contralateral facets slide upward
What is the insertion and origin point of the Iliopsoas?
Iliacus:
I: iliac fossa and the inner lip of the iliac crest, sacro-iliac and iliolumbar ligaments
O: Tendon of psoas major
Psoas Major:
I: Slips arise from T12 to L5, bodies of L1 to L4, and transverse processes of L1 to L5.
O: Apex and the lesser
error free
transfer of skills
lots of variability
slow improvements
intro to dual tasks
What is the difference between radiating and referred pain?
Radiating pain typically stems from back pain with nerve irritation that causes pain down the leg, or neck pain with nerve pain into the arms and hands.
Referred pain is more general and can occur in many places around an injured tissue.
What ligament connects the tips of adjacent spinous processes and is well developed in the upper lumbar region and may terminate at L3?
Supraspinous Ligament
Describe Fryette's 3 law's of motion.
1. Neutral mechanics: Lateral flexion and rotation are coupled to opposite sides
2. Non-Neutral mechanics: Lateral flexion and rotation are coupled to same sides
3. Introducing motion to a vertebral joint in one plane automatically reduces its mobility in the other two planes.
Name all the inner and outer muscle units.
Inner: Pelvic floor, TA, diaphragm, multifidus
Outer: spinal extensors, spinal flexors, lateral flexors, and rotators
According to the article written by Chimenti describe what the mechanism-based approach is.
The mechanism-based approach provides an additional conceptual framework for physical therapists to make educated treatment decisions that incorporate known basic science and clinical evidence with individualized assessments to optimize patient care and clinical effectiveness.
The ventral rami nerve innervates what lumbar musculature?
Psoas major
QL
TA
Obliques
RA