1 mm/hour.
Tissue thickness should be measured in all directions (width, length, height) to ensure the specimen is well fixed.
What is the rate of penetration for formalin?
Stops the autolysis process and maintains the tissue architecture for downstream testing.
What is fixation?
Instrument used to section paraffin-embedded tissue cassettes?
Routine tissue sections are cut at 3-5 microns.
What is a microtome?
The nuclear stain for routine pathology tissue slides.
Made from the bark of a South American tree.
What is hematoxylin?
This special stain requires a specialty deparaffinization procedure consisting of peanut oil and xylene.
What is AFB Fite?
The AFB Fite stain is used to visualize acid-fast bacteria, such as Mycobacterium leprae. If water is introduced too early in the staining process it can cause the loss/damage of the lipids present within the cell walls of these acid-fast organisms. The xylene-peanut oil solution effectively removes paraffin from the slide without damaging these important components.
This substance is commonly used in IHC to produce a visible color change when the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody reacts with the substrate, with examples including DAB (3,3'-diaminobenzidine) and AEC (aminoethylcarbazole).
What is a chromogen?
U.S. federal agency under the department of labor that aims to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for workers
Who is OSHA?
OSHA is responsible for setting and enforcing workplace safety standards, providing training and outreach, and investigating workplace accidents to prevent future incidents.
While staining a rack of sections, it is noted that the water following the rehydrating alcohols turns very cloudy. This can most likely be corrected by:
What is changing the alcohols?
If the water following rehydrating alcohols turns milky, it indicates that xylene is carried over into the water; the alcohols should be changed to correct this.
5 mm
Most surgical protocols are written to this standard. Deviating from it can result in over/under tissue processing.
What is the ideal thickness for tissue sections?
Xylene, Xylene substitutes, and isopropanol are all reagents used for the _______ step of tissue processing.
What is clearing?
Tissue clearing is performed after dehydration. Clearing removes lipids and prepares the tissue for paraffin infiltration.
Wiping forceps between specimens during embedding prevents this.
What is cross-contamination of specimens?
Stain for connective tissue and cytoplasm for routine pathology slide staining. This stain should have 3 shades of pink when performed correctly.
What is eosin?
This property of the Congo Red stain solution can result in nonspecific binding and reduced clarity of amyloid detection if not maintained at an alkaline level.
What is pH?
Congo Red is a pH-sensitive stain. At the wrong pH this stain can bind nonspecifically to other tissue components.
This antigen retrieval method, commonly used in IHC, involves heating formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections in a citrate buffer at a pH of 6.0, and is crucial for unmasking epitopes that are otherwise cross-linked by formalin.
What is HIER? Heat-induced epitope retrieval.
Some other types of epitope retrieval include: Enzyme-induced epitope retrieval, Microwave-induced epitope retrieval, pH-based retrieval, or the "cocktail method" involving a combination of techniques!
Diluting acids is a crucial step when decalcifying. When diluting, one must add _______ to _________.
What is acid to water?
Adding water to acid can cause a violent reaction due to the rapid heat released when the two mix. This heat can cause the solution to boil, spatter and possible explode, leading to burns or other injuries
This is caused by delayed fixation. H&E-stained sections may show a loss of total disappearance of nuclear chromatin.
What is autolysis?
Placing specimens in a fixative solution as soon as possible at the recommended ratio.
Reagent used to set ink when visualizing margins.
What is acetic acid?
Remove unbound water from the specimens during tissue processing.
Proper dehydration removes only the unbound water from samples.
What is the goal of dehydration during tissue processing?
Method of embedding that ensures all layers of the specimen are seen.
Avoid tangential sectioning by using good technique.
What is on edge embedding?
Converts the red-stained nuclei (after hematoxylin staining) to a blue color.
What is ammonia water, Scott's Tap Water, and Bluing?
When used at pH 2.5, Alcian Blue stains both sulfated and carboxylated acid mucins. When used at this pH, it stains only sulfated mucins.
What is pH 1.0?
This type of antibody, used in IHC, is derived from a single B cell clone, resulting in a homogeneous antibody that targets a single epitope on the antigen.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are key in IHC for their specificity and ability to target single epitopes.
An explosive compound that should not be stored in a laboratory
What is Picric acid?
Anhydrous picric acid is very explosive and should always contain at least 10% moisture.
During processing, this can develop when moving from the fixation phase directly into a grade of alcohol higher than 70%.
What are formalin salts?
Formalin salts can cause clogs in automated processors which can create problems within the instrument. The best way to combat this is to go from formalin into alcohol with a concentration of 70% or lower to prevent salt formation.
This latin term is used in the gross description to describe a specimen being submitted without any sectioning. Specimens submitted in the cassette exactly as they were received. Examples: Vas Deferens that is not sectioned, skin biopsies, GI biopsies, prostate biopsies.
What is En Toto?
_______ occurs when the bound water in a tissue sample is removed.
When bound water is removed, there is loss of nuclear and cytoplasmic detail, the architectural integrity of the sample is not maintained, and there can be downstream testing implications.
What is overdehydration?
Additive for paraffin that increases hardness.
What are polymers?
The more polymers=harder paraffin=thinner sections...however, more polymers also requires more infiltration time due to the size of the polymer molecules. These polymers can also impact IHC creating background staining and sometimes resulting in tissue not adhering to the slide properly.
A black pigment present on the H&E stained slides caused by fixation in acidic formalin.
What is Formalin Pigment?
Faint or absent staining of fungal elements on a GMS-stained slide may result from skipping or underperforming this critical oxidation step.
What is chromic acid?
*Also acceptable: What is periodic acid?
GMS relies on oxidation to convert fungal polysaccharides to aldehydes, which then bind silver.
This type of antibody, often used in IHC, is more likely to cause increased background staining due to its recognition of multiple epitopes, leading to non-specific binding and higher background compared to monoclonal antibodies.
What is a polyclonal antibody?
Under what OSHA standard does Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B (HBV) fall under?
What is Bloodborne Pathogen Standard?
HIV and HBV are bloodborne pathogens and therefore fall under OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. This standard is intended for the protection of all workers who might come into contact with potentially infectious material, especially specimens from patients who are HIV-positive or who have been infected with the hepatitis B virus.
A blue-black precipitate seen on an H&E-stained sections can be prevented by:
What is filtering the hematoxylin?
On standing most hematoxylin solutions will develop a metallic sheen of oxidized dye, actually aluminum-hematein; this may cause a precipitate on stained sections if solution is not filtered.
Name the fixative; 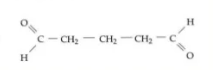
What is Gluteraldehyde?
It is most frequently used for the fixation of specimens for electron microscopy because it preserves ultrastructure the best of any aldehydes. It tends to overharden tissue so fixation should not be prolonged.
Vacuum: speeds up paraffin infiltration by forcing paraffin into tissue gently; vacuum can also enhance dehydration if no heat is used during the step.
Heat: Heat reduces the time needed for processing when applied to any of the steps: fixation, dehydration, clearing, and infiltration. Heating must be gentle to avoid damaging epitopes.
Reagent Agitation: Agitation speeds up any step when applied
What are mechanical methods used in tissue processing to accelerate processing?
This image identifies these parts of the blade and blade holder.
What is bevel angle, wedge, and clearance?
Artifact on this slide demonstrates this...
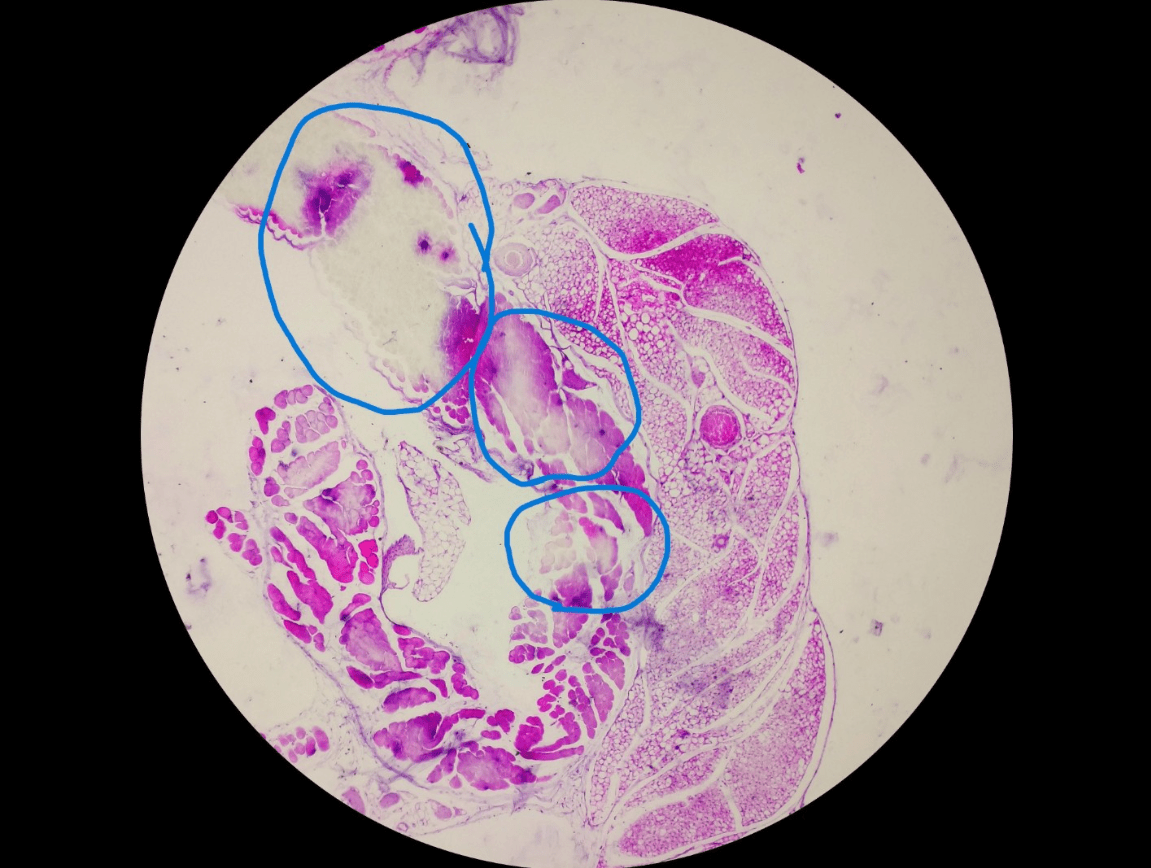
What is incomplete deparaffinization?
This stain, relying on ammoniacal silver nitrate and formalin as a reducing agent, selectively highlights intraneuronal fibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques by binding abnormally aggregated tau proteins and beta-amyloid.
What is a Bielschowsky stain?
Strong background staining despite using a well-optimized antibody. This issue is most commonly caused by endogenous activity, especially in tissues like liver and kidney, where these enzymes are abundant.
What is endogenous peroxidase activity?
Endogenous peroxidase activity can cause non-specific staining. The use of peroxidase blockers can reduce this background. Other factors such as over-fixation, antibody optimization, and protocol timing can all impact this activity.
0.75 ppm. You also have to review the 15 min weighted average. The 15-minute PEL is 2.0 ppm.
What is the OSHA permissible limit for formalin exposure in an 8-hour period?
This type of artifact appears as parallel lines or grooves across tissue sections and is most commonly caused by a nick or debris on this part of the microtome.
What is a damaged or dirty microtome blade?