The appendix works closely with Payer's Patches and is located here.
What is in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen?
Receiving a vaccination is an example of this type of immunity.
What is acquired specific immunity?
This is an example of an external barrier involved in immunity defense.
What is a mucous membrane?
These lymphatic organs are located just under the jaw bone on either side of the neck.
What are tonsils?
This substance is what triggers an immune response.
What is an antigen?
These, along with the appendix, filter bacteria from food.
What are Payer's Patches?
This type of immunity occurs when an infant receives antibodies from its mother via breastfeeding.
What is passive natural immunity?
This type of molecule activates the B-cell in order to begin an immune response.
What is an antigen?
This is found in lymph organs but not lymph nodules.
What are capsules?
This type of fluid is found between cells.
What is interstitial fluid?
This prevents backwards flow of fluid in the lymph vessels.
What are valves?
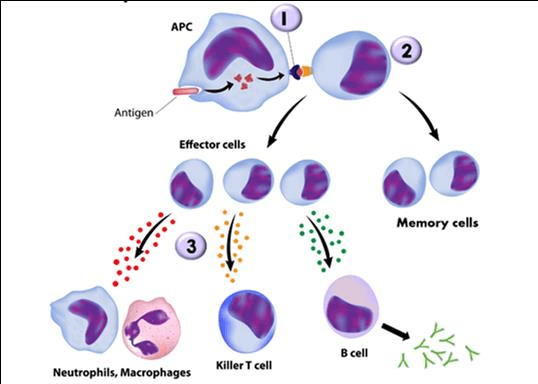
This image shows what type of immunity?
What is cell-mediated immunity?
Enzyme secretion is a form of pathogen elimination that occurs primarily in this area of the body.
What is the gastrointestinal tract?
This lymph organ is located under the sternum.
What is the thymus?
These molecules are responsible for causing a fever during an immune response.
What are pyrogens?
This lymph organ is responsible for filtering lymph.
What are lymph nodes?
Lymphocytes are responsible for this type of immunity.
What is the acquired/ specific immune response?
These chemical signals activate other cells during an immune response.
What are cytokines?
This is where B-cells mature.
What is bone marrow?
These are considered a lymph nodule rather than an organ of the lymphatic system.
What are tonsils?
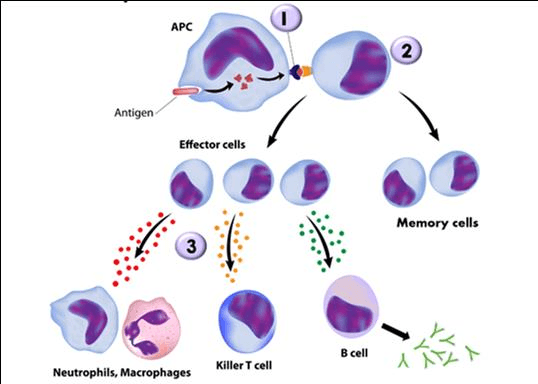
This receptor at location 1, presents antigen fragments.
What is MHC-II?
The final step of humoral immunity produces this Y-shaped structure that will aid in the elimination of foreign antigens.
What is an antibody?
These cells CANNOT display antigens to another cell.
What are cytotoxic T-cells?
This is where T-Cells mature.
What is the thymus?
This duct does NOT return lymph to the cardiovascular system.
What is the left lymphatic duct?