(in case of a tie)
This substance, which dilates afferent arterioles, is secreted in a person with volume overload
What is Atrial Natriuretric Peptide (ANP)?
This EKG change is characteristic for severe hypokalemia
What are U-waves?
Both high and low levels of this electrolyte can cause hypoparathyroidism
What is Magnesium?
This marker of kidney function is least influenced by muscle mass
What is cystatin C?
This glomerulonephritis is associated with mesangial hypercellularity and matrix expansion due to immune complex deposition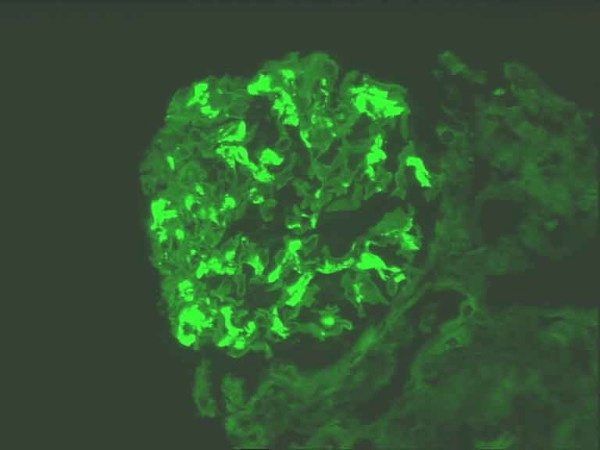
What is IgA nephropathy?
These diuretics have a known side effect of ototoxicity
What are loop diuretics?
A person with increased ADH, urine osmolarity of 80 mOsm/L and plama osmolarity of 310 mOsm/L has this disorder
What is Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus?
This diuretic is more likely to cause hyponatremia than hypernatremia
Thiazide diuretics
Elevated serum PTH level will have this effect on 1,25-hydroxylase activity
What is stimulation?
This class of antihypertensive agents is associated with hypokalemia and hypocalciuria
What are thiazide diuretics?
The pattern of glomerular injury on this picture is commonly associated with this viral infection
What is Hepatitis C?
pH of the depicted urine sample will be in this range

What is urine pH 7-9 (will accept very alkaline)
The nephron segment that reabsorbs Na+ through Na+ channels and reabsorbs urea by facilitated diffusion
What is Inner medullary collecting duct?
This condition will not show any change in urine osmolarity with water deprivation
What is Diabetes Insipidus?
This glomerular injury pattern is typical for both Diabetic Nephropathy and Renal Amyloidosis
What is Nodular Glomerulosclerosis?
This stage of HTN is defined as BP > 140/90 mm Hg
What is Stage 2 HTN?
This type of vasculitis is not associated with immune complex presence in the glomeruli
What is ANCA-associated vasculitis (Pauci-Immune GN)?
A urinalysis that is positive for blood yet shows no RBCs on microscopy is suggestive of this condition
What is rhabdomyolysis?
A person with chronic respiratory acidosis and a serum HCO3- of 24 mEq/L also has this acid-base disorder
What is Metabolic Acidosis?
This is the mechanism of hyperosmolar hyponatremia, like in hyperglycemic state
What is transcellular shift?
This cystic kidney disease occurs when ureteric bud never comes in contact with metanephric blastema during embryonic development
What is Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney?
This percentage is an appropriate level of BP reduction in the first hour of HTN emergency
What is 10-20%?
This characteristic of SUB-EPITHELIAL deposits will help you distinguish between membranous nephropathy and infection-associated GN?
What is the size of deposits compared to the thickness of the GBM?
Most common antibodies found in primary Membranous Nephropathy
What is PLA2R antibodies?
A person with hypercalcemia and a lumen-positive potential difference in thick ascending limb must have a defect in this receptor
What is calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR)?
This acid-base disorder should be considered in a patient with Sjogren's syndrome, a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and urine pH of 6
What is Type I RTA (Distal RTA)?
This condition should be considered in a patient with sickle cell trait presenting with fever, flank pain, acute kidney injury and filling defects in renal collecting system by urography
What is Papillary Necrosis?
This finding on fundoscopic exam warrants ICU admission in a patient with blurred vision and BP 180/120
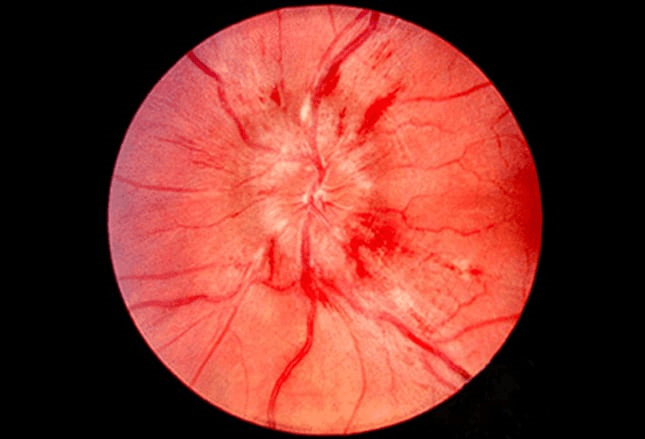
What is papilledema?
This biopsy finding is seen both in Minimal change disease and FSGS
What is podocyte foot process effacement?
Name any 4 manifestations of evil renal effects of NSAIDs
What are Prerenal AKI, Fluid retention, Worsening HTN, Acute Interstitial Nephritis, Ischemic Nephropathy, Hyponatremia, Analgesic Nephropathy and Minimal change disease? (will accept any 4)
This is the first line treatment for both severe hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia
What is intravenous Calcium Gluconate?