The state of matter with the strongest intermolecular forces.
What is a solid?
The opposite phase change to vaporization.
What is condensation?
The four states of matter.
What are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma?
The phase change from gas to solid.
The most abundant state of matter in the universe.
What is plasma?
The weakest intermolecular force.
What are London Dispersion Forces?
The effect of lowering the temperature on particle speed.
What is particles slow down?
The state of matter that has an indefinite shape but definite volume.
What is liquid?
Definition of the deionization of plasma.
What is when plasma changes into gas.
The reason the temperature remains constant during a phase change.
What is the absorbed or released energy is potential energy.
The intermolecular force (IMF) occurs when polar molecules are attracted to one another.
What is dipole-dipole?
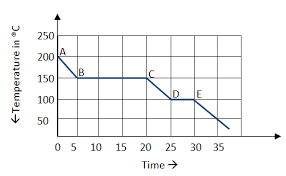 The curve above demonstrates this type of energy changes.
The curve above demonstrates this type of energy changes.
What is exothermic?
The only two elements that are liquid at room temperature and pressure.
What is mercury and bromine?
The triple point on a phase diagram.
What is the point where solids, liquids, and gases can all exist at the same time?
A list of the three exothermic phase changes.
What is freezing, condensing, deposition?
(In any order.)
The difference between an intermolecular force and an intramolecular force (also give an example of each).
Intramolecular force - force WITHIN the same molecule (ionic, covalent, metallic)
Intermolecular force - force BETWEEN two different particles (London, Dipole & Hydrogen bonding)
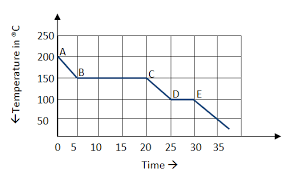
The sections of the curve that involve kinetic energy.
What is sections A to B, C to D and E onwards.
The two states of matter which have essentially no forces of attraction.
What is gas and plasma?
When energy is removed from a liquid, these are the two changes that may take place.
What is a phase change (into a solid) or the particles move slower?
These forces determine which state of matter a substance exists as at room temperature.
What is intermolecular forces?
The intermolecular forces found in a sample of water (H2O) (listed weakest to strongest).
What are London Dispersion Forces, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding?
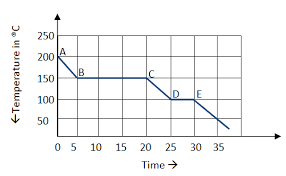 The temperature of the freezing point.
The temperature of the freezing point.
What is 100 @ C?
The description of the movement and arrangement of particles of plasma.
What is they are free electrons & positive ions in constant, random motion spreadvery far apart from
each other.
When you decrease the pressure on a solid, and it becomes a gas, this phase change has taken place.
What is sublimation?
The three elements which experience hydrogen bonding (along with hydrogen).
What is fluorine, nitrogen, oxygen