If actual activity is greater than planned, what kind of variance would you expect in variable expenses (favorable, unfavorable, not enough info)? (Ch. 9)
Unfavorable (had to spend more money to support making more units/working more hours)
Cost object: Pappajohn Business Building
Classify as direct or indirect: Electric bill for the University of Iowa (Ch. 1)
Indirect
See Session Slides (Ch. 5)
$0.61 per machine hour, $25.10 per batch
A project with an initial investment of $400,000 will bring in cash flows of $65,000 per year. What is the payback period of this investment? Round your answer to the closest year. (Ch. 7)
6 years
Goodman Inc. allocates variable expenses at a rate of $5 per hour. This year, they budgeted 1,000 hours, but the carpeting division actually used 1,100 hours. How much variable expense should be allocated to the carpeting division? (Ch. 11)
$5,500
The variance between the actual and flexible budget is called _______ and is due to ________. (Ch. 9)
Revenue and spending variance, differences between selling prices and the cost of variable/fixed expenses.
Given a sales volume of 300, total sales of $500,000, total variable expenses of $200,000, and fixed expense of $100,000, calculate the break even point in units sold. (Ch. 2)
100 units
True or False: Contribution margin lost from a decline in sales is an opportunity cost. (Ch. 6)
True
Using the cost formula provided, how much would be spent on equipment rental if 100 diving hours were used? (Ch. 9)
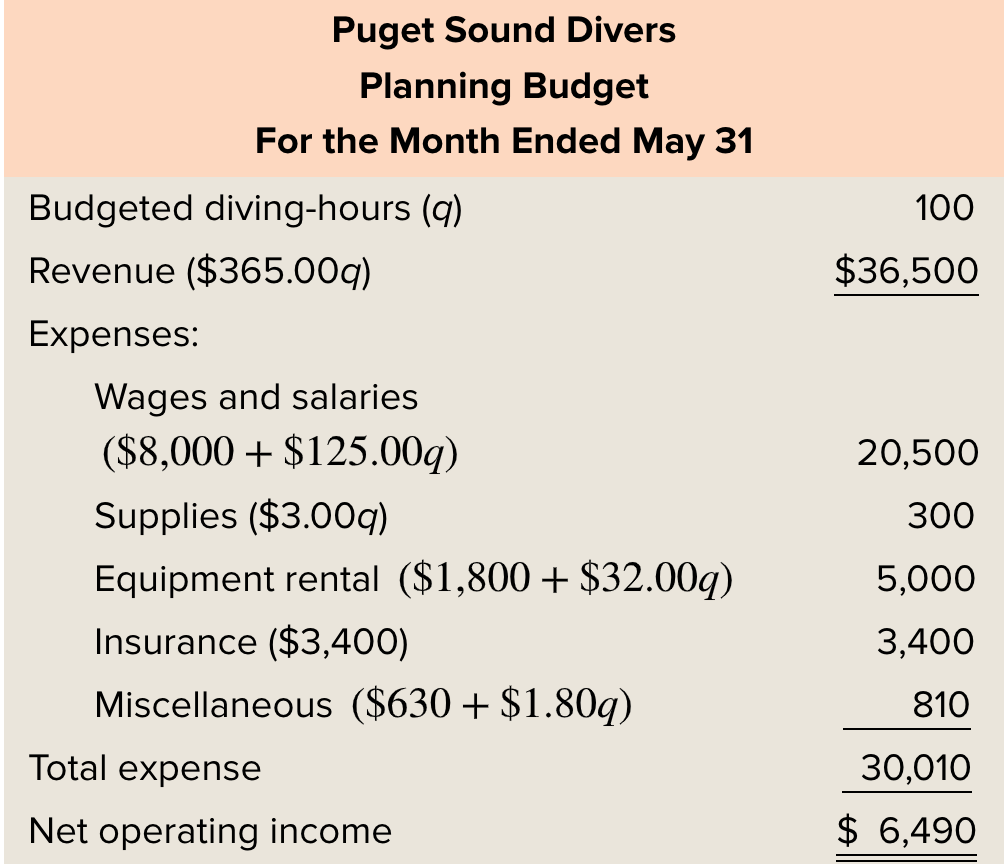
$5000
Bandar Industries manufactured 35,000 helmets last month using 22,500 kg of plastic. The plastic cost the company $171,000. According to the standard cost card, each helmet should require 0.6 kg of plastic, at a cost of $8/kg.
What is the material quantity variance? (Ch. 10)
$12,000 U
A factory is operating at less than 100% capacity. Potential additional business will not use up the remainder of the capacity. Which of the following costs should be ignored when deciding whether to produce a special order? (Ch. 6)
Variable selling expenses, fixed factory overhead, direct labor, contribution margin of additional units
Fixed factory overhead
Your company generally uses $350,000 of MOH in a year, and estimates that the employees will complete 3400 direct labor hours. What is your POHR if the allocation base is DLH? (Ch. 3)
$103
Wishnell Toys can make 1,000 toy robots with the following costs: DM = $70,000, DL = 26,000, VMOH = $15,000, FMOH = $15,000. The company can purchase the robots externally for $120,000. The avoidable fixed costs are $5000 if the units are purchased externally. What is the cost savings if the company makes the robots? (Ch. 6)
$4000
Name the 5th baby step of financial freedom. (Ch. 8)
Save for your children's college fund
If variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production on the basis of direct labor hours and the direct labor efficiency variance is unfavorable, will the variable overhead efficiency be favorable or unfavorable, or could it be either? Explain. (Ch. 10)
The variable overhead efficiency variance will be the same - so in this case, unfavorable.
A manager has responsibility and authority over revenues, costs and assets in which type of center? (Ch. 11)
Investment
Classify the following as a product or period cost: Research and Development Costs (Ch. 1)
Period - this is an administrative cost
Castaway Company reports the following first year production cost information. 53,000 units produced, 50,000 units sold. Sales price = $150/unit, DL = $8/unit, DM = $4/unit, VMOH = $2,173,000, FMOH = $3,339,000, Operating Expenses = $1,000,000.
What is NOI under absorption costing? (Ch. 4)
$700,000
Your annual cash flows equal $70,000. Your boss tells you that you have a piece of equipment that cost $50,000 to purchase that the company will no longer use in 6 years. You can then sell this piece of equipment for $4000. Factoring in the straight-line depreciation of the equipment, what is your yearly NOI? (Ch. 7)
$62,333
"Lost sales due to out-of-stock merchandise" would fall under which category of a balanced scorecard? (Ch. 12)
Internal business processes
Name 2 or the 4 purposes of managerial accounting. (Ch. 1)
Preparing financial statements, predicting cost behavior, making decisions, assigning costs to cost objects
Given: sales volume of 300 units, total sales of $500,000, total variable expenses of $200,000, total fixed expenses of $50,000. If you increase units sold by 10%, what is the new break-even point? (Ch. 2)
50 units
Sort of a trick question - changing units sold WILL NOT change the break even point!
Castaway Company reports the following first year production cost information. 53,000 units produced, 50,000 units sold. Sales price = $150/unit, DL = $8/unit, DM = $4/unit, VMOH = $2,173,000, FMOH = $3,339,000, Operating Expenses = $1,000,000.
What is NOI under variable costing? (Ch. 4)
$511,000
Given that the discount rate is 12%, what is the NPV of Project y? (Ch. 7)
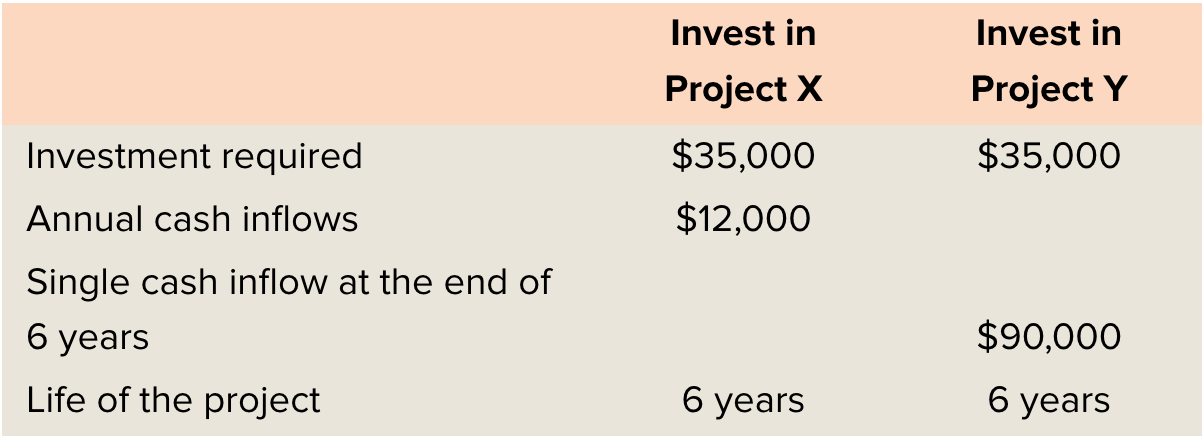
$10,594
Columbus Corp. has revenues of 1.5M resulting in an operating income of $105,000. Average invested assets total $750,000. If sales increase by 10% and the investment level remains constant, what is the investment turnover? (Ch. 11)
2.2